QT
2024 年 12 月 16 日
[QT5] 常用控件介绍I: QWidget是什么? 了解 控件常用公共属性, QT的qrc资源管理机制...
QT是一种GUI开发框架, 它内置有许多各种各样的控件, 接下来就对常用控件做一些介绍
QT中已经内置了许多的控件: 点击按钮、单选按钮、复选按钮、文本框、下拉框、状态栏…一个完善的
QT桌面程序, 是由许多的控件组成的所以, 控件是非常重要的内容, 常用的控件需要逐一了解
了解QT内置控件
在前面的文章中, 简单的使用过两个控件
QPushButton和QLabel, 对应点击按钮和文本标签除此之外,
QT内置了种类非常丰富的控件(但是颜值并不高), 打开QT Creator->Designer(双击QT项目的.ui文件)就能看到QT内置的控件: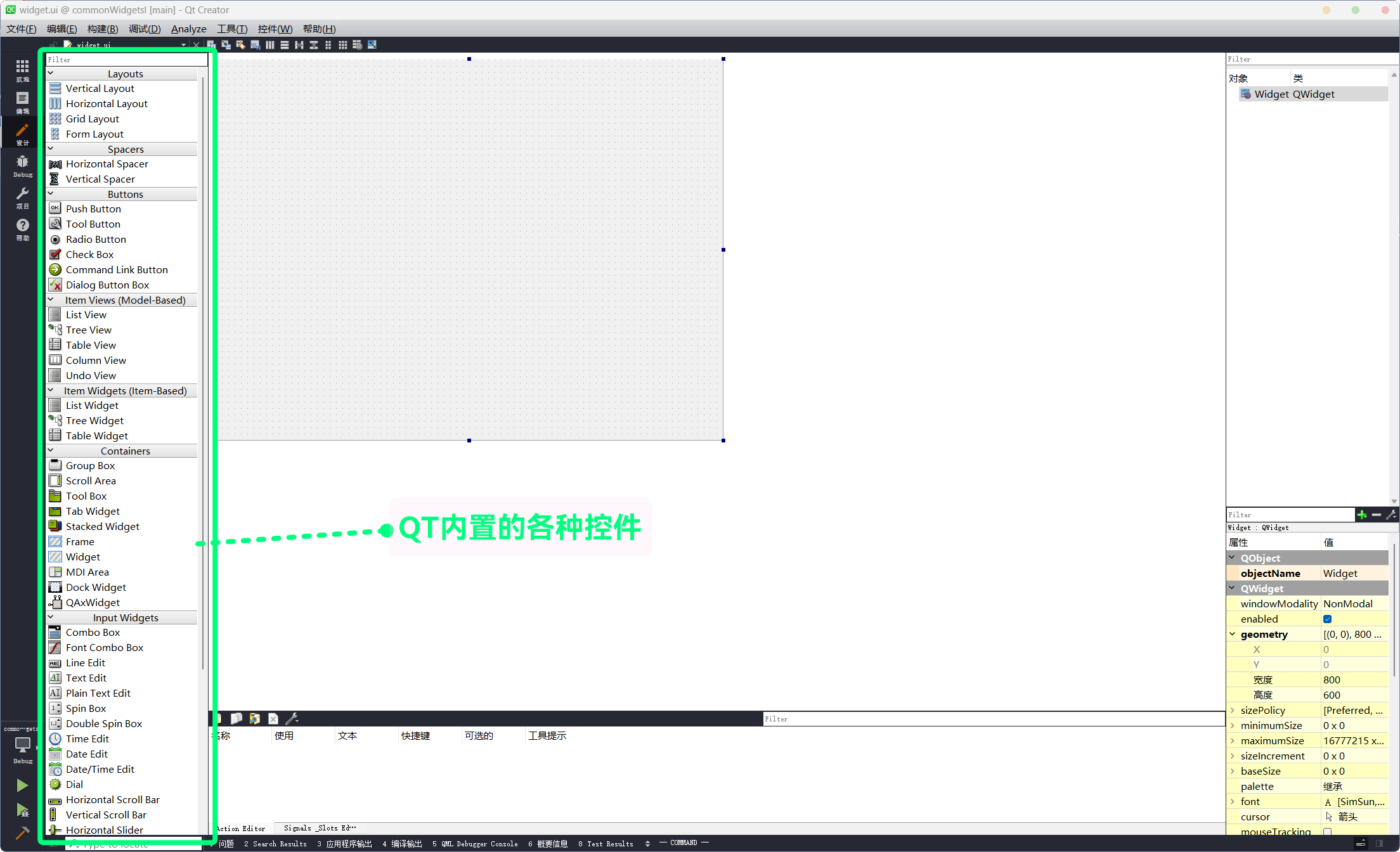
在了解各种控件类之前, 先了解一下
QWidget类QWidget是QT中控件的通用属性类, 在QT Designer中查看: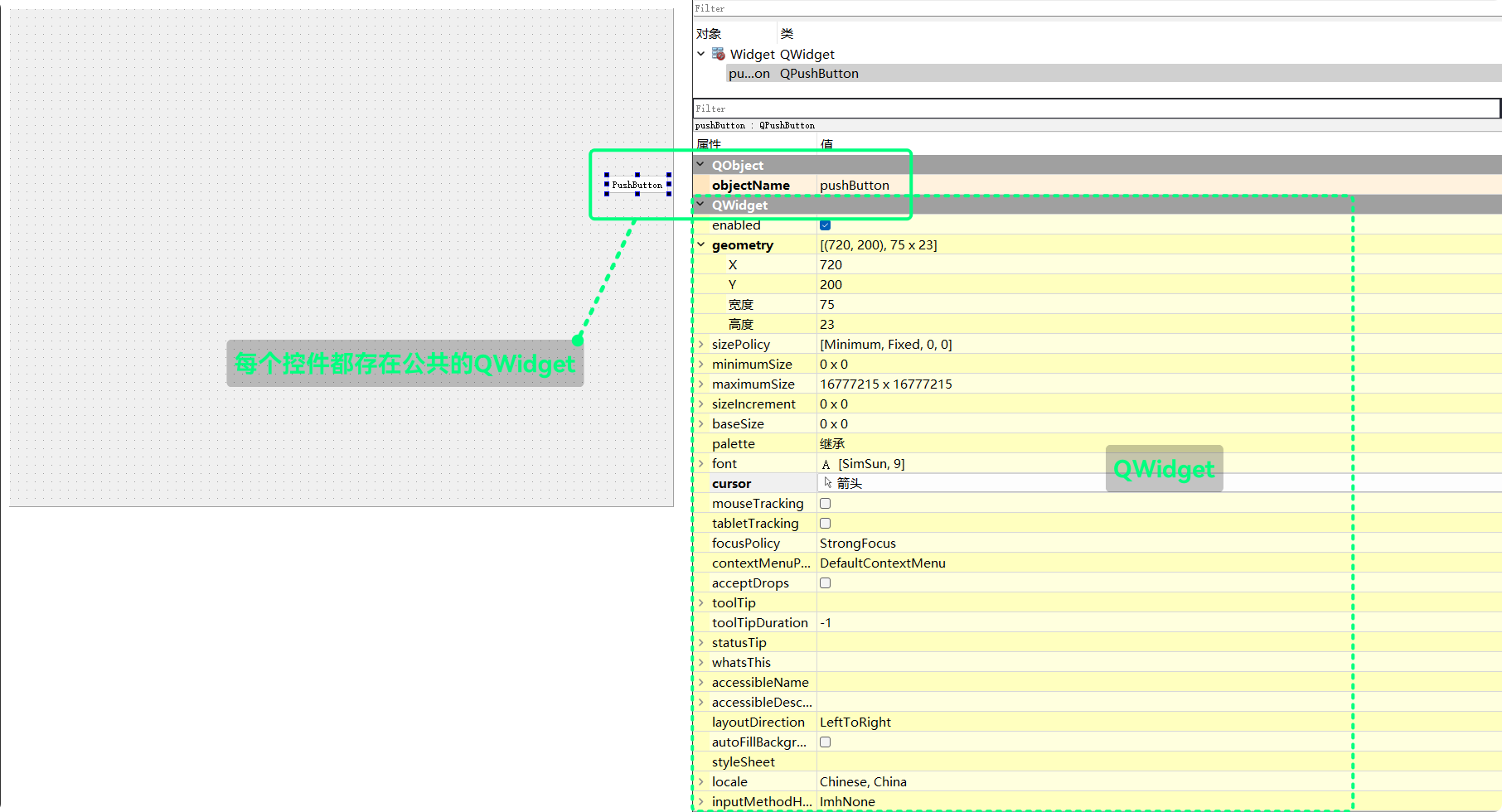
QWidget **
QWidget拥有很多属性, 可以直接在QT的文档中查看:
也可以在
QT Designer中查看: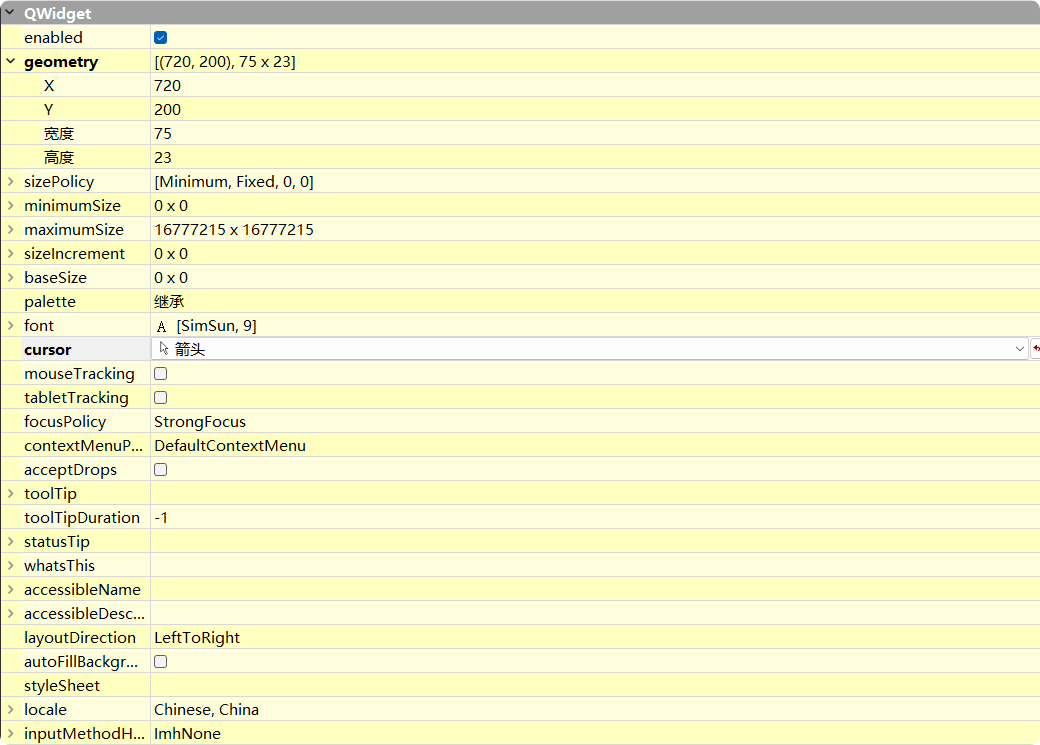
对于常用的公共属性, 可以一一进行介绍一下
enabled
此属性, 用于设置控件的可用状态
QT提供了相关的接口:| 接口 | 功能 |
|---|---|
bool isEnabled() const; | 获取控件当前enabled值 |
void setEnabled(bool); | 设置控件可用状态 |
添加两个
QPushButton, 并将enabled属性设置为false和truewidget.cc:#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QPushButton>
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
QPushButton* btn1 = new QPushButton(this);
btn1->setText("按钮1");
btn1->move(200, 200);
btn1->setEnabled(false);
QPushButton* btn2 = new QPushButton(this);
btn2->setText("按钮2");
btn2->move(300, 300);
btn2->setEnabled(true);
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
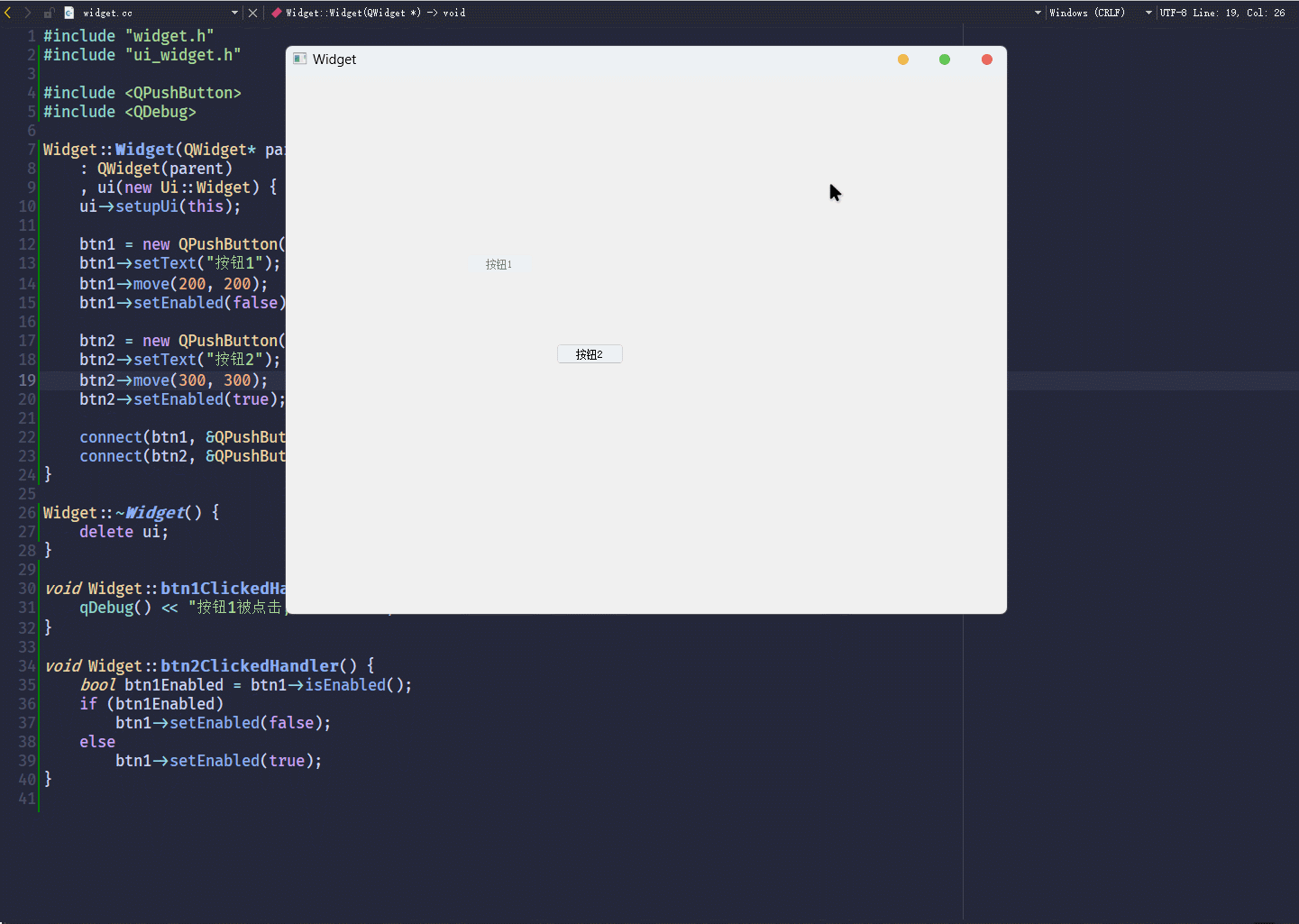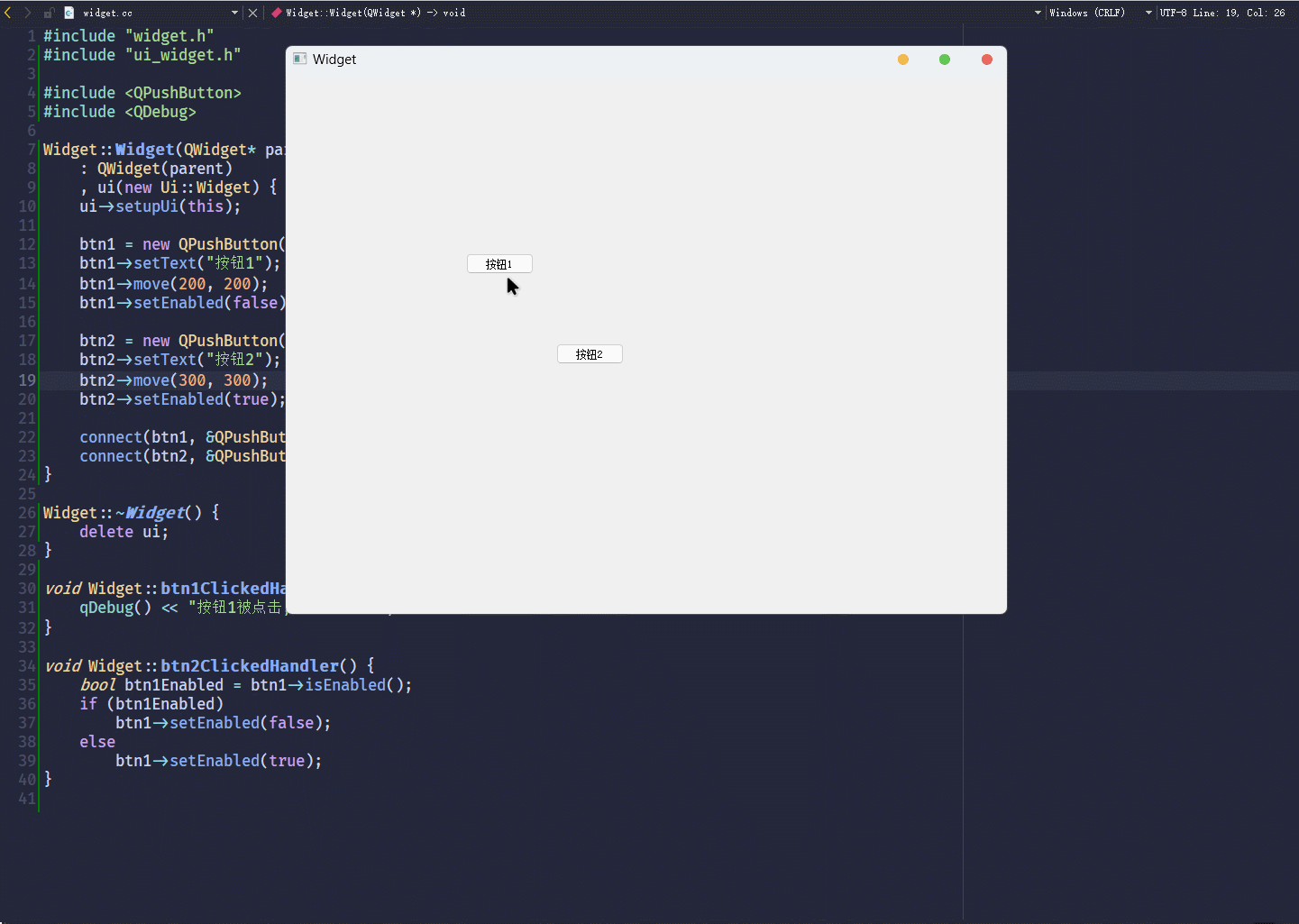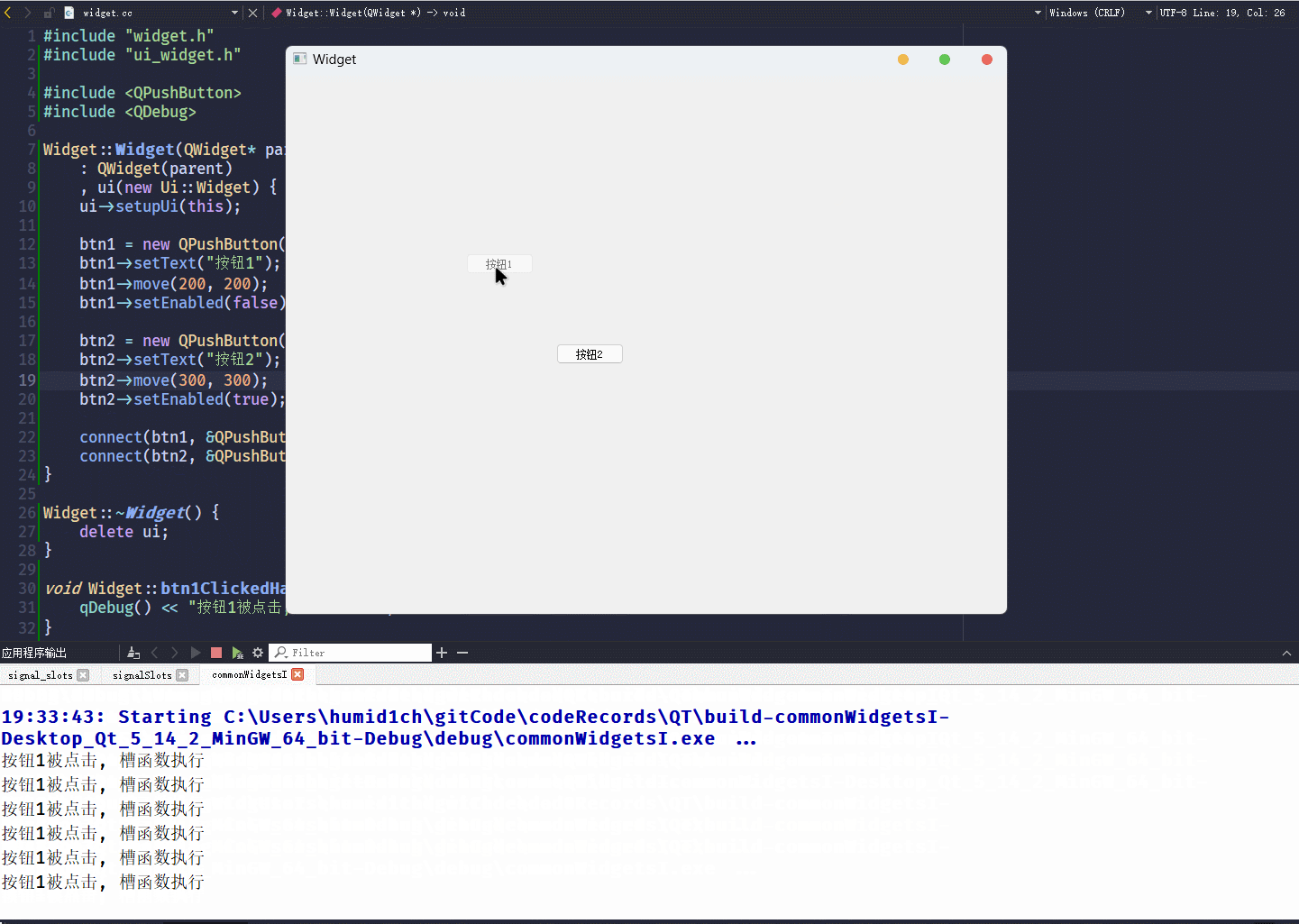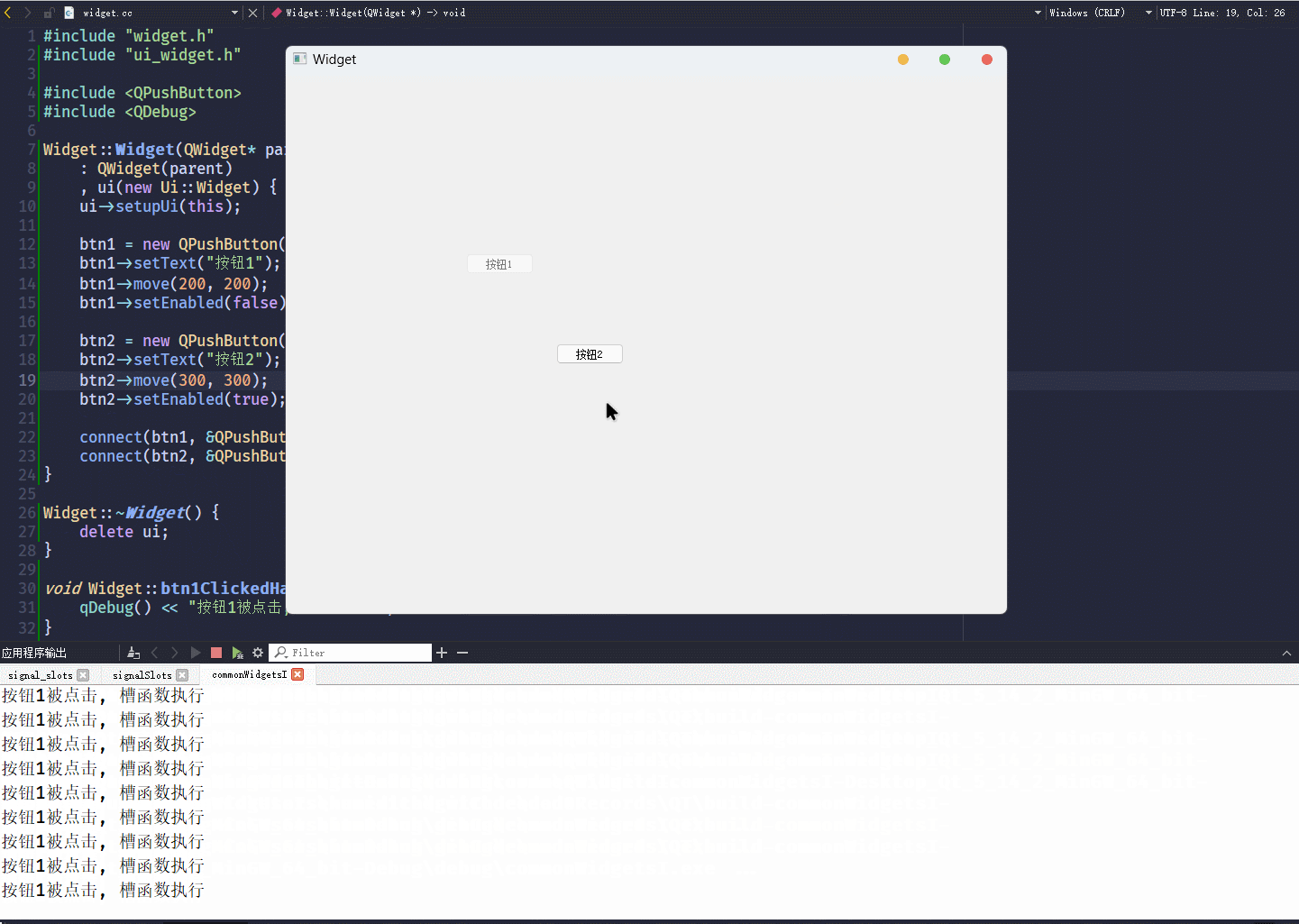
}执行结果为:
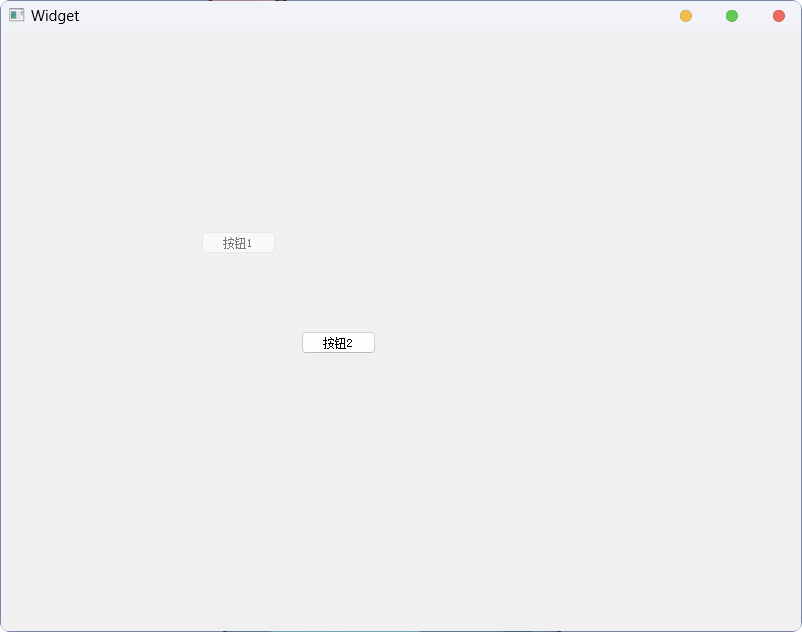
可以看到, 按钮1为灰色, 处于不可选中状态; 按钮2, 则处于正常状态
控件的
enabled属性是可以随时改变的:widget.h:#ifndef WIDGET_H
#define WIDGET_H
#include <QWidget>
#include <QPushButton>
QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
namespace Ui {
class Widget;
}
QT_END_NAMESPACE
class Widget : public QWidget {
Q_OBJECT
public:
Widget(QWidget* parent = nullptr);
~Widget();
private slots:
void btn1ClickedHandler();
void btn2ClickedHandler();
private:
Ui::Widget* ui;
QPushButton* btn1;
QPushButton* btn2;
};
#endif // WIDGET_Hwidget.cc:#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QPushButton>
#include <QDebug>
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
btn1 = new QPushButton(this);
btn1->setText("按钮1");
btn1->move(200, 200);
btn1->setEnabled(false);
btn2 = new QPushButton(this);
btn2->setText("按钮2");
btn2->move(300, 300);
btn2->setEnabled(true);
connect(btn1, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &Widget::btn1ClickedHandler);
connect(btn2, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &Widget::btn2ClickedHandler);
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
}
void Widget::btn1ClickedHandler() {
qDebug() << "按钮1被点击, 槽函数执行";
}
void Widget::btn2ClickedHandler() {
bool btn1Enabled = btn1->isEnabled();
if (btn1Enabled)
btn1->setEnabled(false);
else
btn1->setEnabled(true);
}这段代码的执行结果为:
geometry
此属性, 用于设置当前控件的位置和尺寸, 即
(x, y)和(width, height)QT为geometry提供了几个接口, 用于获取当前控件的位置和尺寸或设置当前控件的位置和尺寸| 接口 | 功能 |
|---|---|
inline const QRect &QWidget::geometry() const; | 获取控件当前geometry属性 |
inline void setGeometry(int x, int y, int w, int h); | 通过4个int设置控件的geometry属性 |
void setGeometry(const QRect &); | 通过QRect设置控件的geometry属性 |
实际的使用:
widget.cc:#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QPushButton>
#include <QDebug>
#include <QRect>
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
btn1 = new QPushButton(this);
btn1->setText("按钮1");
btn1->move(200, 200);
btn1->setEnabled(false);
btn2 = new QPushButton(this);
btn2->setText("按钮2");
btn2->move(300, 300);
btn2->setEnabled(true);
QRect btn1Geom = btn1->geometry();
QRect btn2Geom = btn2->geometry();
qDebug("按钮1 坐标: (%d, %d), 尺寸: (%d, %d)", btn1Geom.x(), btn1Geom.y(), btn1Geom.width(), btn1Geom.height());
qDebug("按钮2 坐标: (%d, %d), 尺寸: (%d, %d)", btn2Geom.x(), btn2Geom.y(), btn2Geom.width(), btn2Geom.height());
connect(btn1, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &Widget::btn1ClickedHandler);
connect(btn2, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &Widget::btn2ClickedHandler);
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
}
void Widget::btn1ClickedHandler() {
qDebug() << "按钮1被点击, 槽函数执行";
}
void Widget::btn2ClickedHandler() {
QRect btn1Geom = btn1->geometry();
qDebug("按钮1 坐标: (%d, %d), 尺寸: (%d, %d)", btn1Geom.x(), btn1Geom.y(), btn1Geom.width(), btn1Geom.height());
bool btn1Enabled = btn1->isEnabled();
if (btn1Enabled) {
// 可用
btn1->setEnabled(false);
btn1Geom.setX(200);
btn1Geom.setY(200);
btn1Geom.setWidth(100);
btn1Geom.setHeight(30);
btn1->setGeometry(btn1Geom);
qDebug("重新设置按钮1 坐标: (%d, %d), 尺寸: (%d, %d)", btn1Geom.x(), btn1Geom.y(), btn1Geom.width(), btn1Geom.height());
}
else {
// 不可用
btn1->setEnabled(true);
btn1Geom.setX(500);
btn1Geom.setY(500);
btn1Geom.setWidth(200);
btn1Geom.setHeight(30);
btn1->setGeometry(btn1Geom);
qDebug("重新设置按钮1 坐标: (%d, %d), 尺寸: (%d, %d)", btn1Geom.x(), btn1Geom.y(), btn1Geom.width(), btn1Geom.height());
}
}这段代码的执行结果为:
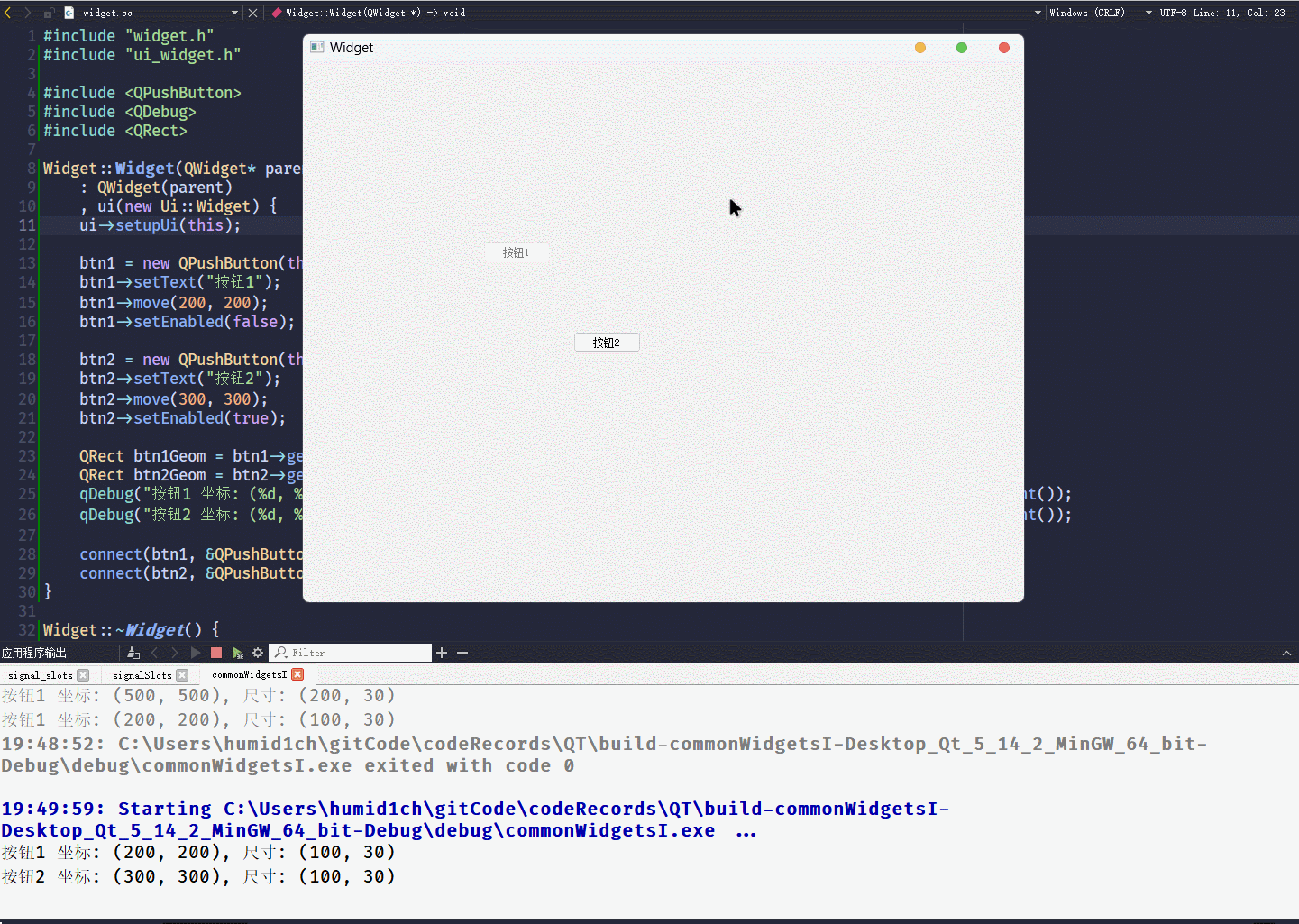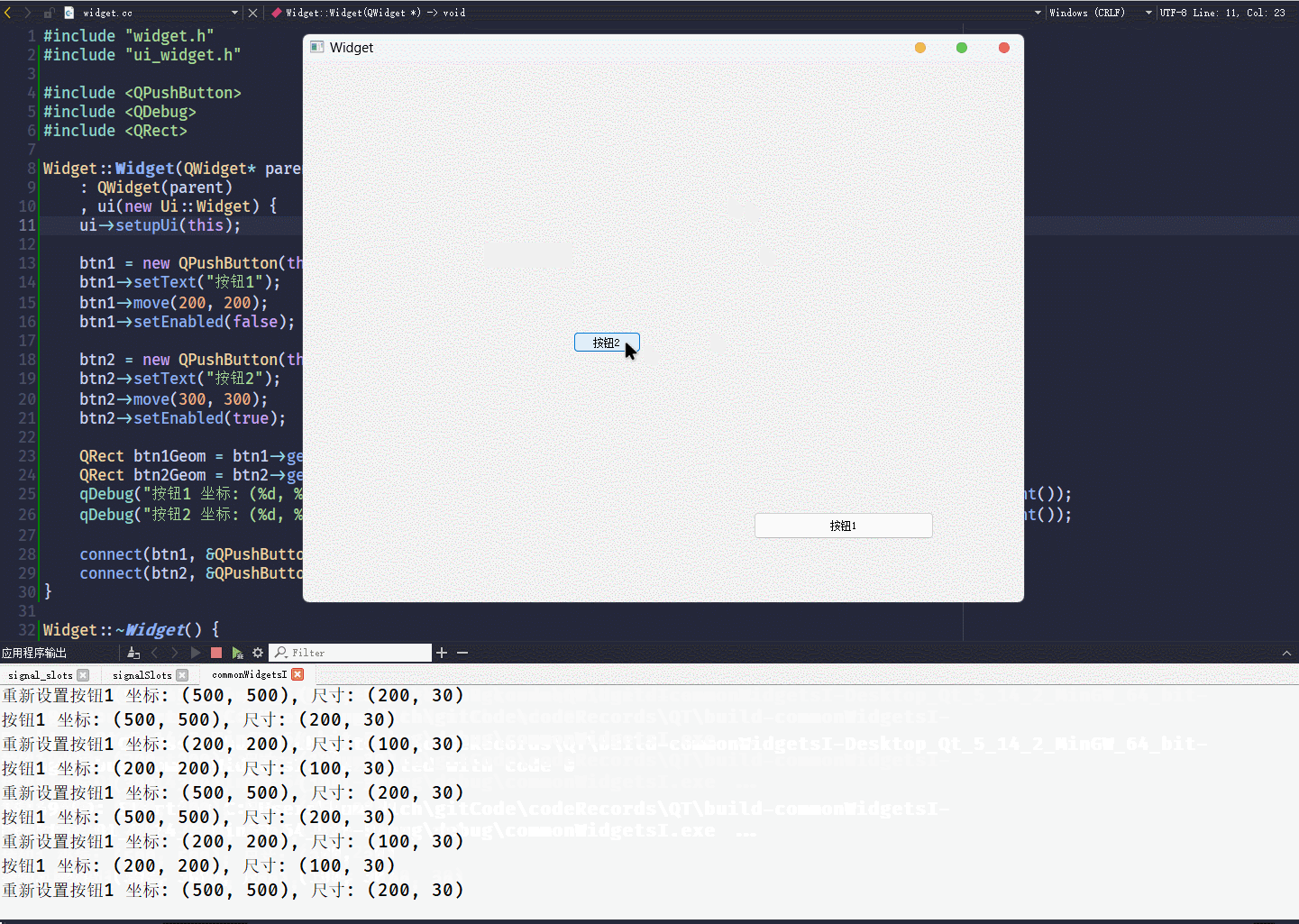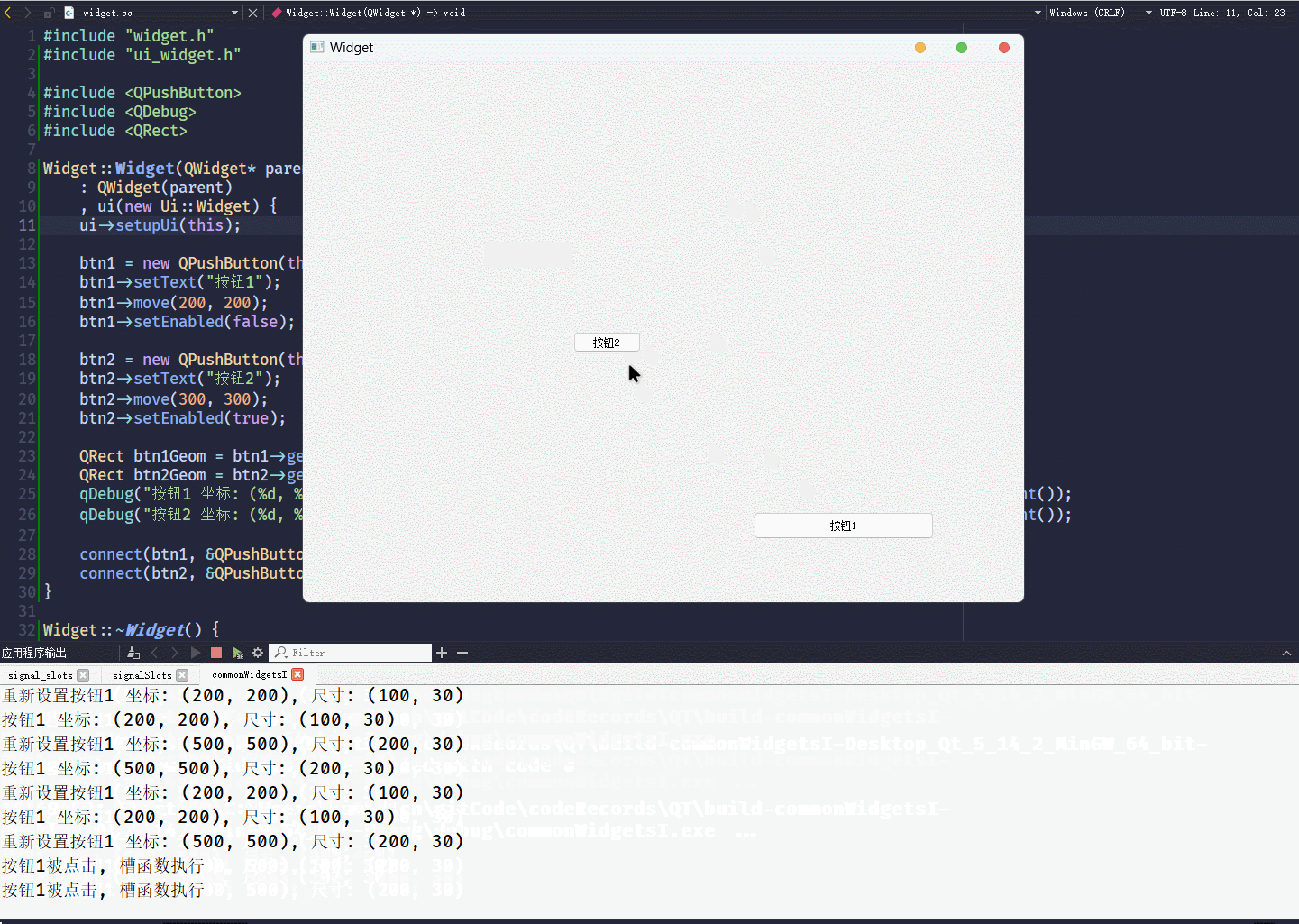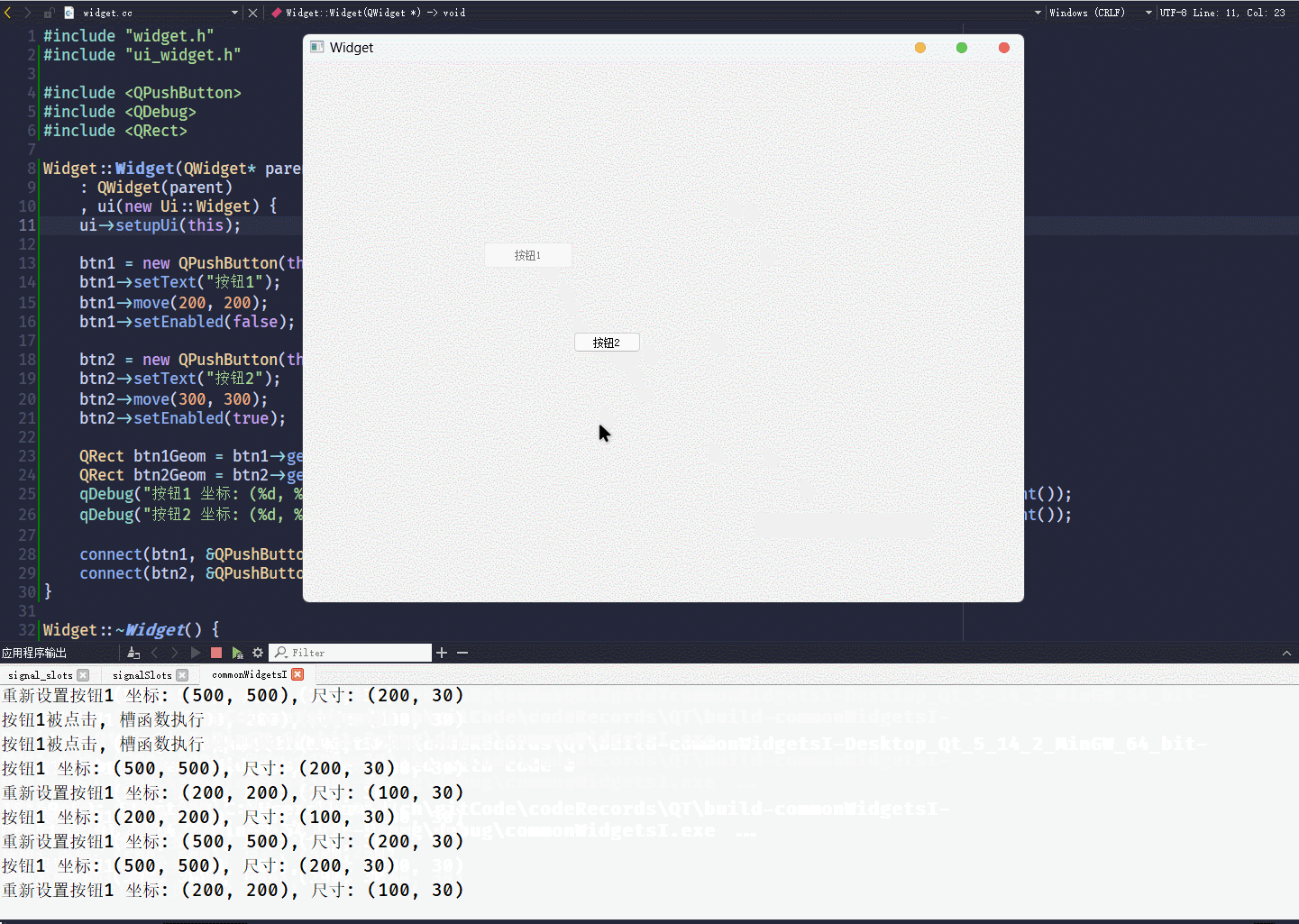
geometry()接口, 可以获取控件当前的坐标和尺寸, 返回值是一个QRect对象QRect对象包含x y width height, 四个属性
QRect对象, 可以通过qDebug() << QRect直接打印坐标和尺寸信息
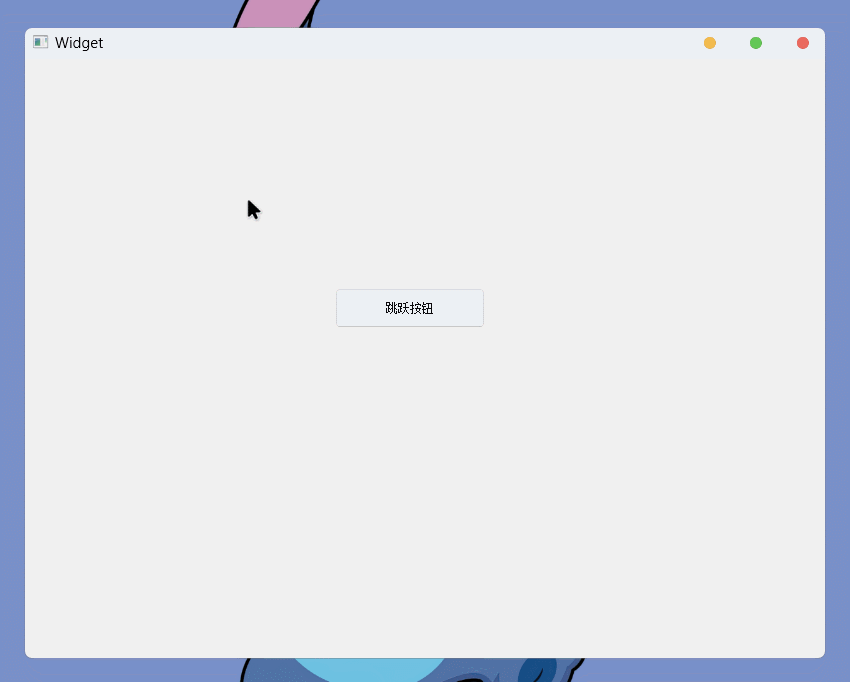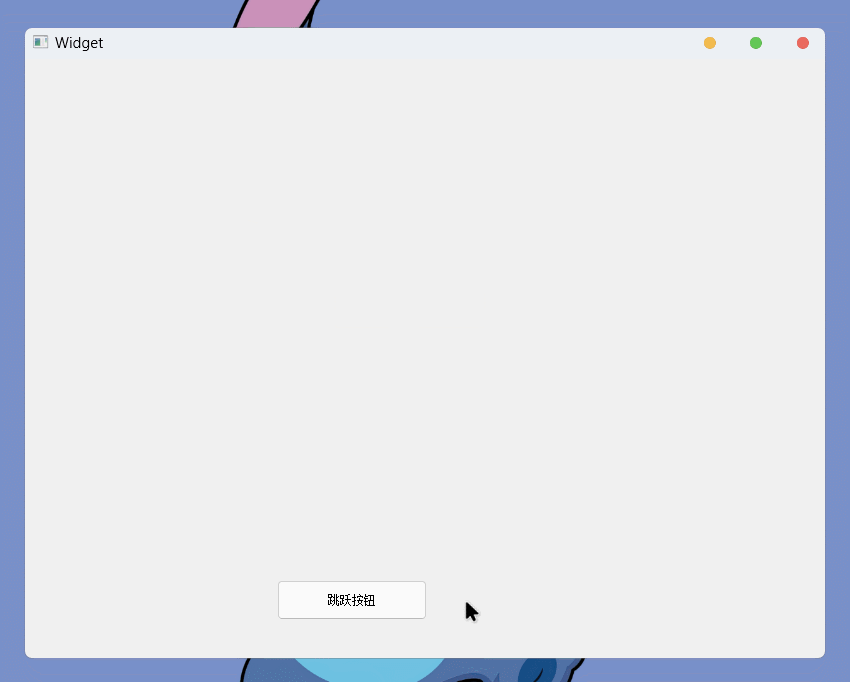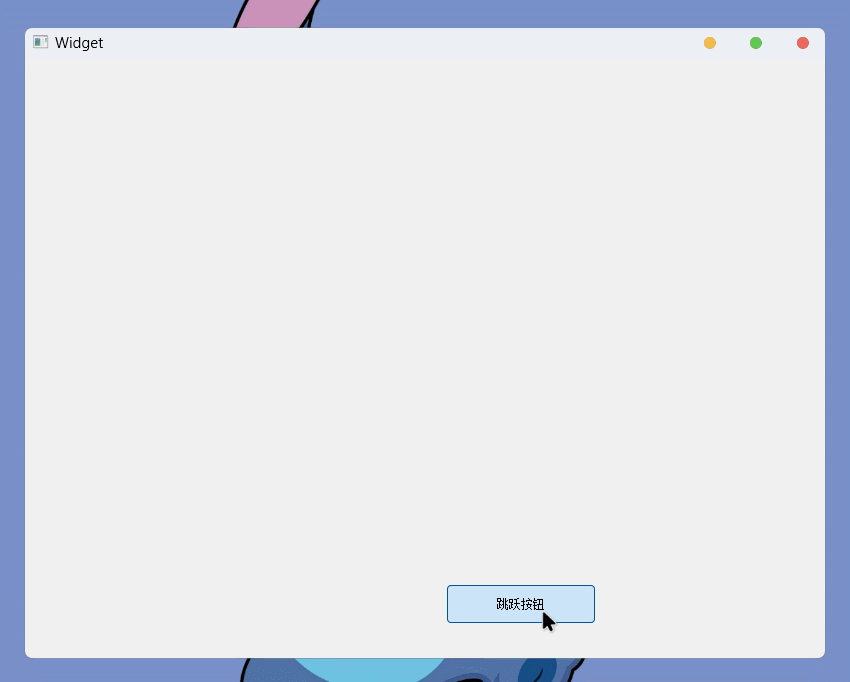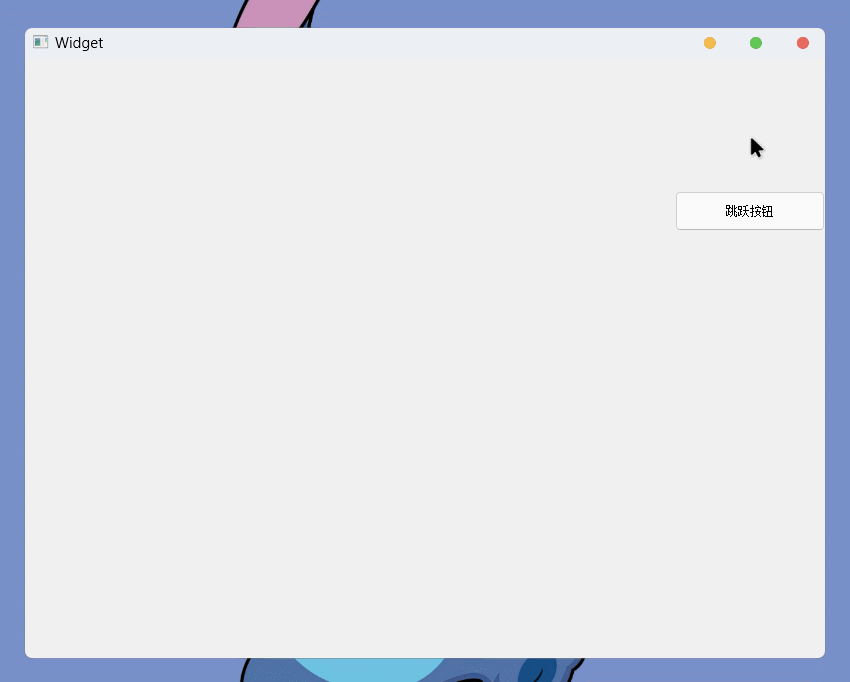
setGeometry()接口, 则可以设置控件的坐标和尺寸, 可以通过传入QRect对象, 也可以通过传入四个int跳跃的按钮(小玩具程序)
先通过图形化创建
QPushButton控件, 并创建clicked信号的槽然后实现槽函数就可以了:
#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <ctime>
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
srand(time(nullptr));
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
}
void Widget::on_pushButton_clicked() {
// 获取窗口的尺寸, 防止按钮跳跃出窗口
int winWidth = this->geometry().width();
int winHeight = this->geometry().height();
int x = rand() % winWidth;
int y = rand() % winHeight;
// 防止按钮越界
x > (winWidth - ui->pushButton->geometry().width()) ? (x = winWidth - ui->pushButton->geometry().width()) : x;
y > (winHeight - ui->pushButton->geometry().height()) ? (y = winHeight - ui->pushButton->geometry().height()) : y;
ui->pushButton->setGeometry(x, y, ui->pushButton->geometry().width(), ui->pushButton->geometry().height());
}这样一个简单的小游戏就实现了:
不过, 上面是实现了对
clicked信号的槽, 还有一个信号是pressedclicked是被点击, 而pressed是被按压clicked由两个动作完整组成: 按压 和 抬起, 而pressed则仅表示被按压:#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <ctime>
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
srand(time(nullptr));
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
}
void Widget::on_pushButton_pressed() {
// 获取窗口的尺寸, 防止按钮跳跃出窗口
int winWidth = this->geometry().width();
int winHeight = this->geometry().height();
int x = rand() % winWidth;
int y = rand() % winHeight;
x > (winWidth - ui->pushButton->geometry().width()) ? (x = winWidth - ui->pushButton->geometry().width()) : x;
y > (winHeight - ui->pushButton->geometry().height()) ? (y = winHeight - ui->pushButton->geometry().height()) : y;
ui->pushButton->setGeometry(x, y, ui->pushButton->geometry().width(), ui->pushButton->geometry().height());
}对
pressed信号实现槽, 可以实现鼠标左键不松的状态下, 光标移动到按钮上, 按钮就跳跃移动:
WindowFrame的影响 **
WindowFrame一般是由系统的桌面环境提供的, 它通常是窗口默认的标题栏、边框等元素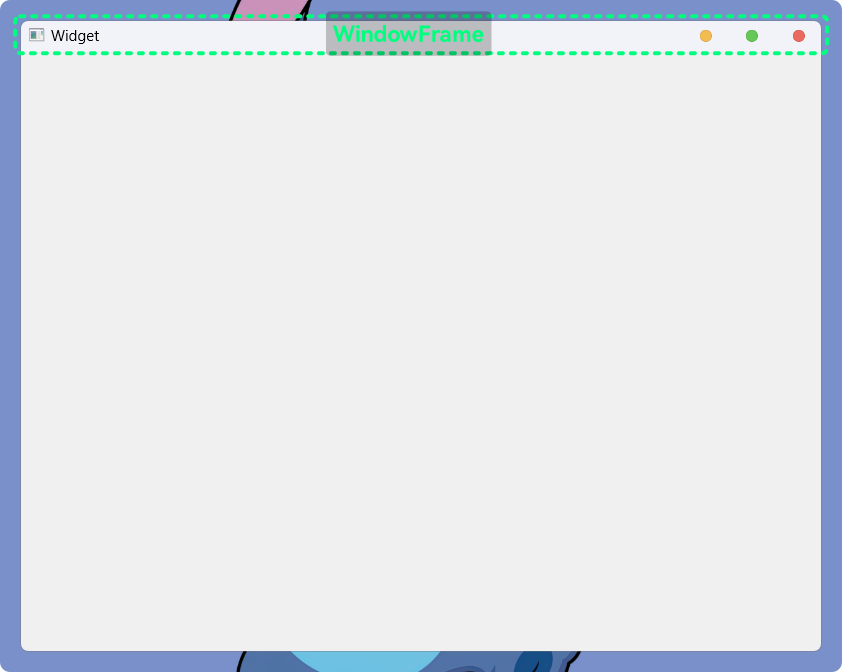
边框也算
WindowFrame的一部分之前的代码中,
QPushButton控件move()、geometry()、setGeometry()接口, 设置或获取的都是控件相对于Widget本体的位置信息(左上角为(0, 0)):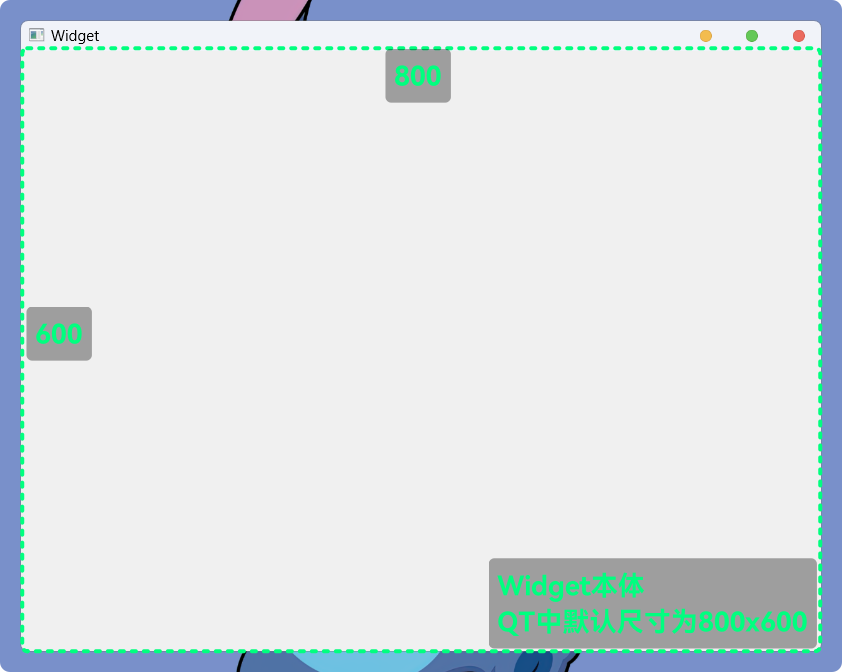
窗口的
WindowFrame元素是没有被计算在内的不过
QT也提供了针对WindowFrame的接口对于一个窗口,
QT提供了一些接口, 能够获取当前窗口的位置、尺寸信息:| 接口 | 功能 |
|---|---|
int x() const; | 获取窗口相对于桌面的横坐标, 包含WindowFrame计算 |
int y() const; | 获取窗口相对于桌面的纵坐标, 包含WindowFrame计算 |
QPoint pos() const; | 获取窗口相对于桌面的位置, 包含WindowFrame计算 返回的 QPoint包含(x, y)相关信息 |
QSize frameSize() const; | 获取窗口的尺寸, 包含WindowFrame计算 返回的 QSize包含(width, height)相关信息 |
QRect frameGeometry() const; | 获取窗口相对于桌面的位置及尺寸, 包含WindowFrame计算 |
int width() const; | 获取窗口内Widget本体的宽, 不包含WindowFrame计算 |
int height() const; | 获取窗口内Widget本体的高, 不包含WindowFrame计算 |
QSize size() const; | 获取窗口内Widget的尺寸, 不包含WindowFrame计算 |
QRect rect() const | 获取窗口内Widget本体的位置及尺寸, 不包含WindowFrame计算 |
const QRect geometry() const; | 获取窗口内Widget本体的位置及尺寸, 不包含WindowFrame计算 |
void setGeometry(); | 设置Widget本体或控件的位置及尺寸, 不包含WindowFrame计算 |
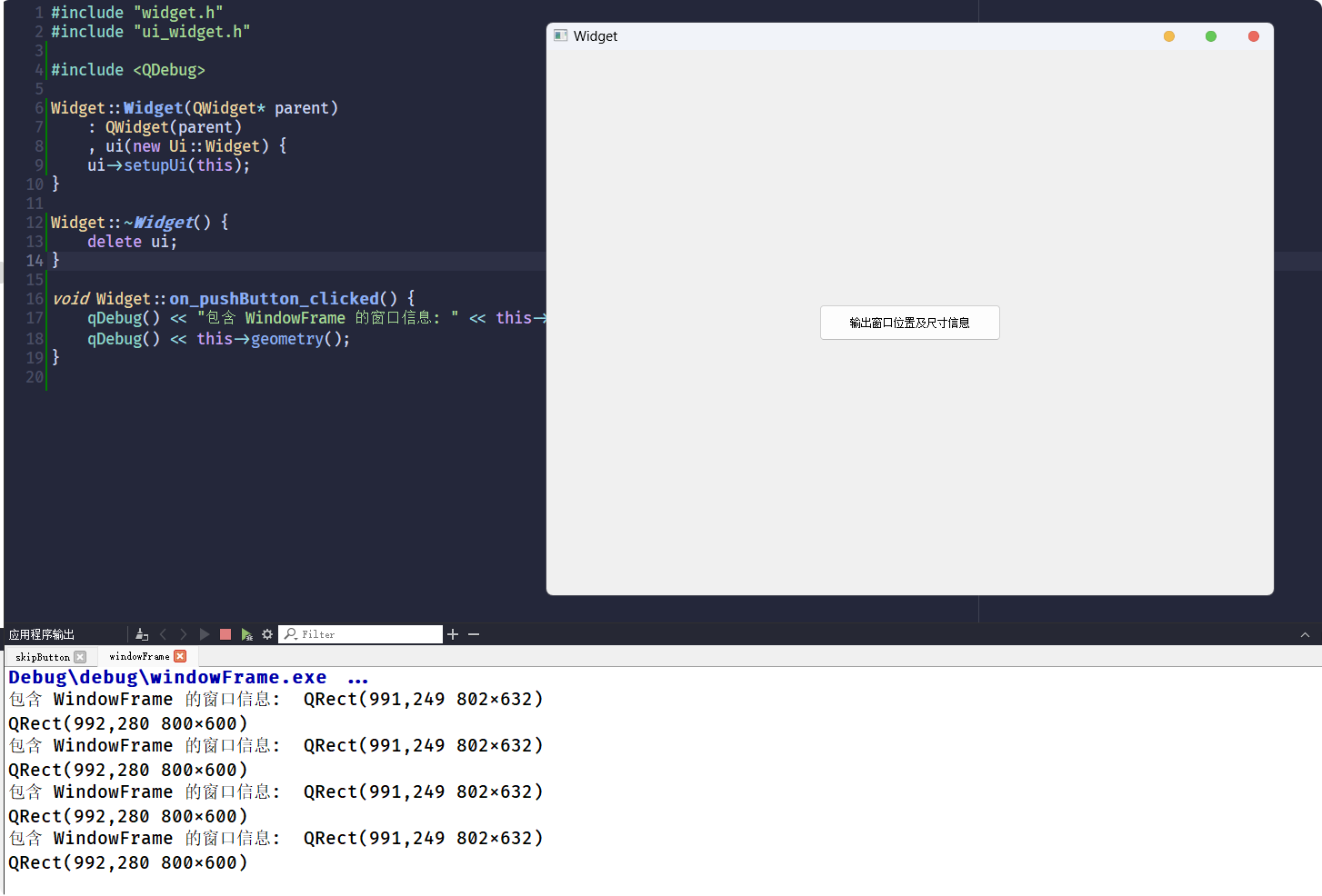
使用这段代码可以查看计算
WindowFrame的窗口信息:#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QDebug>
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
}
void Widget::on_pushButton_clicked() {
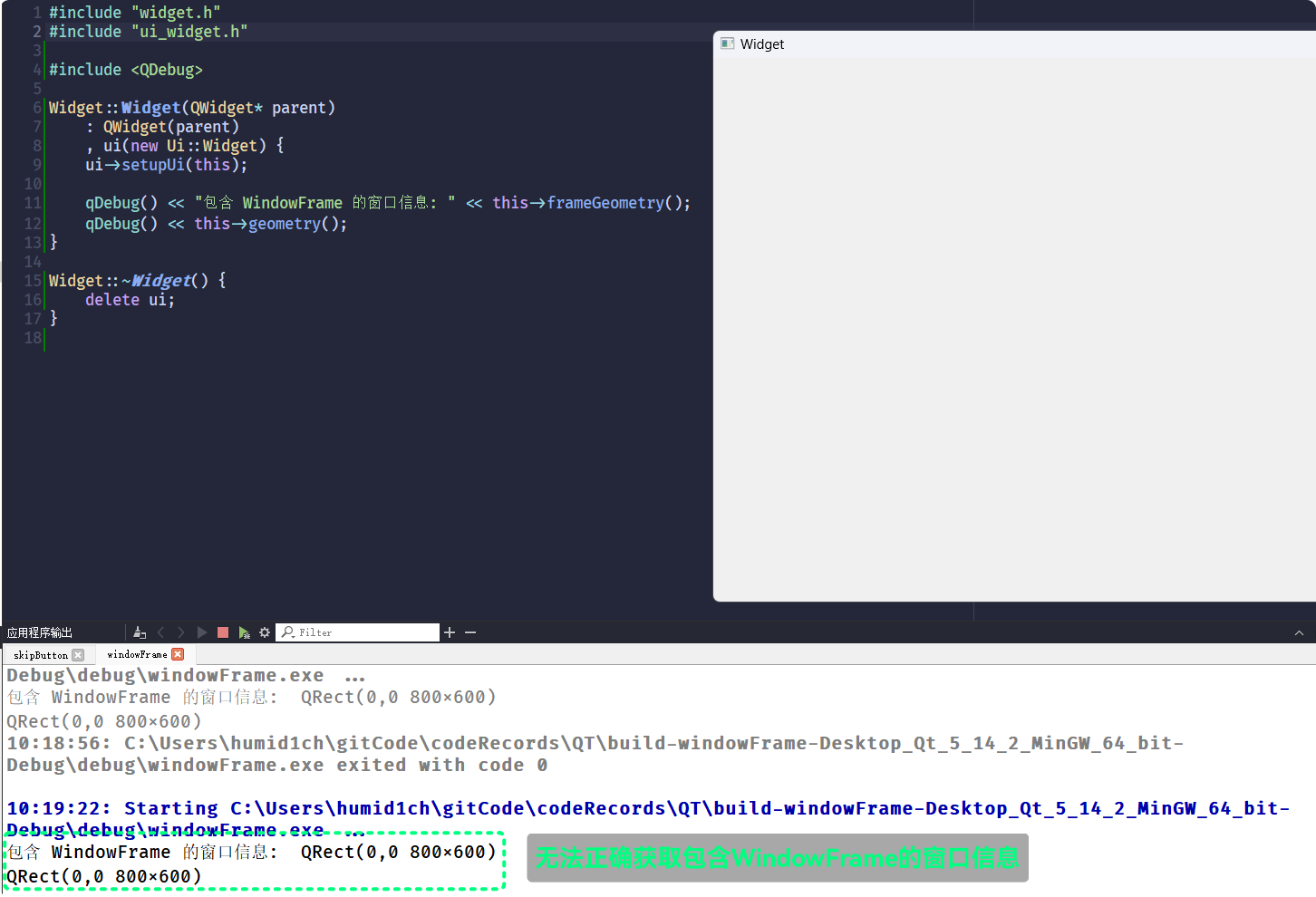
qDebug() << "包含 WindowFrame 的窗口信息: " << this->frameGeometry();
qDebug() << this->geometry();
}
要想获取包含了
WindowFrame的窗口属性不能在窗口构造阶段进行获取, 因为
WindowFrame是由系统的桌面环境提供的所以, 在窗口构造阶段,
WindowFrame还没有被添加, 无法正确获取:
windowTitle
上面
QT Designer中, 对于QPushButton属性的展示 并没有关于窗口的属性, 因为这部分属性对QPushButton没有什么用, 所以 QT Designer没有进行展示点击
Widget窗口就能够看到window...的相关属性: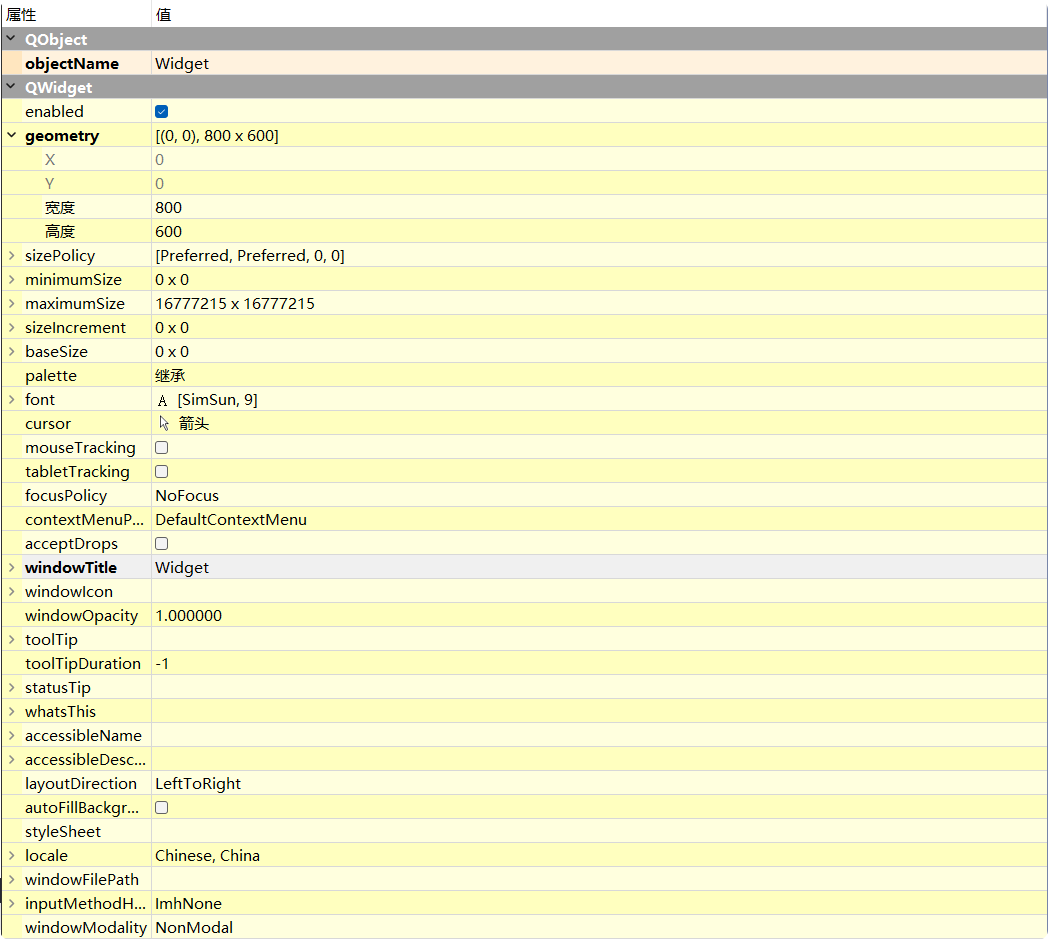
此属性, 用于设置窗口标题, 且只有对独立的窗口设置才有效
QT提供了两个相关接口:| 接口 | 功能 |
|---|---|
QString windowTitle() const; | 获取窗口标题 |
void setWindowTitle(const QString &); | 设置窗口标题 |
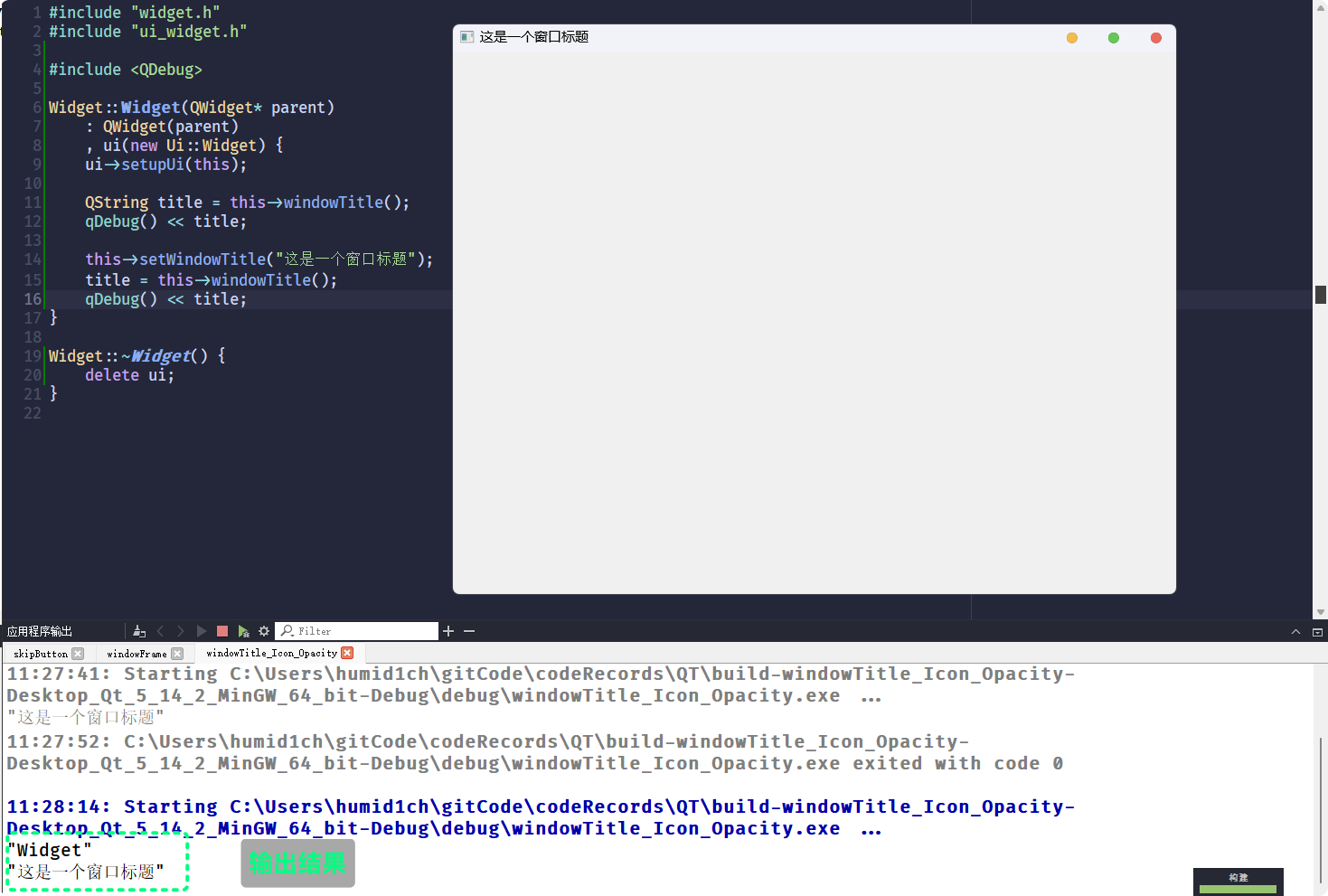
可以直接在
Widget的构造函数里使用, 获取结果:Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
QString title = this->windowTitle();
qDebug() << title;
this->setWindowTitle("这是一个窗口标题");
title = this->windowTitle();
qDebug() << title;
}
windowTitle这个属性只对独立的窗口有效, 不过 其他控件设置并不会报错:#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QDebug>
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
QString title = this->windowTitle();
qDebug() << title;
this->setWindowTitle("这是一个窗口标题");
title = this->windowTitle();
qDebug() << title;
btn = new QPushButton(this); // btn 添加为成员变量
btn->setText("这是一个按钮");
connect(btn, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &Widget::btnClickedHandler);
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
}
void Widget::btnClickedHandler() {
btn->setWindowTitle("给按钮设置标题??");
}执行代码, 点击按钮
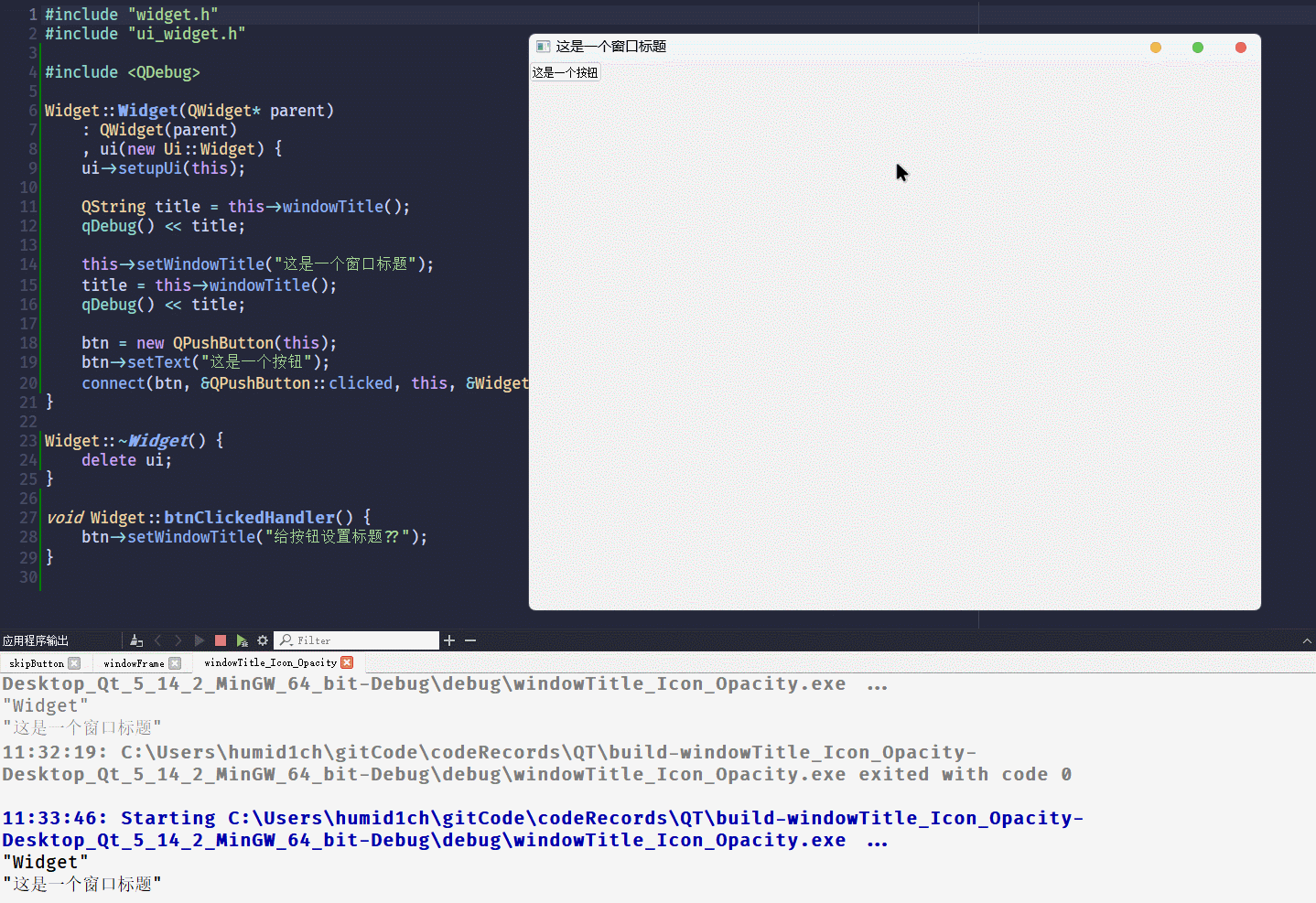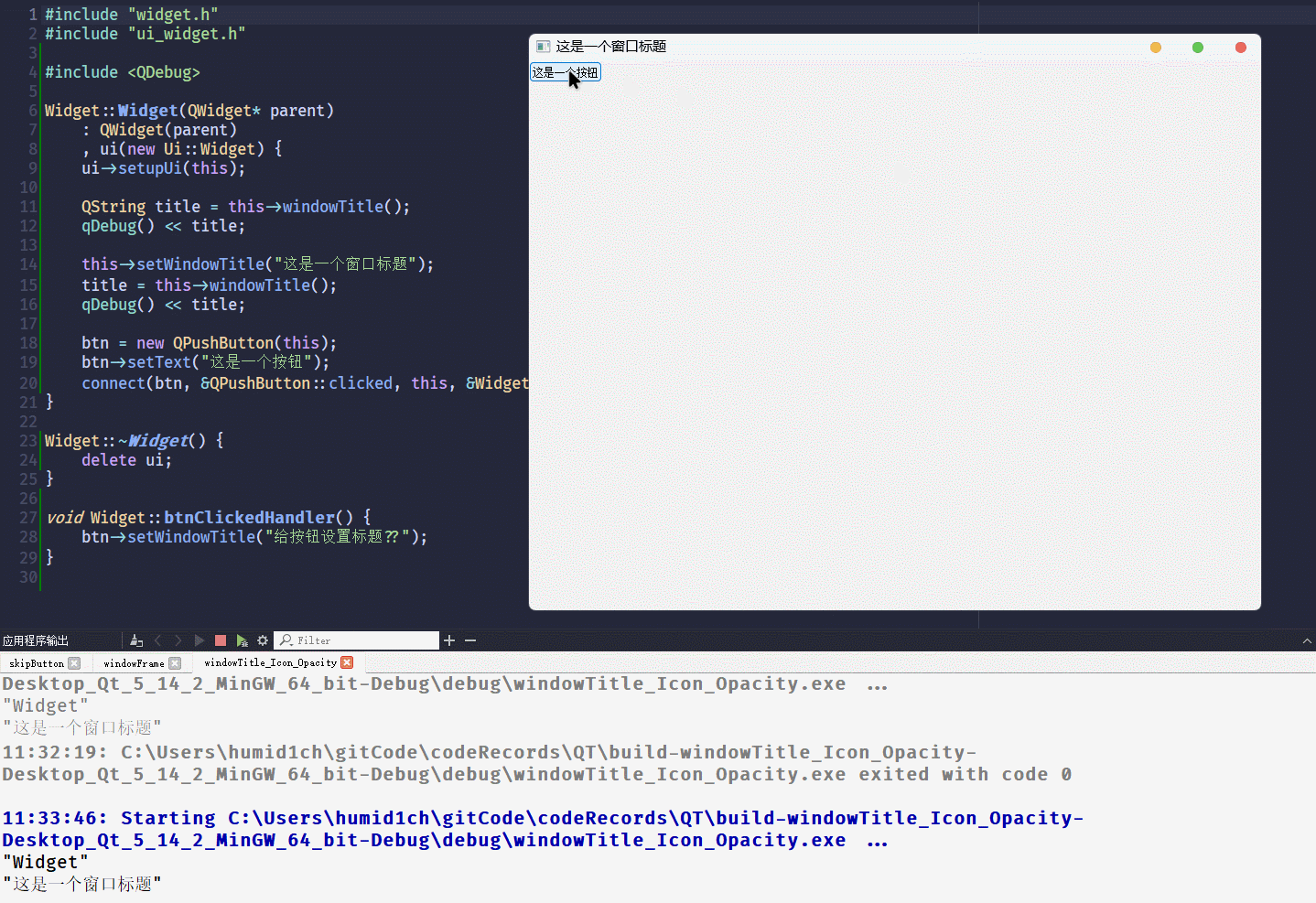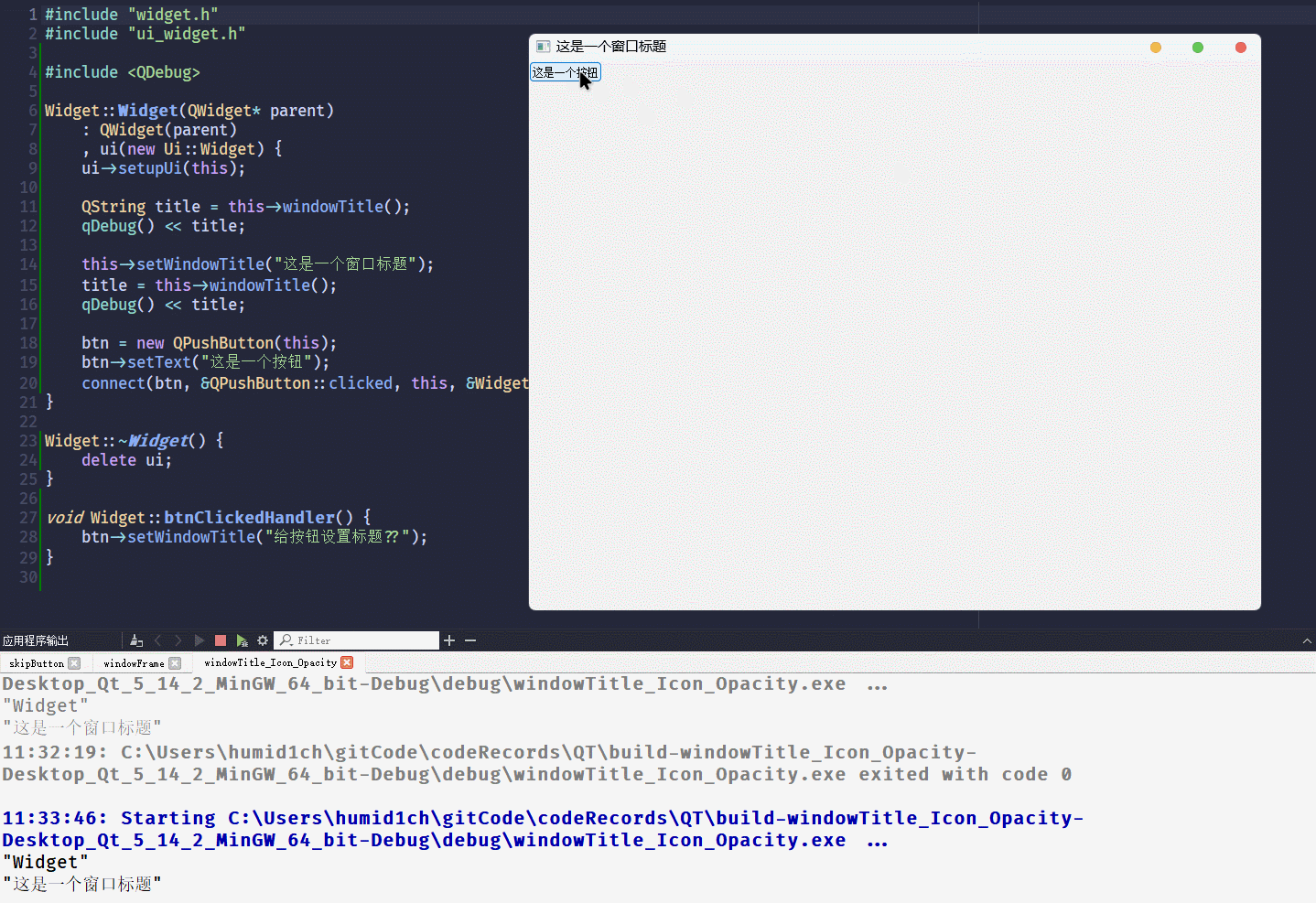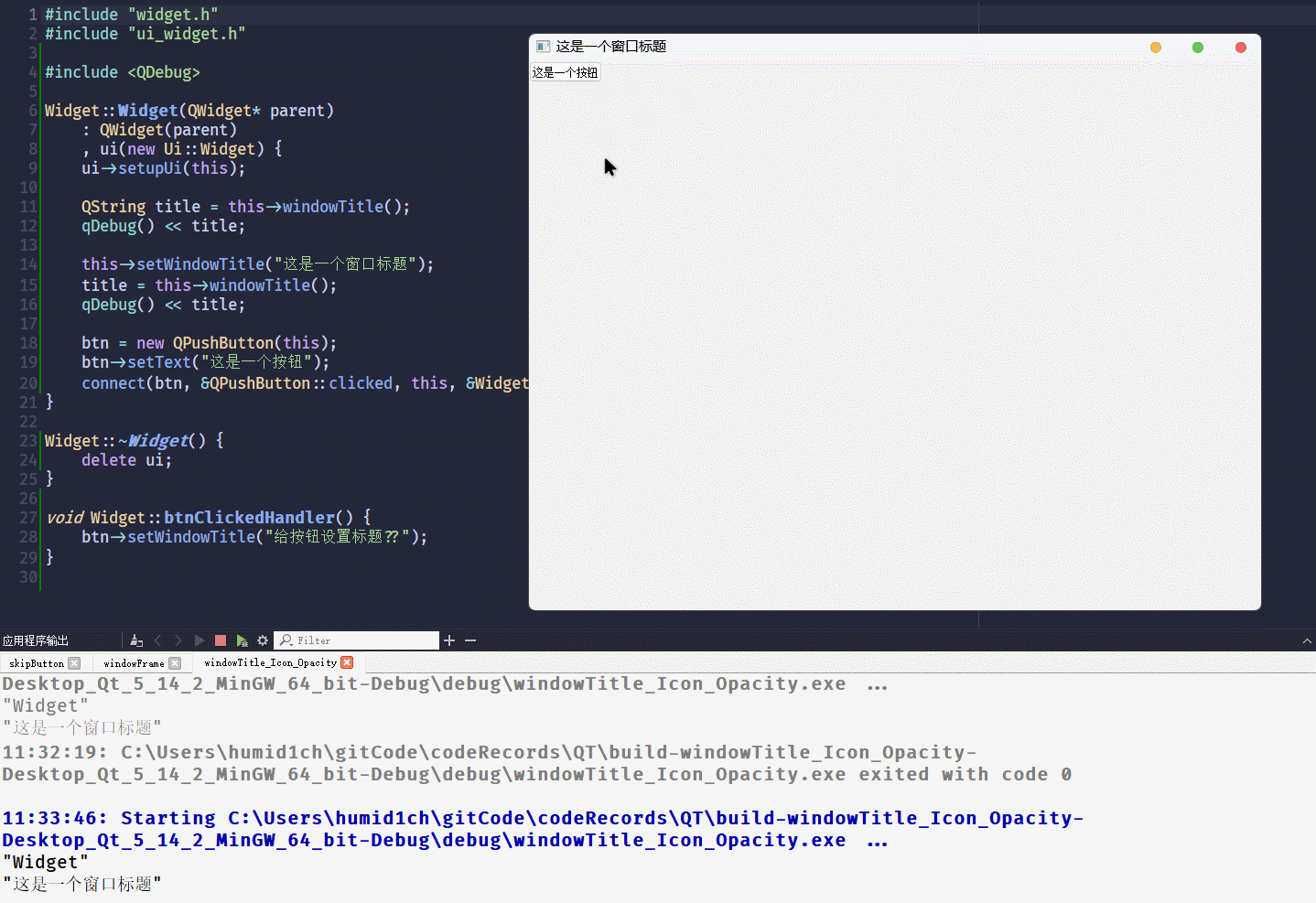
什么事都没有发生
从结果来看, 给非独立窗口设置
windowTitle不会发生报错, 所以 当预期是设置窗口的标题没有报错, 却又没有实现时, 可以查看一下是不是设置错控件了windowIcon
此属性, 用于设置窗口的图标, 且此属性同样对独立窗口有效
QT提供的接口:| 接口 | 功能 |
|---|---|
QIcon windowIcon() const; | 获取窗口当前图标属性 |
void setWindowIcon(const QIcon &icon); | 设置窗口图标属性 |
设置
windowIcon属性, 需要借助一个类QIconQIcon这个类虽然拥有很多成员, 但在这是windowIcon时, 用法非常简单只需要通过图标文件路径实例化出
QIcon对象就可以:widget.cc:#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QDebug>
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
QString title = this->windowTitle();
qDebug() << title;
this->setWindowTitle("这是一个窗口标题");
title = this->windowTitle();
qDebug() << title;
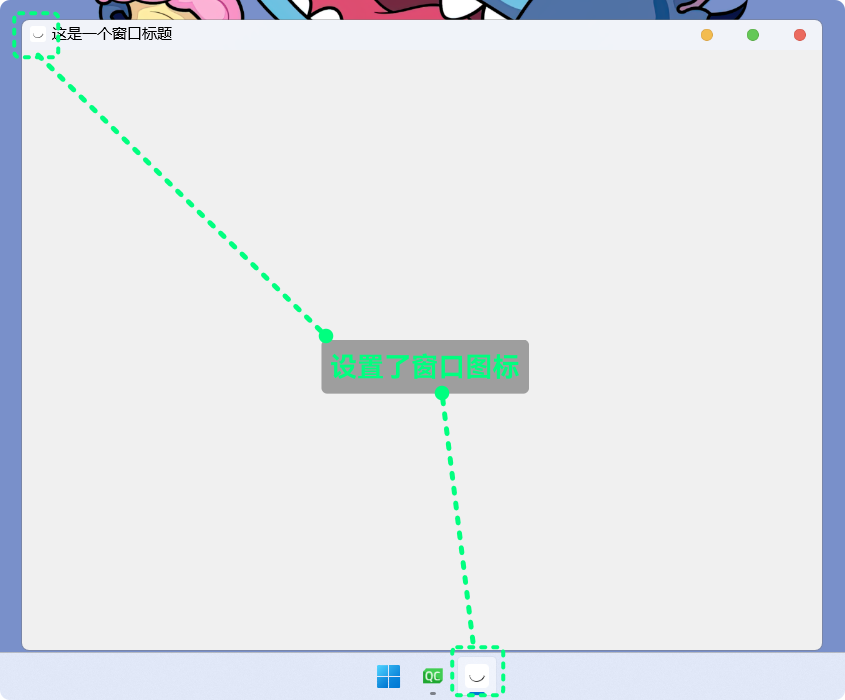
QIcon winIcon("c:/Users/humid1ch/smile.png");
this->setWindowIcon(winIcon);
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
}
QIcon的图标路径, 除了绝对路径之外, 也可以使用相对路径这里的相对路径, 是相对可执行程序的执行路径
我的项目路径在:
C:\Users\humid1ch\gitCode\codeRecords\QT
可执行程序的所在目录是
build-xxxxx的debug/release目录下: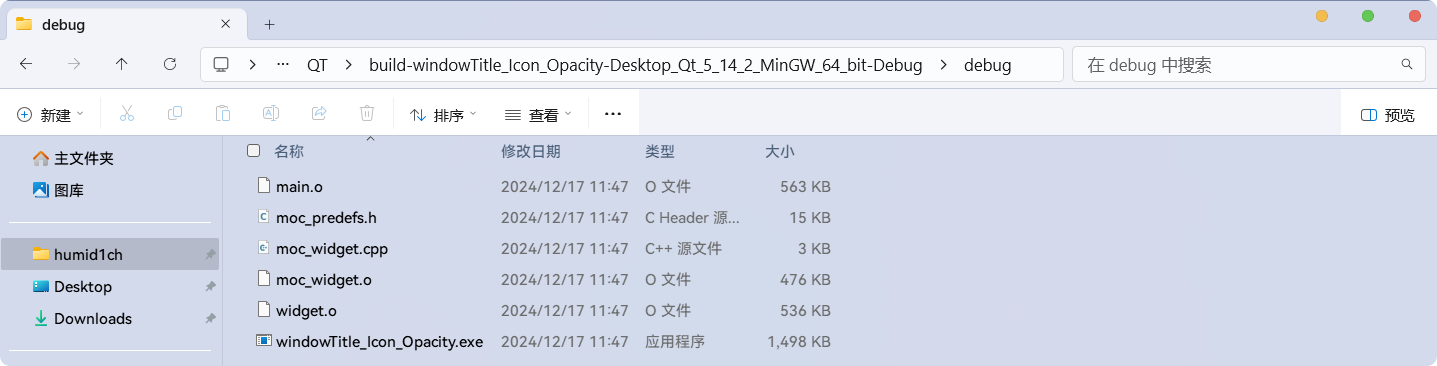
而,
QT Creator运行可执行程序时所在目录, 会在build-xxxxx目录下所以, 修改
QIcon的图标路径为./smile.png, 并将图标放在build-xxxxx目录下#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QDebug>
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
QString title = this->windowTitle();
qDebug() << title;
this->setWindowTitle("这是一个窗口标题");
title = this->windowTitle();
qDebug() << title;
QIcon winIcon("./smile.png");
this->setWindowIcon(winIcon);
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
}编译运行, 同样可以实现窗口图标的设置:
但是, 无论是绝对路径或是相对路径, 实际上都不能保证程序能实际找到图片资源
所以,
QT提供有另一个方式来管理程序的资源: qrcqrc资源管理机制 **
什么是
qrc?QT中, .qrc是一种xml类型的文件, .qrc的内容通常是文件资源的路径被
.qrc文件描述的文件资源, 在QT Creator编译代码时, 会以二进制的形式加载到可执行程序中, 以实现程序直接对文件资源的使用, 不需要在磁盘中在保存一份即, 被
qrc机制管理的文件, 不需要在磁盘中保存一份, 程序也不需要以资源在磁盘中的相对或绝对路径访问资源, 而是可以直接通过特殊的路径, 访问已经被加载到可执行程序中的文件资源QT Creator创建.qrc文件很简单: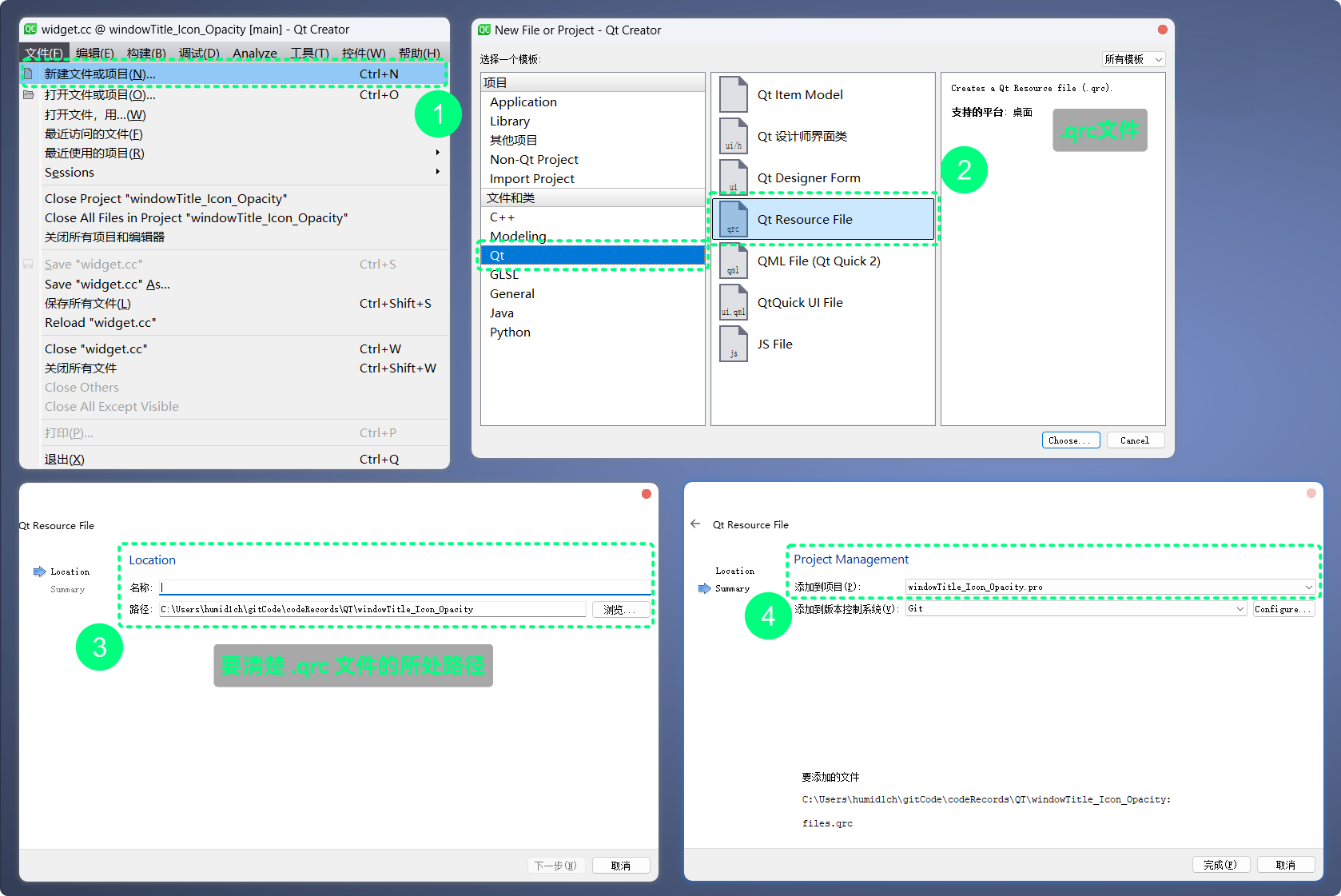
要清楚
.qrc文件的所在路径, 因为需要被.qrc管理的文件, 要与.qrc文件处于同级目录或子目录下创建好
.qrc文件之后, 就可以通过QT Creator添加要管理的文件资源了: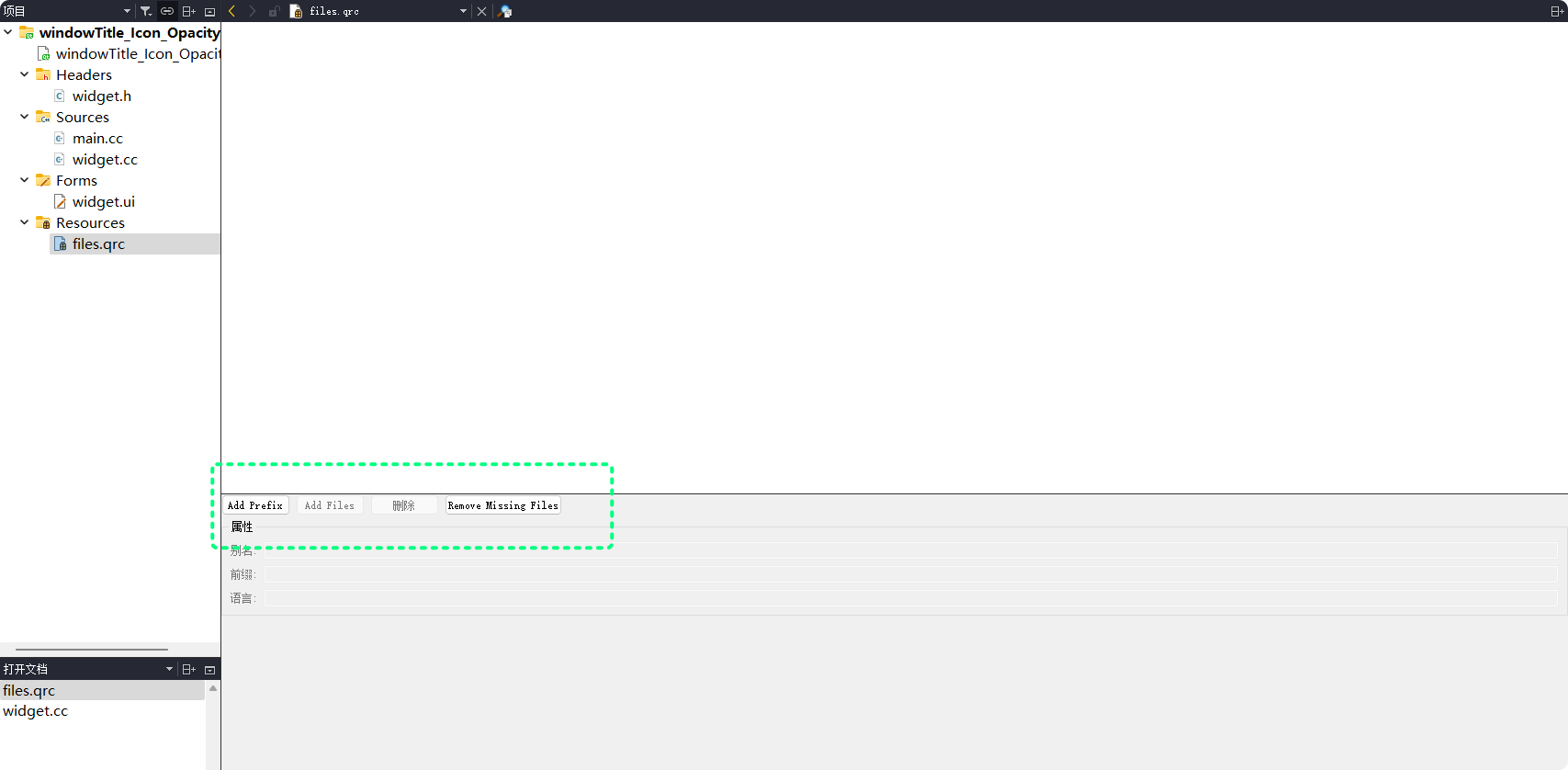
首先要添加
Prefix, 即 前缀, 前缀是什么, 在代码中访问资源的路径就需要添加什么, 一般为/然后可以在已添加的
Prefix下添加文件, 点击Add Files添加文件资源, 且文件要处与.qrc同级目录或子目录下: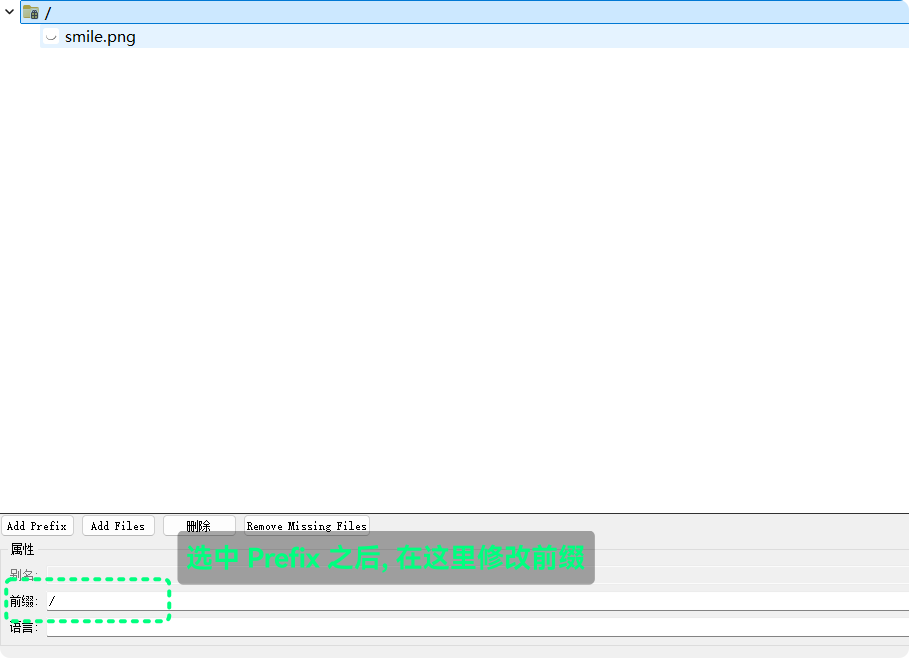
此时,
.qrc文件内容为: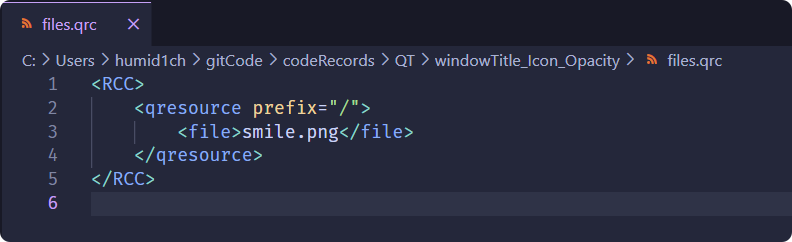
然后, 就可以在代码中使用
:/smile.png访问到文件资源:#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QDebug>
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
QString title = this->windowTitle();
qDebug() << title;
this->setWindowTitle("这是一个窗口标题");
title = this->windowTitle();
qDebug() << title;
// : 访问qrc管理的资源, / 就是前缀
QIcon winIcon(":/smile.png");
this->setWindowIcon(winIcon);
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
}
QT Creator实际是将被qrc管理的文件资源, 以二进制形式编译进了可执行程序中在
build-xxxxx的子目录下可以看到qrc相关的.cpp文件:
这个数组, 就是文件的二进制数据, 数组的每一个元素都是1字节
unsigned char此文件, 在
QT Creator编译代码时 会一同编译进可执行程序中
qrc机制更适合于小文件资源, 如果太大, 不适合直接被加载到可执行程序中, 只会造成性能损耗
windowOpacity
此属性, 用于设置窗口的不透明度, 且此属性同样对独立窗口有效
QT提供了两个相关的接口:| 接口 | 功能 |
|---|---|
qreal windowOpacity() const; | 获取窗口当前的不透明度 |
void setWindowOpacity(qreal level); | 设置窗口的不透明度 |
qreal实际就是double类型, 所以 使用也很简单:widget.cc:#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QDebug>
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
QString title = this->windowTitle();
qDebug() << title;
this->setWindowTitle("这是一个窗口标题");
title = this->windowTitle();
qDebug() << title;
QIcon winIcon(":/smile.png");
this->setWindowIcon(winIcon);
btn1 = new QPushButton(this);
btn1->setGeometry(300, 210, 200, 40);
btn1->setText("按钮1: +");
connect(btn1, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &Widget::btn1ClickedHandler);
btn2 = new QPushButton(this);
btn2->setGeometry(300, 330, 200, 40);
btn2->setText("按钮2: -");
connect(btn2, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &Widget::btn2ClickedHandler);
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
}
void Widget::btn1ClickedHandler() {
qreal winOpacity = this->windowOpacity();
if (winOpacity > 1) {
return;
}
this->setWindowOpacity(winOpacity + 0.05);
qDebug() << this->windowOpacity();
}
void Widget::btn2ClickedHandler() {
qreal winOpacity = this->windowOpacity();
if (winOpacity < 0) {
return;
}
this->setWindowOpacity(winOpacity - 0.05);
qDebug() << this->windowOpacity();
}这段代码的运行结果为:
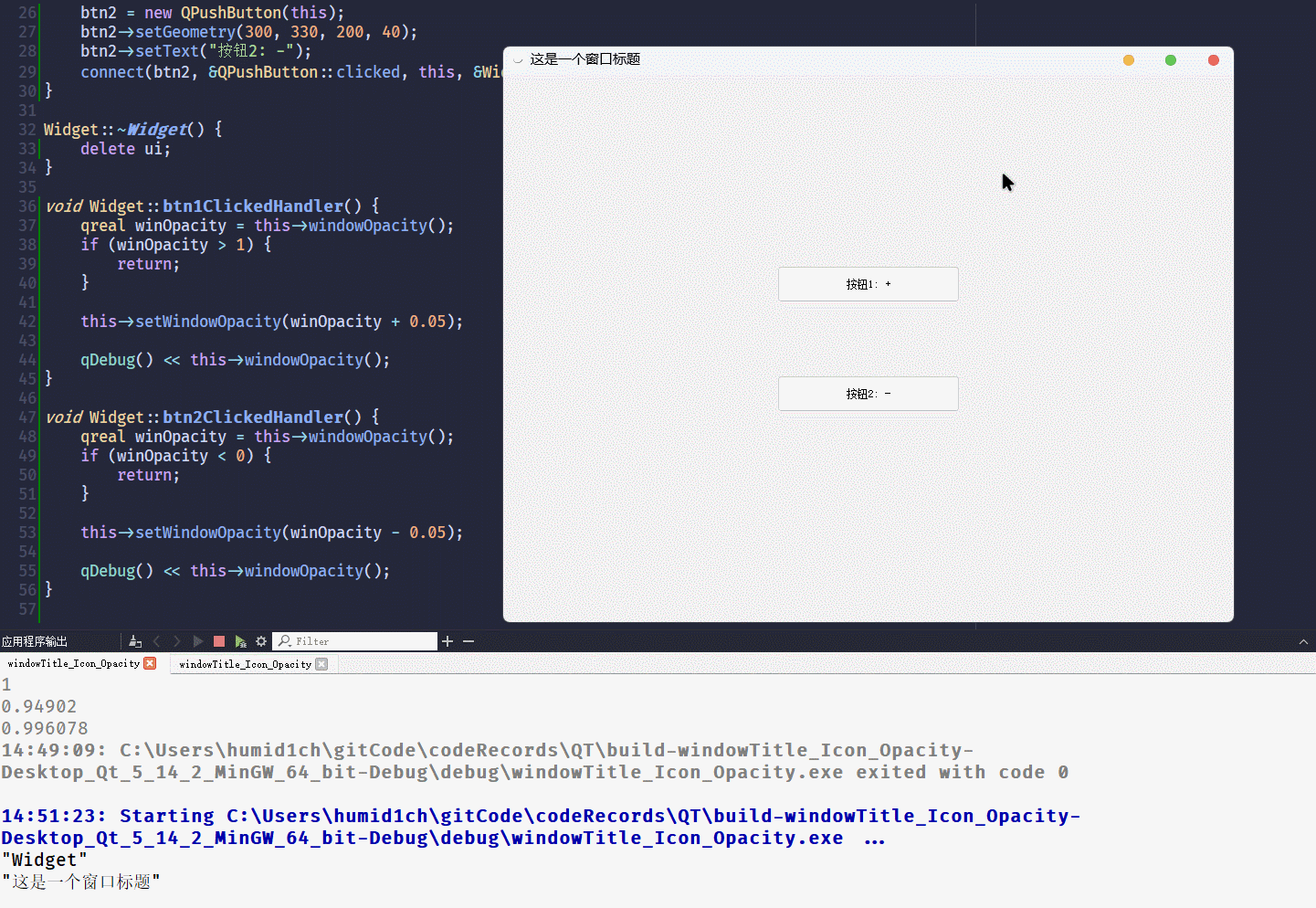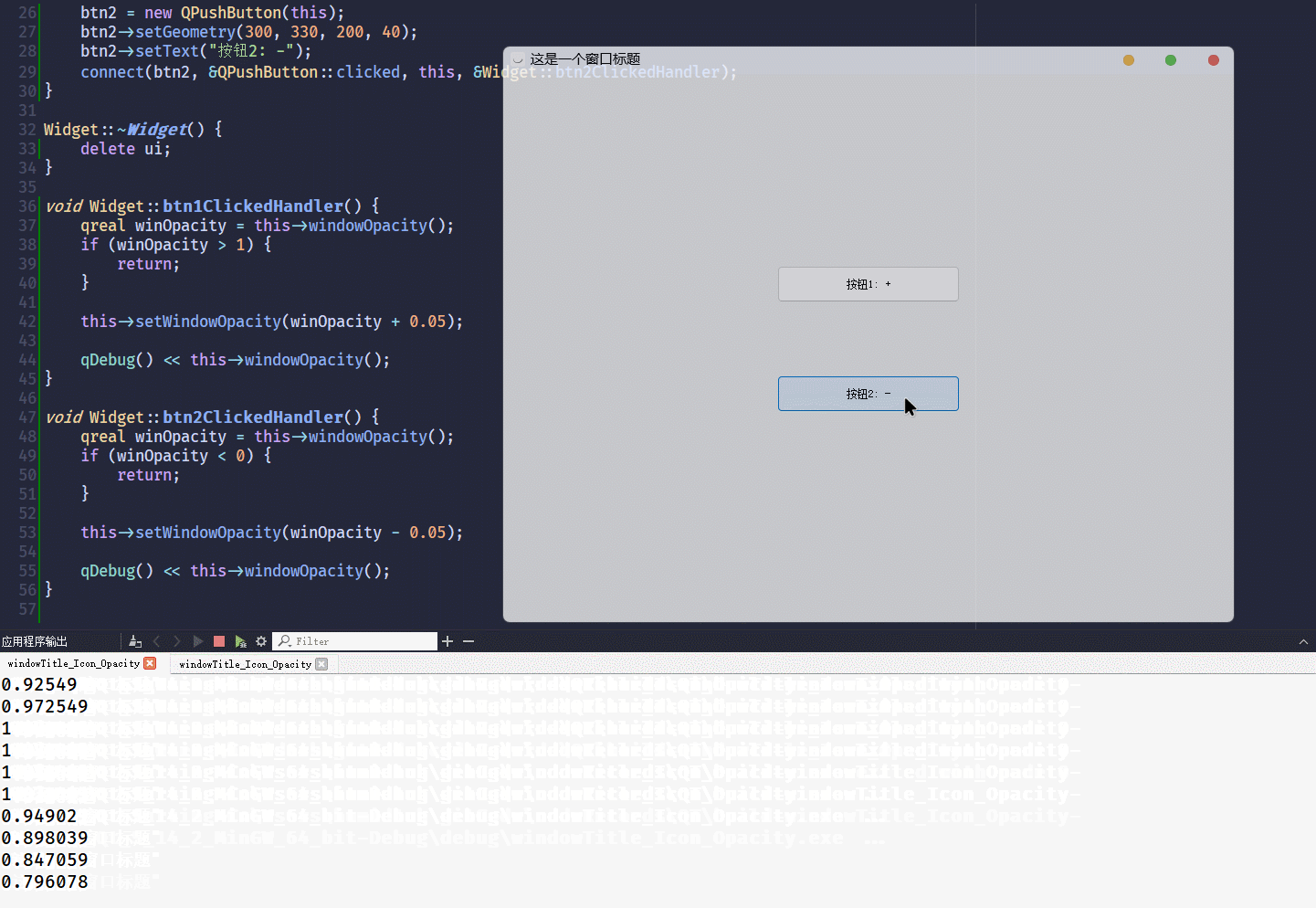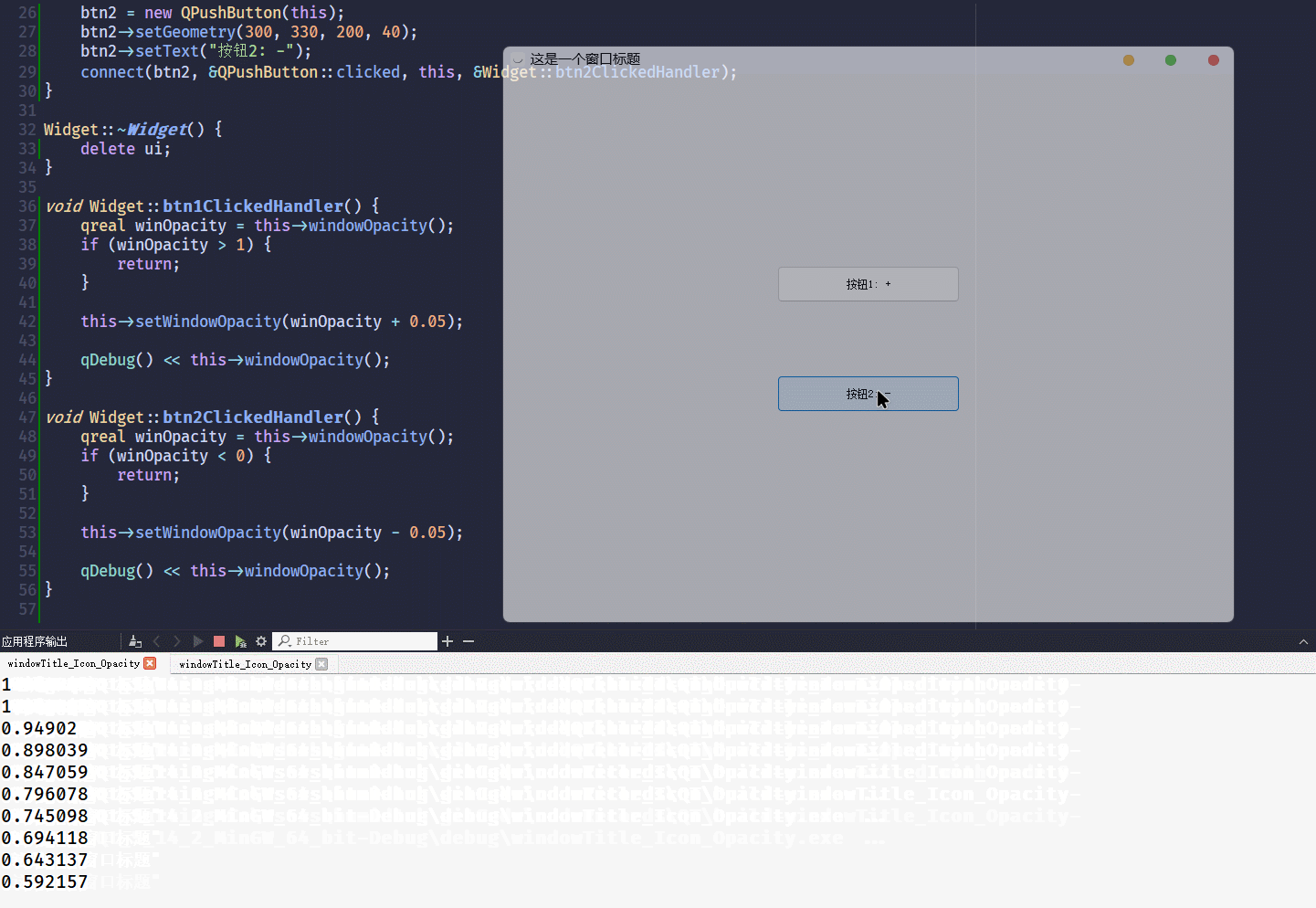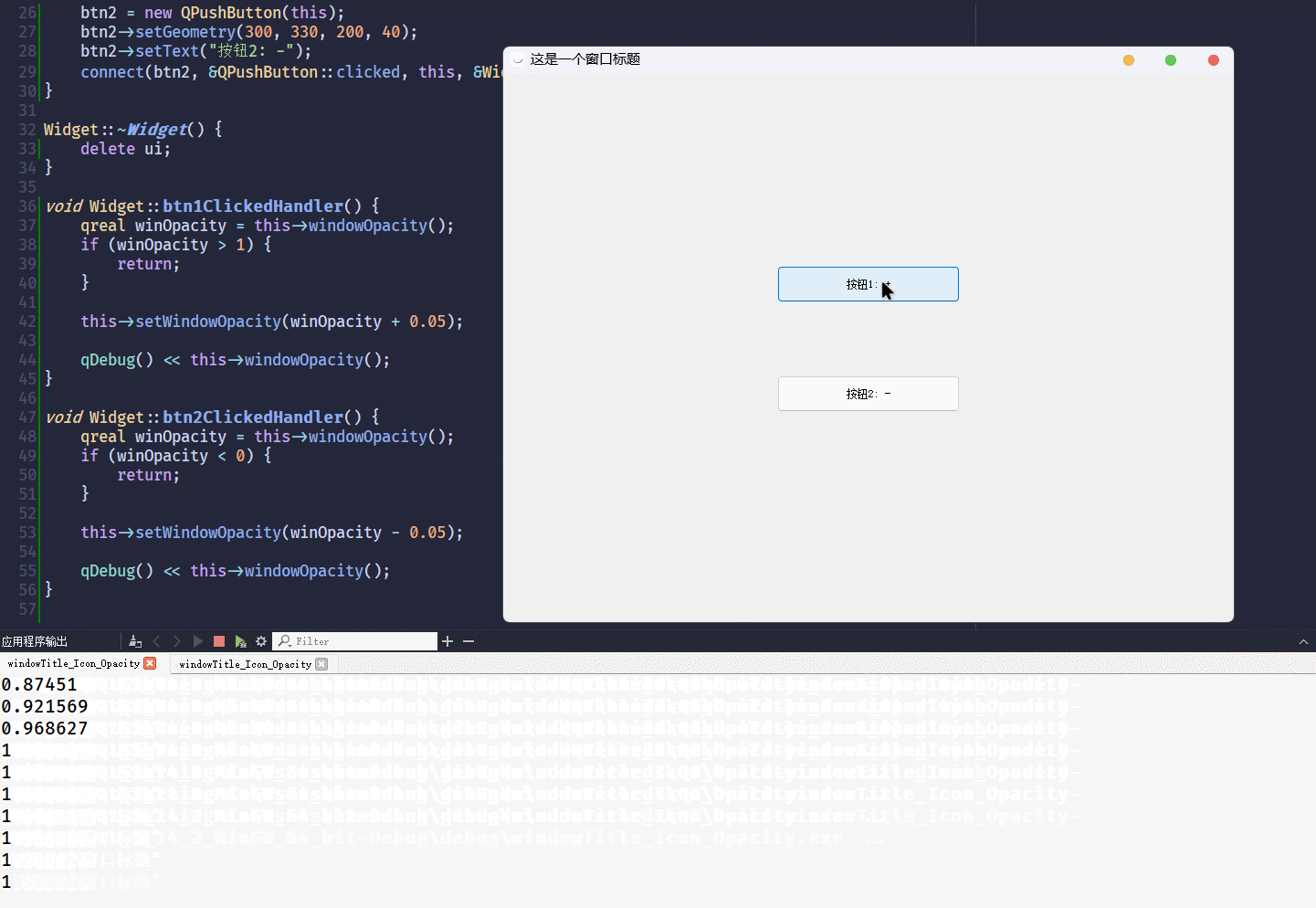
从结果可以看到,
windowOpacity这个属性, 是自带范围控制的[0, 1]不建议把不透明度设置为
0, 窗口会变成无法选中状态
cursor
此属性, 用于设置控件范围内光标的样式
光标就是这个东西:

QT可以设置光标在控件范围时的光标形式, 可以在QT Designer中直接选择控件进行设置, 也可以通过代码的方式进行设置
设置
Widget的cursor为上箭头, pushButton的cursor为等待设置完之后, 运行结果如下:
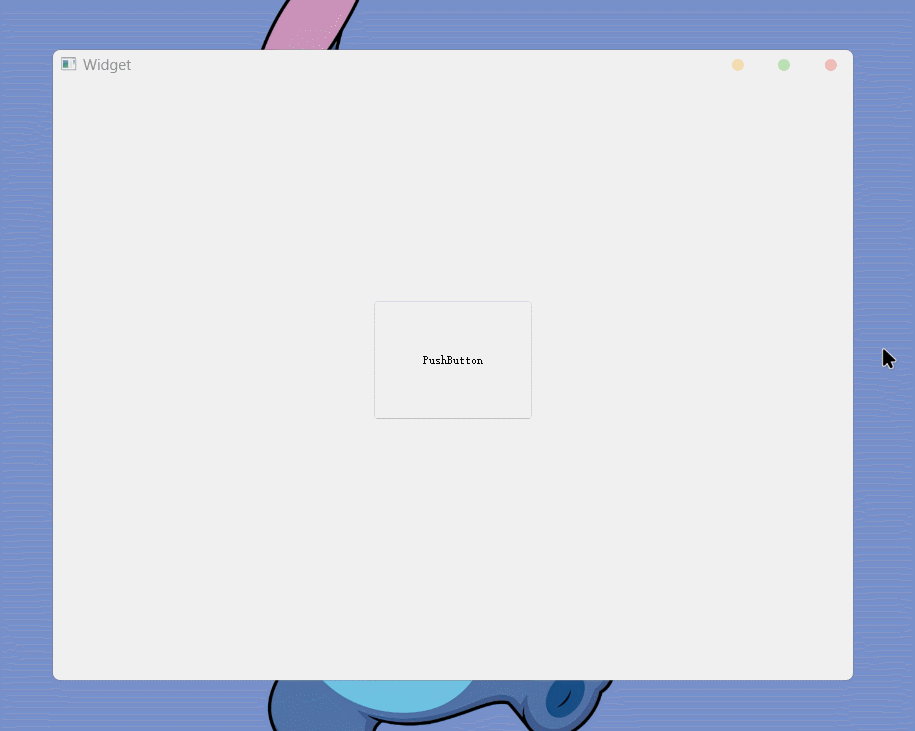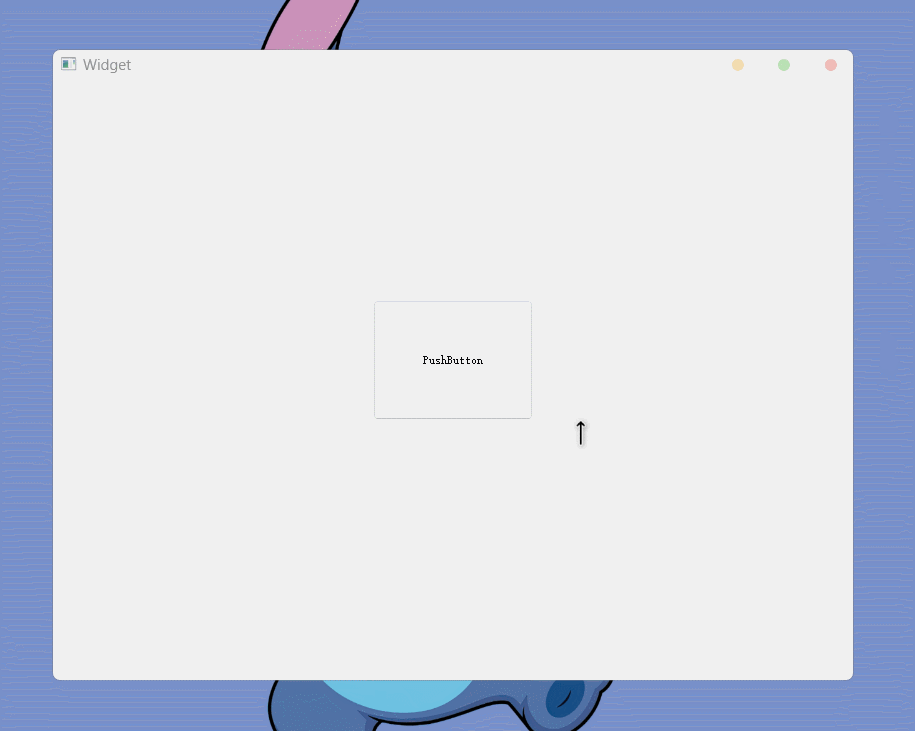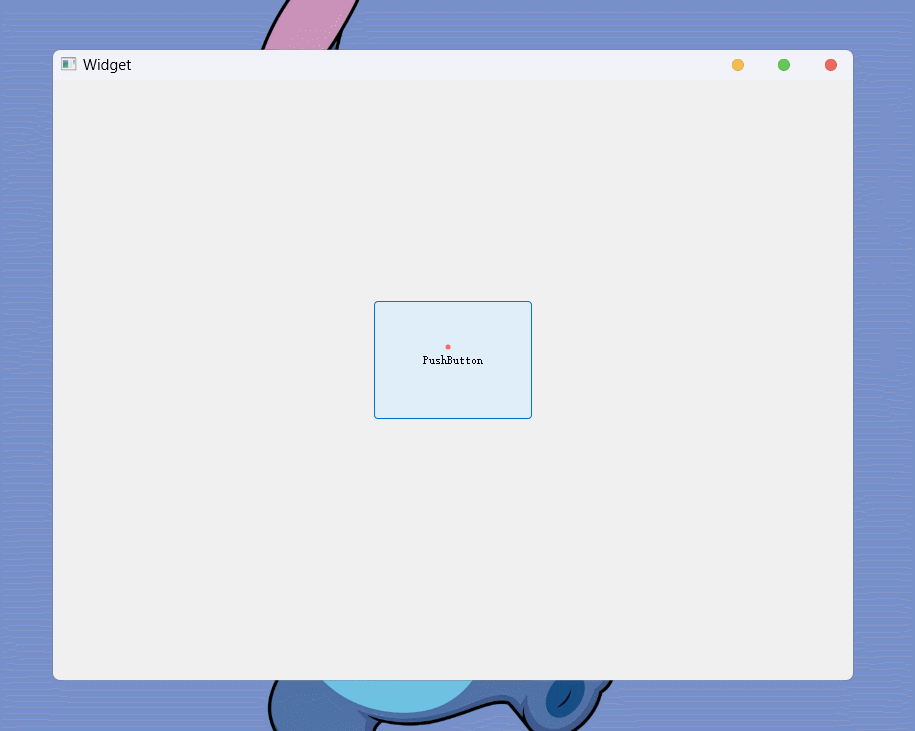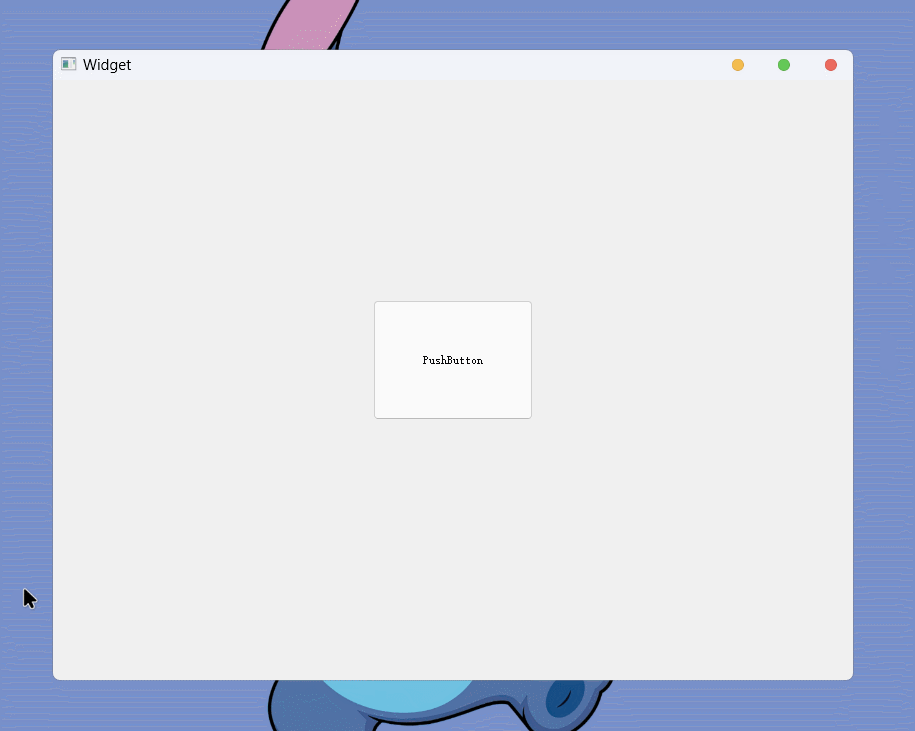
也可以通过代码进行设置,
QT提供了相应的接口| 接口 | 功能 |
|---|---|
QCursor cursor() const; | 获取控件当前光标样式 |
void setCursor(const QCursor &); | 设置控件的光标样式 |
void QGuiApplication::setOverrideCursor(const QCursor& cursor); | 设置全局光标样式, 对整个程序中所有的控件生效, 会覆盖setCursor()设置的样式 |
QCursor是一个光标类, 可以用来设置控件的cursor属性widget.cc:#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QPushButton>
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
QCursor csr(Qt::CrossCursor);
this->setCursor(csr);
csr = Qt::IBeamCursor;
ui->pushButton->setCursor(csr);
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
}程序运行结果为:
QT提供了许多的cursor类型, 都可以在QCursor对象中设置:
自定义光标样式
除了内置的光标样式之外,
QT还能够自定义光标样式可以使用图片, 作为控件的光标样式, 接口还是
setCursor(), 参数也还是QCursor类型但是,
QCursor对象的实例化就不能是enum CursorShape了需要使用图片资源实例化
QCursor对象:| 接口 | 功能 |
|---|---|
QCursor(const QPixmap &pixmap, int hotX=-1, int hotY=-1); | 以图片资源QPixmap实例化QCursor对象的构造函数 |
QPixmap类, 就是用于使用图片资源的类, 使用图片之前可以用qrc将图片资源管理起来
widget.cc:#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QPushButton>
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
QPixmap csrPic(":/heartWings.png");
QCursor csr(csrPic);
this->setCursor(csr);
ui->pushButton->setCursor(csr);
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
}程序运行的结果为:
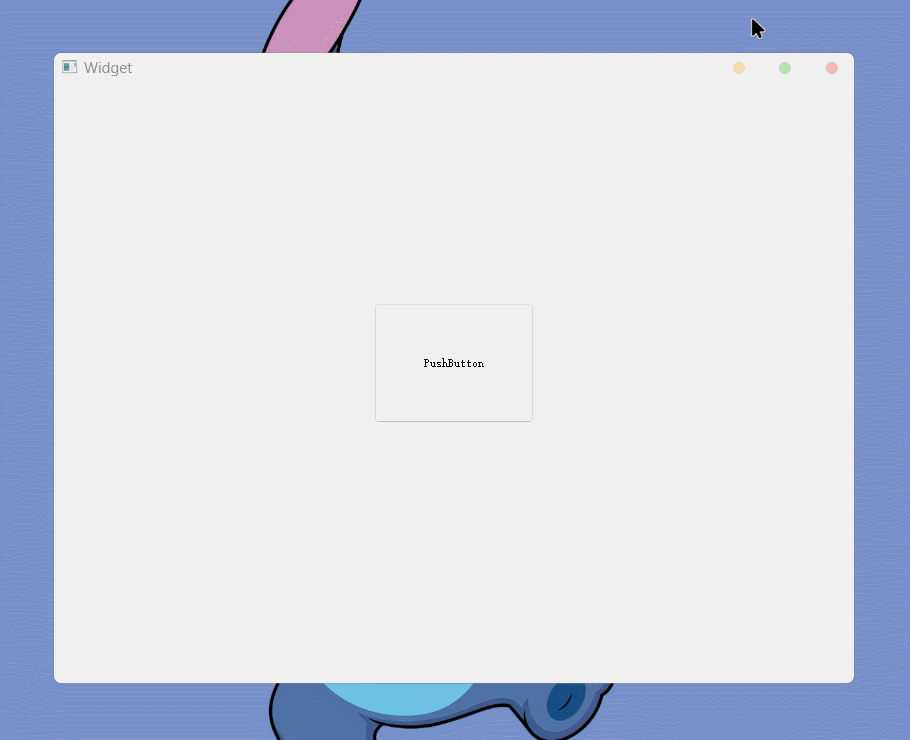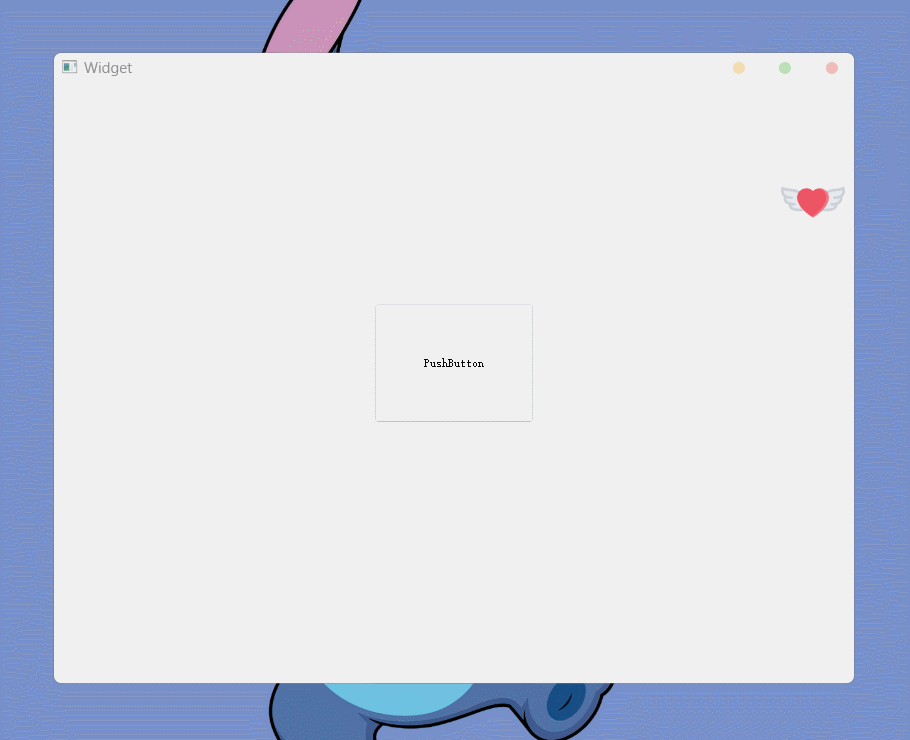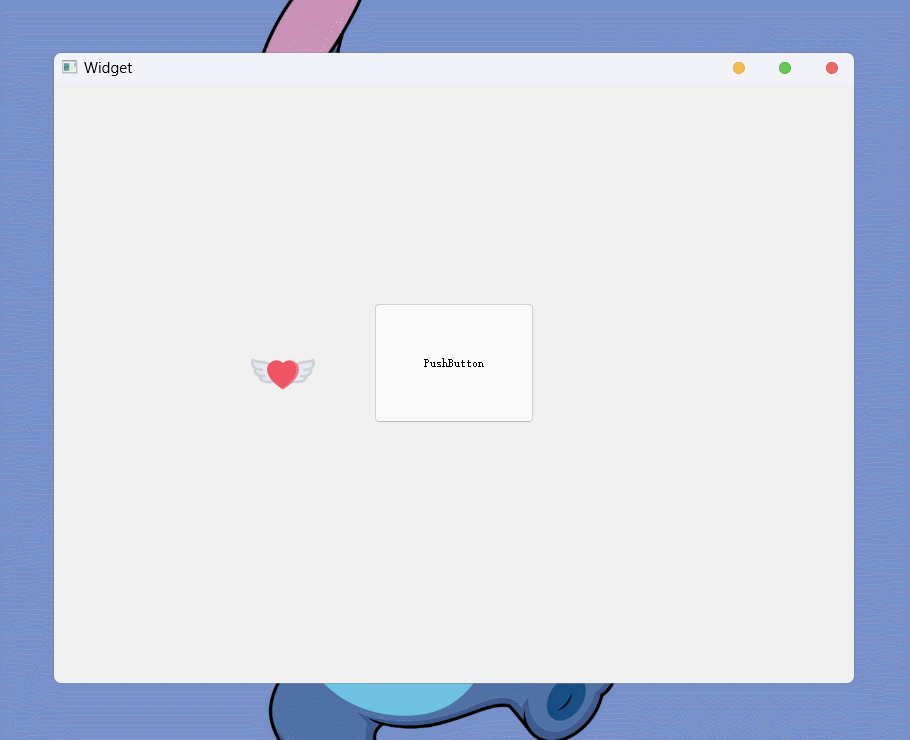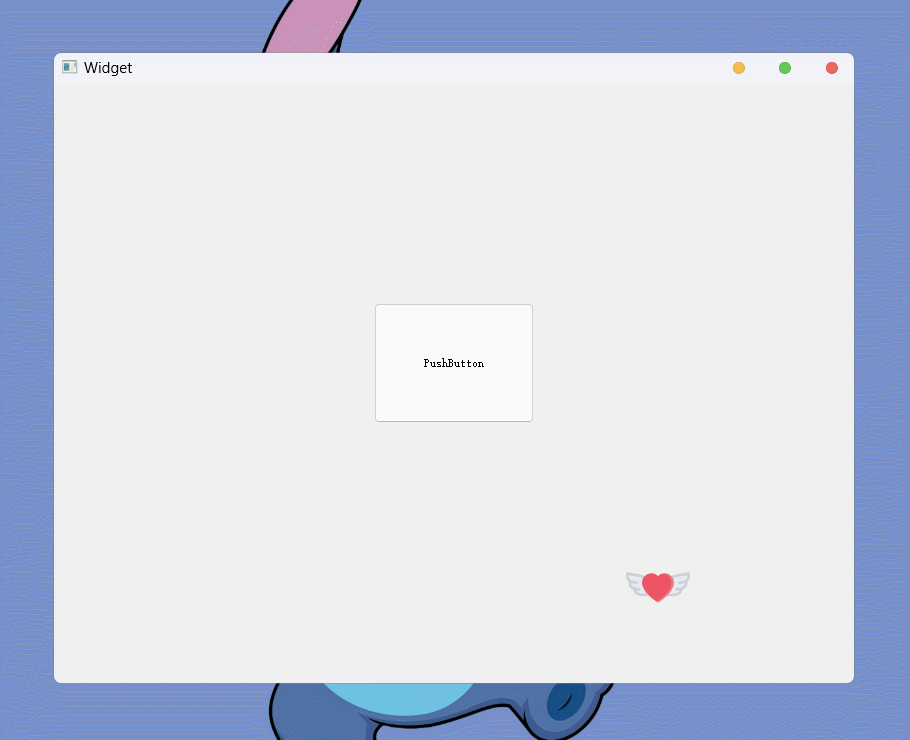
在使用图片自定义光标时, 如果没有特殊情况 默认的有效点击位置是图片的左上角
(0, 0)的位置, 有效点击位置被叫做热点什么是特殊情况呢, 如果图片的
(0, 0)位置是透明的, 就是特殊情况此时, 光标的热点就会默认被设置为图片的中心位置(上面例子中使用的图片就是64x64的四周透明的
png图片)通过
QCursor::hotSpot()可以查看光标的热点:
也可以在
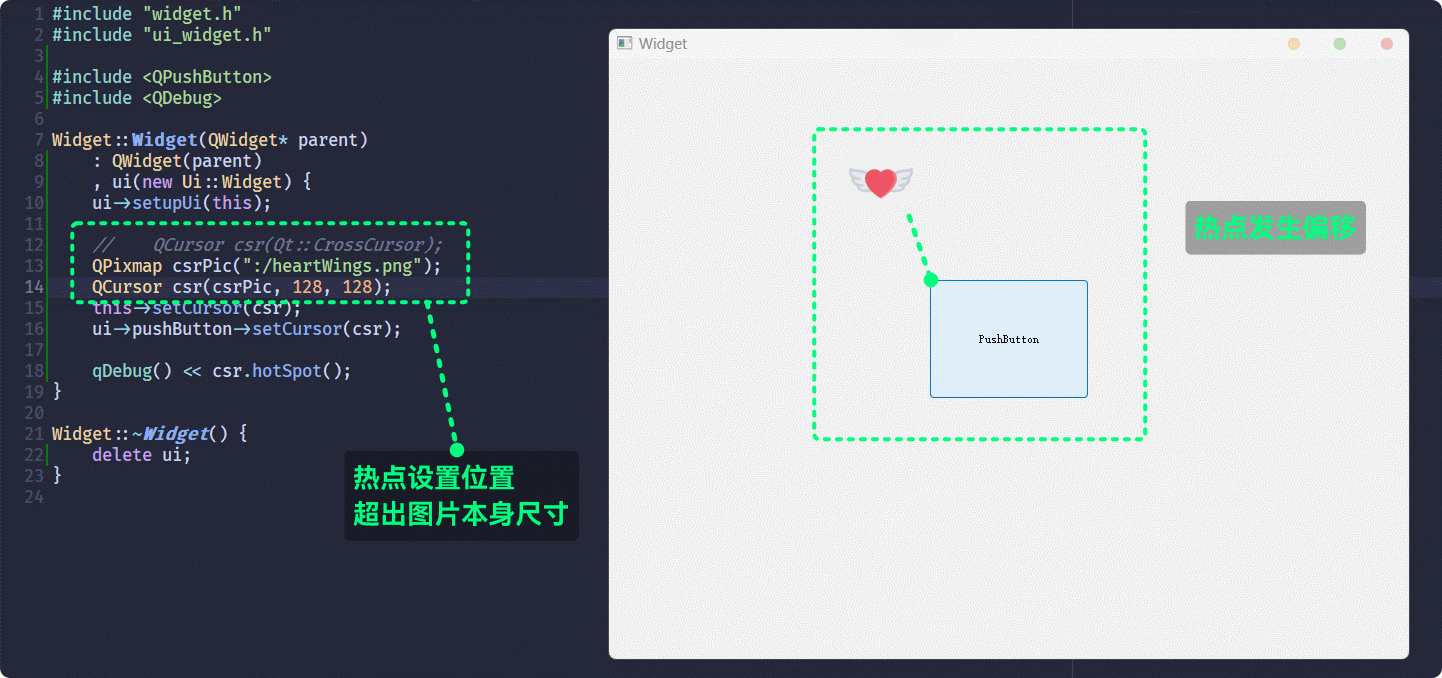
QCursor对象实例化时 构造函数传参设置光标的热点, 或通过成员函数setPos()设置光标的热点: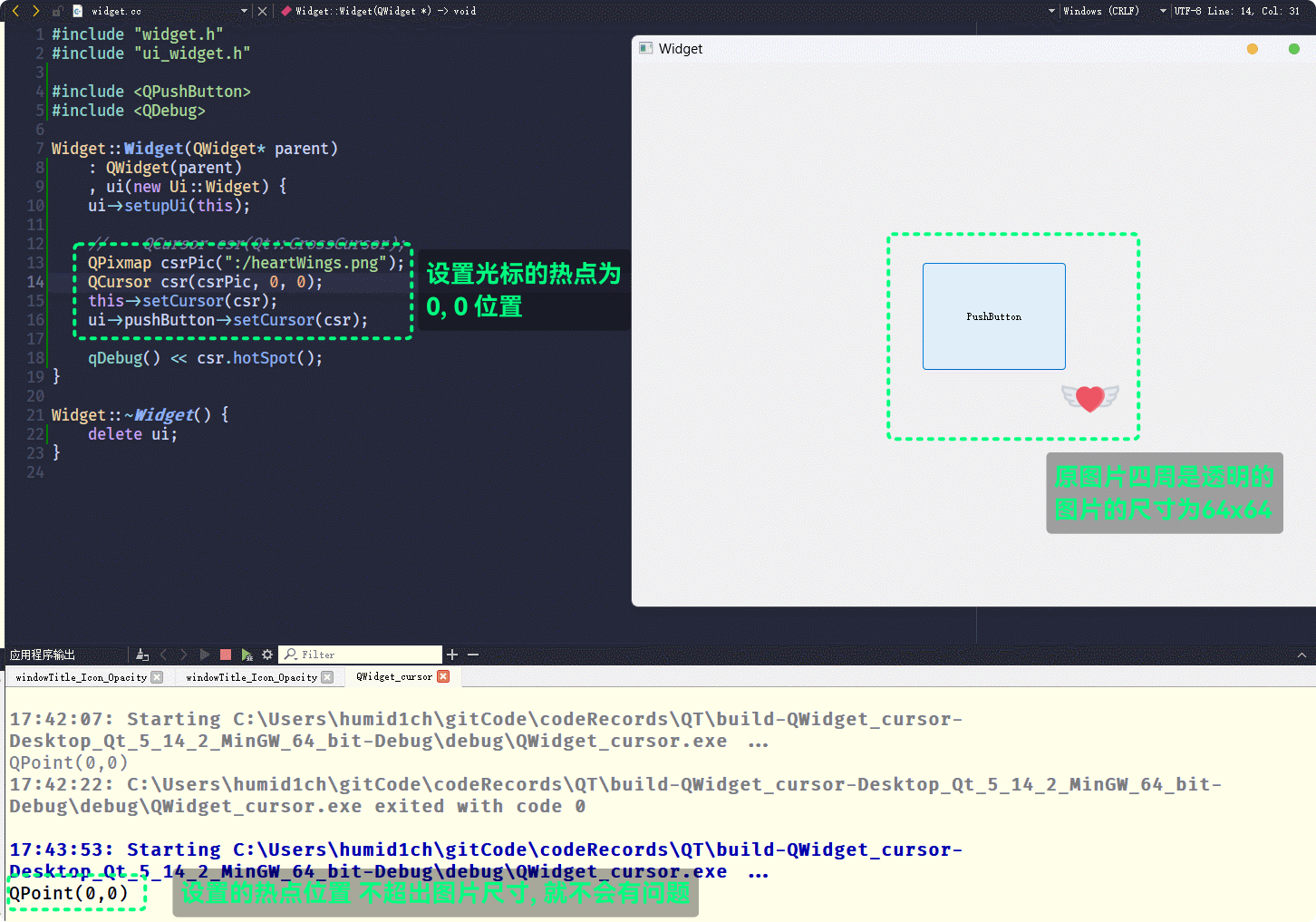
如果, 设置的热点位置超出了图片尺寸, 则光标热点会发生偏移:
font
此属性, 用于设置控件文本的字体样式
QT Designer可以直接设置控件的font属性, 并且在QT Designer中可以实时预览: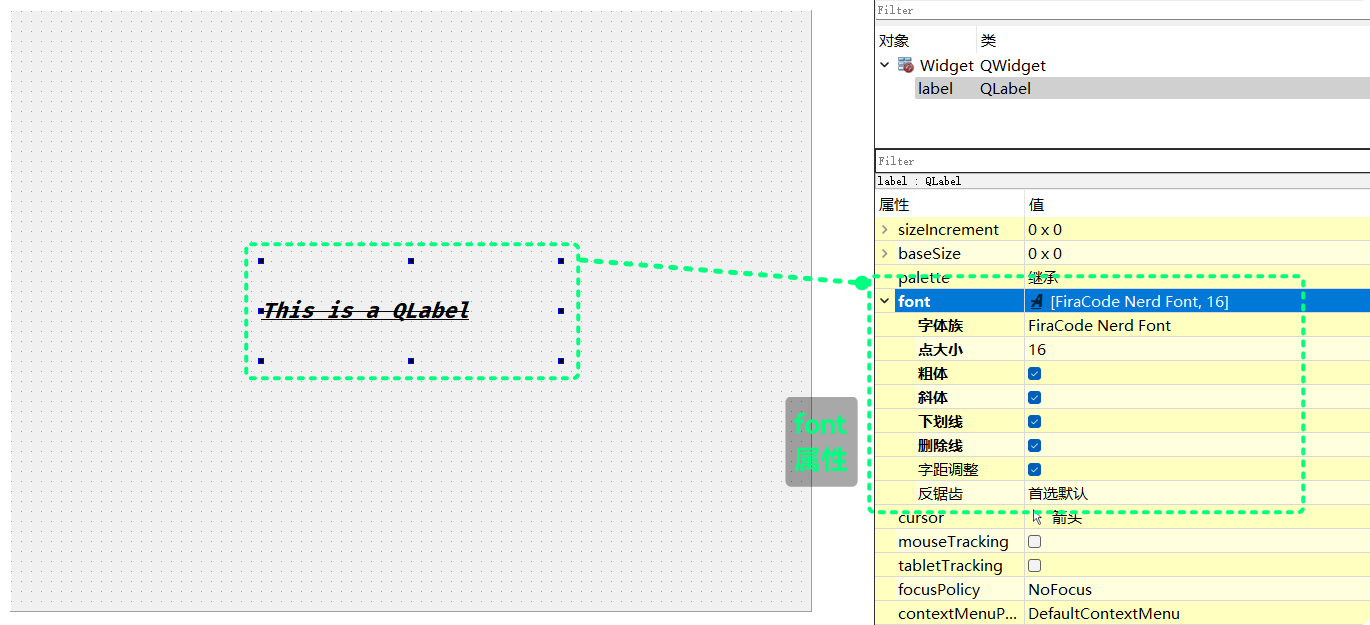
也可以通过代码的形式设置控件的
font属性QT的相关接口有:| 接口 | 功能 |
|---|---|
const QFont &font() const; | 获取控件当前文本的font属性 |
void setFont(const QFont &); | 设置控件文本的font属性 |
这两个接口的用法很简单, 使用了
QFont类QFont类拥有一个字体的属性的成员, 通过设置QFont对象的成员, 再调用setFont()就能实现对控件文本的font属性的设置QFont拥有许多的成员, 不过不用一一了解, 通常只需要了解一些常用的接口来设置font常用属性就可以了font的常用属性已经在QT Designer中展示出来了:字体族
(font-family) 点大小(point-size) 粗体(bold) 斜体italic 下划线(underline) 删除线(strikeout) 字距调整(kerning)点大小设置的就是字体大小
还有另外常用的: 字体风格
(style) 字体宽度(weight)这些都可以通过
QFont的成员函数获取或设置, 下面只罗列设置:| 接口 | 功能 |
|---|---|
void setFamily(const QString &); | 设置字体族, 即 什么字体, 通常需要保证系统中已安装 |
void setPointSize(int); | 设置字体大小 |
inline void setBold(bool); | 设置是否粗体 |
inline void setItalic(bool); | 设置是否斜体 |
void setUnderline(bool); | 设置是否有下划线 |
void setStrikeOut(bool); | 设置是否有删除线 |
void setKerning(bool); | 设置是否调整字体间距 |
void setStyle(Style style); | 设置字体风格, 与 字体粗细 倾斜等有关 |
void setWeight(int); | 设置字体宽度, 与 字体粗细有关 |
对
QFont对象设置这些属性, 可以设置一个字体风格若需要使用字体文件设置字体族, 则需要使用其他接口设置一个
QString表示字体族然后再调用
setFamily()设置字体族
widget.cc:#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QFont>
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
QFont fonts;
fonts.setFamily("FiraCode Nerd Font"); // 设置 字体族
fonts.setPointSize(14); // 设置 字体大小14
fonts.setBold(true); // 开启 粗体
fonts.setItalic(false); // 关闭 斜体
fonts.setUnderline(false); // 关闭 下划线
fonts.setStrikeOut(true); // 开启 删除线
fonts.setKerning(true); // 关闭 字距调整
ui->label->setFont(fonts);
ui->label->setText("This is a QLabel.");
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
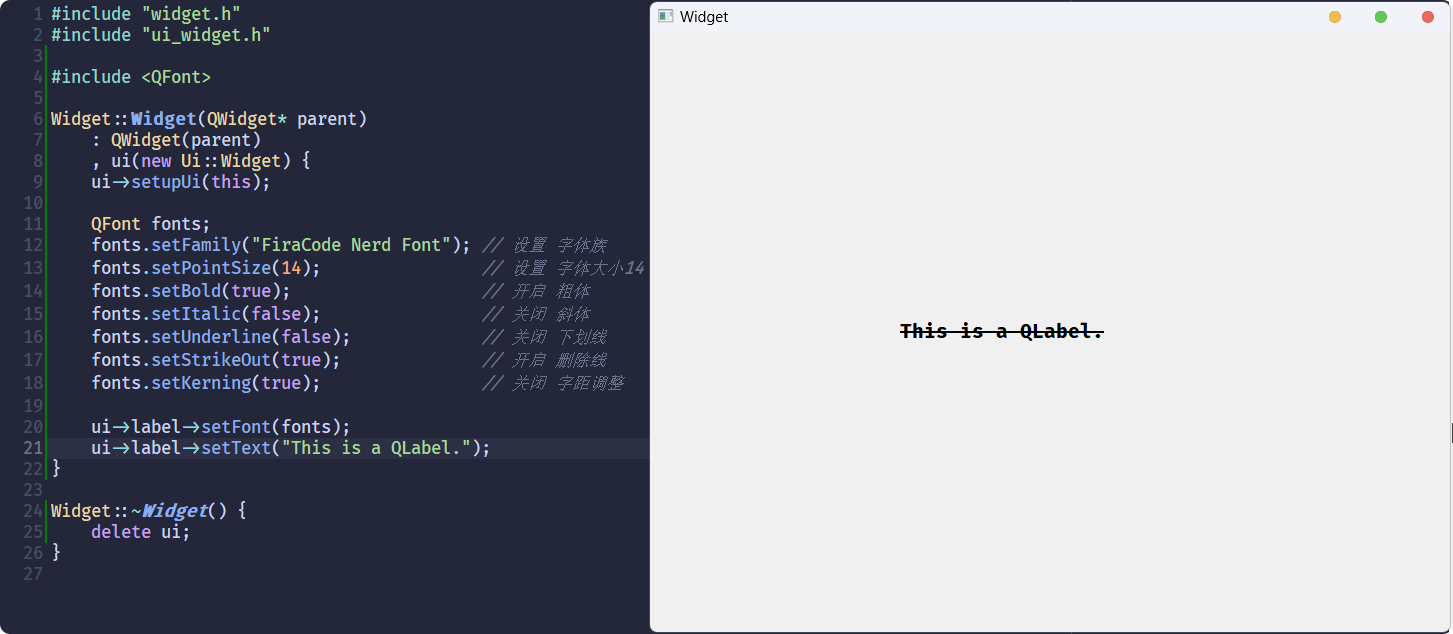
}程序的执行结果为:
tooltip
此属性, 用于设置光标悬停在控件上时, 给出的提示
什么意思呢, 举个例子:
这样的提示就是
tooltip可以显示的内容QT Designer中有相关的设置: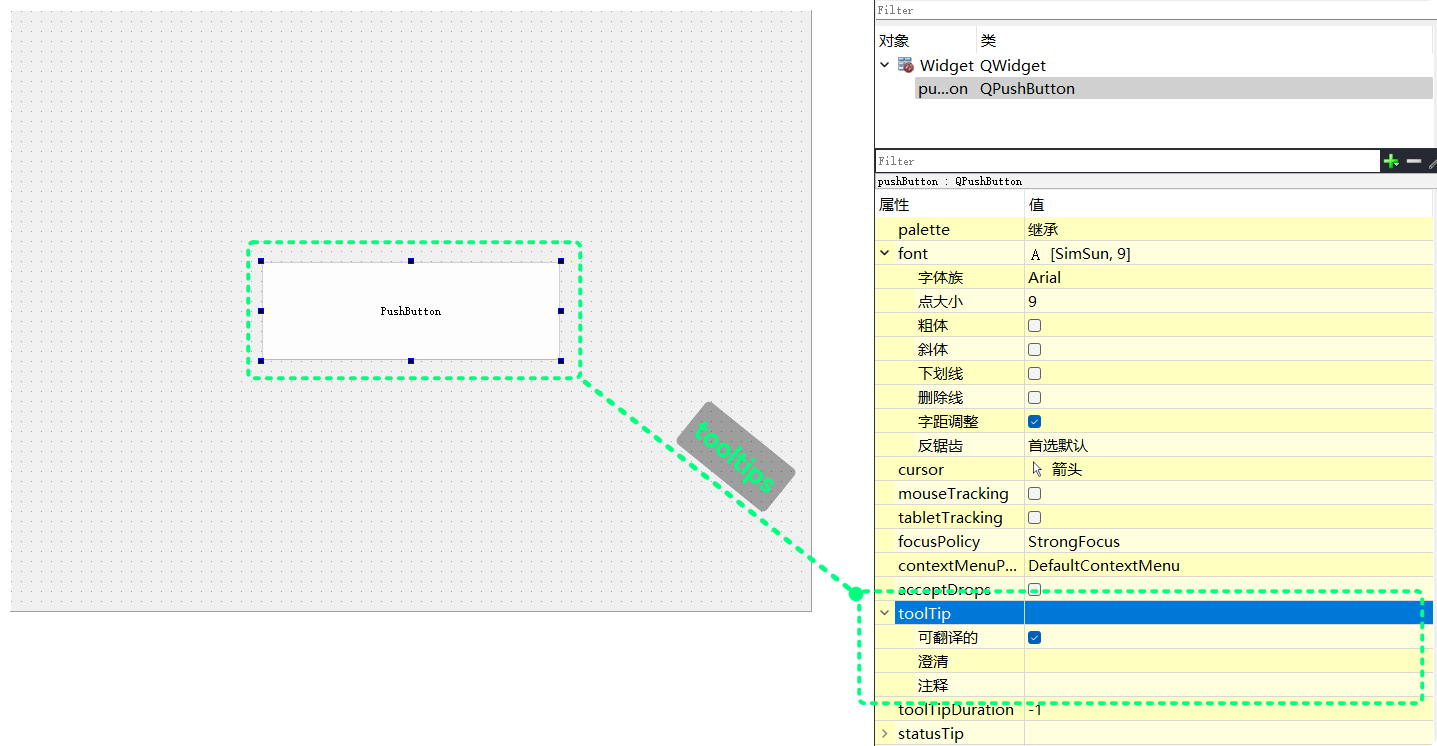
也可以直接通过代码设置,
QT相关的接口有:| 接口 | 功能 |
|---|---|
QString toolTip() const; | 获取控件当前的tooltip |
void setToolTip(const QString &); | 设置控件的tooltip |
int toolTipDuration() const; | 获取控件当前tooltip的持续显示时间, 单位ms |
void setToolTipDuration(int msec); | 设置控件tooltip的持续显示时间, 单位ms |
对
PushButton设置tooltip: “这只是一个什么用都没有的按钮”, 持续显示时间为5000mswidget.cc:#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
ui->pushButton->setToolTip("这只是一个什么用都没有的按钮");
ui->pushButton->setToolTipDuration(5000);
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
}程序运行结果为:
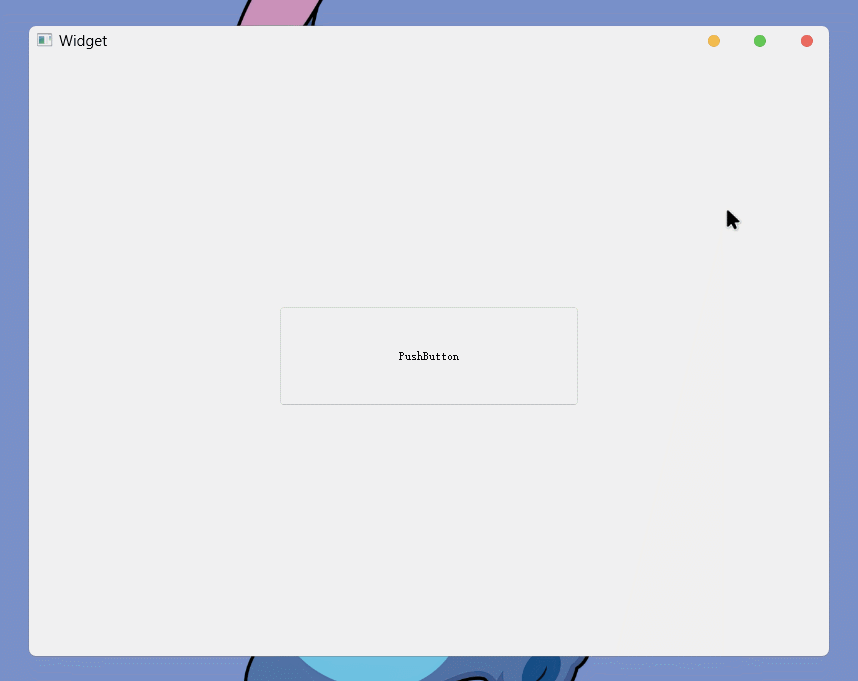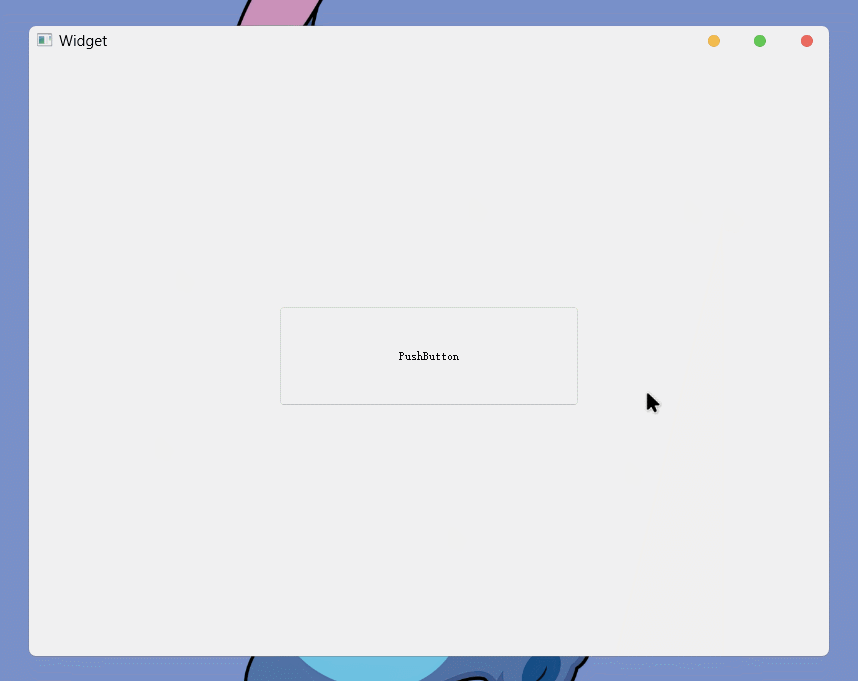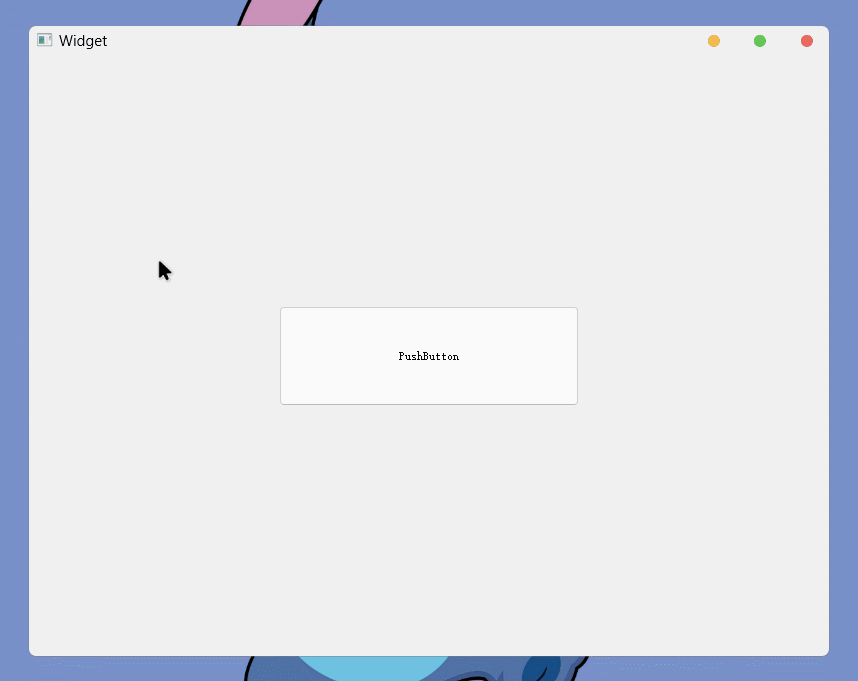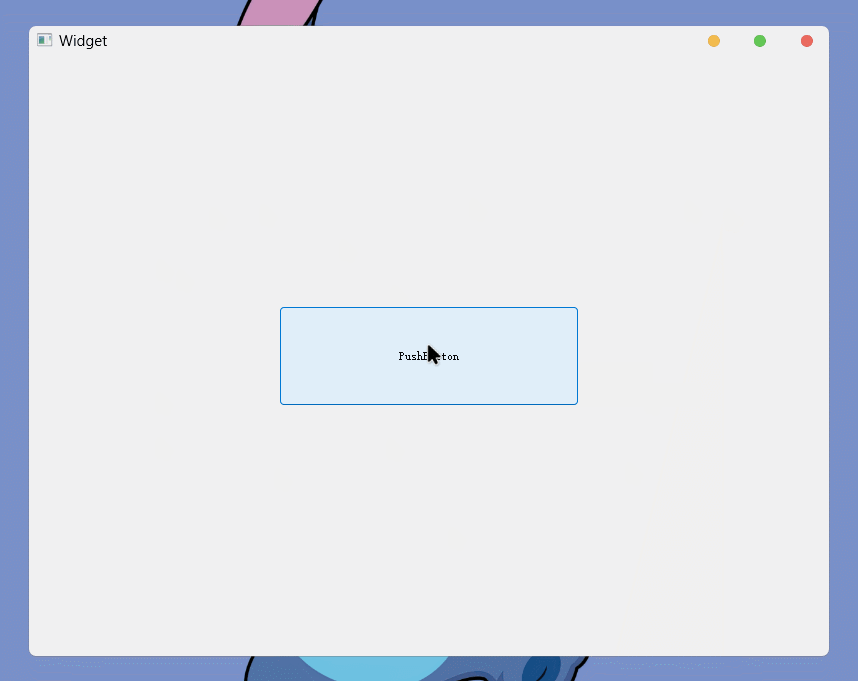
focusPolicy
此属性, 用于设置控件的聚焦方式
要理解聚焦方式, 首先要理解聚焦, 什么是聚焦?
在上网的过程中, 一定遇到过各种登录的场景, 比如:
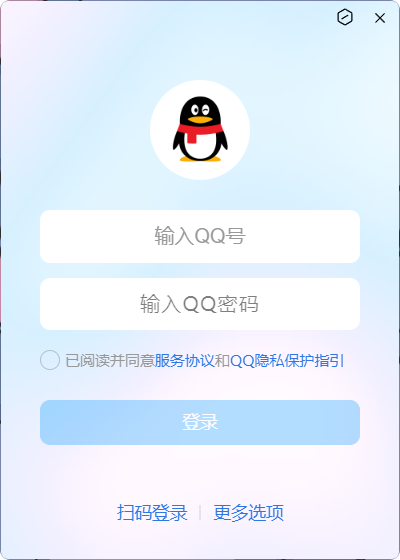
在需要从键盘输入数据时, 需要先点击单行文本编辑框, 将输入焦点聚焦在单行文本编辑框上
然后才能将文本输入到聚焦的单行文本编辑框中:

并且, 可以通过点击或
Tab的方式, 切换所聚焦的单行文本编辑框:
而
focusPolicy就是设置这些控件的聚焦方式Qt::FocusPolicy是一枚举类型:enum FocusPolicy {
NoFocus = 0, // 不接收键盘焦点, 即 无法聚焦
TabFocus = 0x1, // 可以且只能通过Tab键获取焦点
ClickFocus = 0x2, // 可以且只能通过点击获取焦点
StrongFocus = TabFocus | ClickFocus | 0x8, // 可以同时通过Tab或点击获取焦点
WheelFocus = StrongFocus | 0x4 // 还可以通过滚轮滚动获取焦点
};在
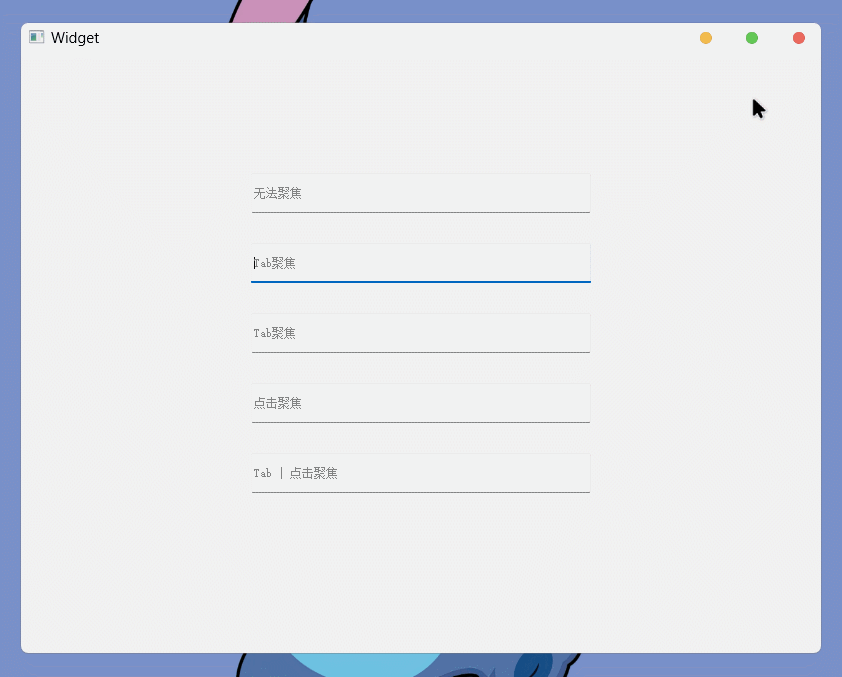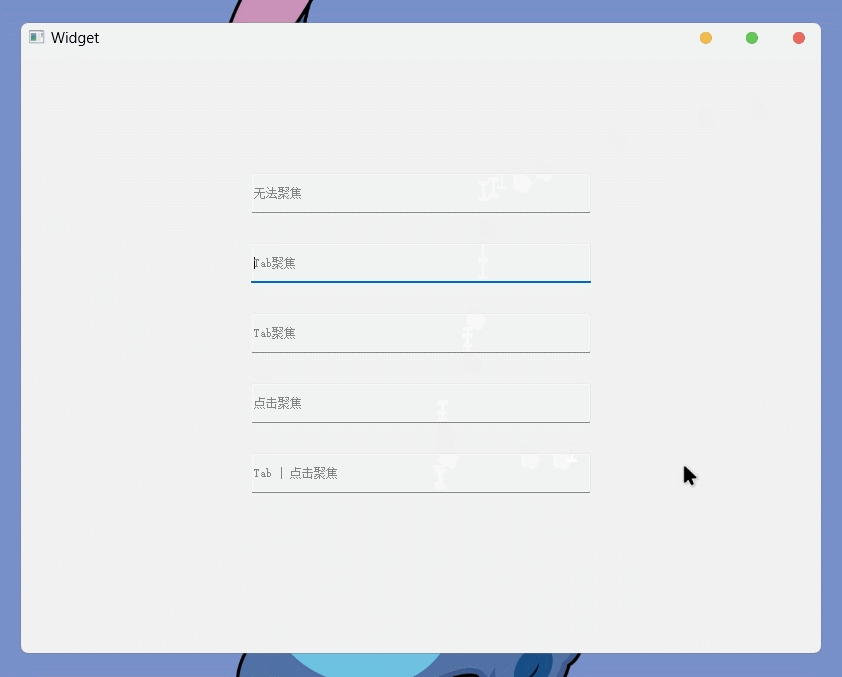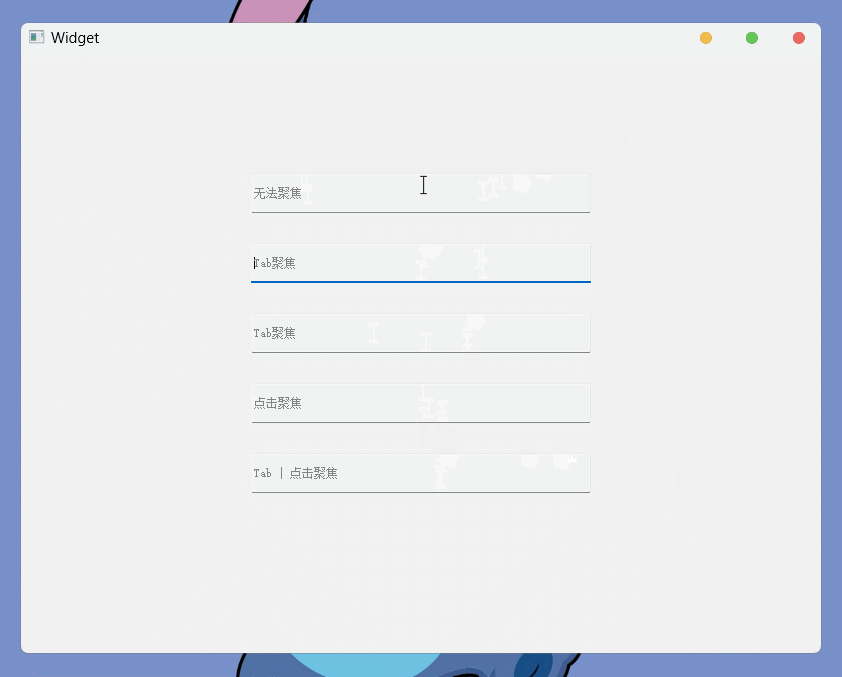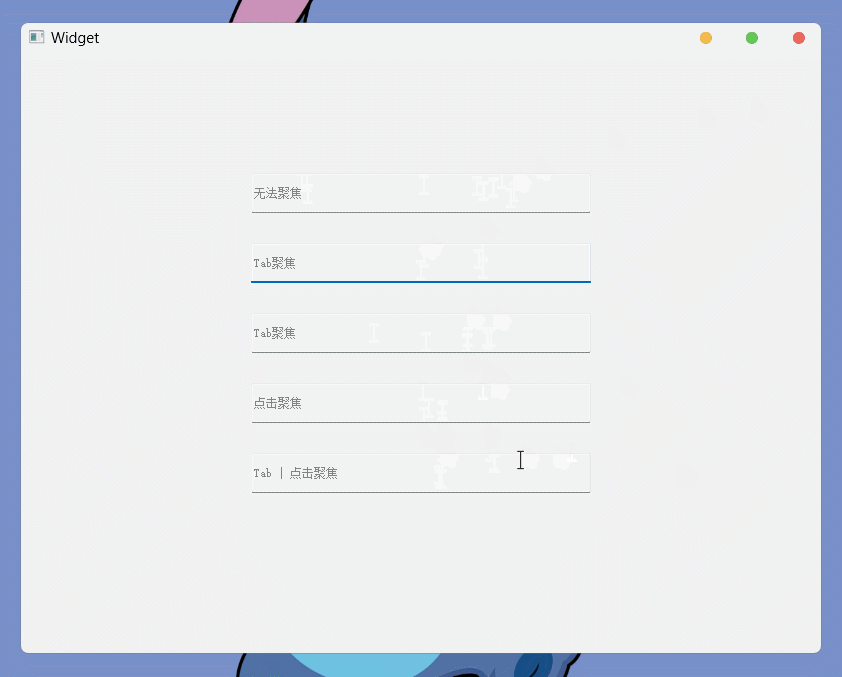
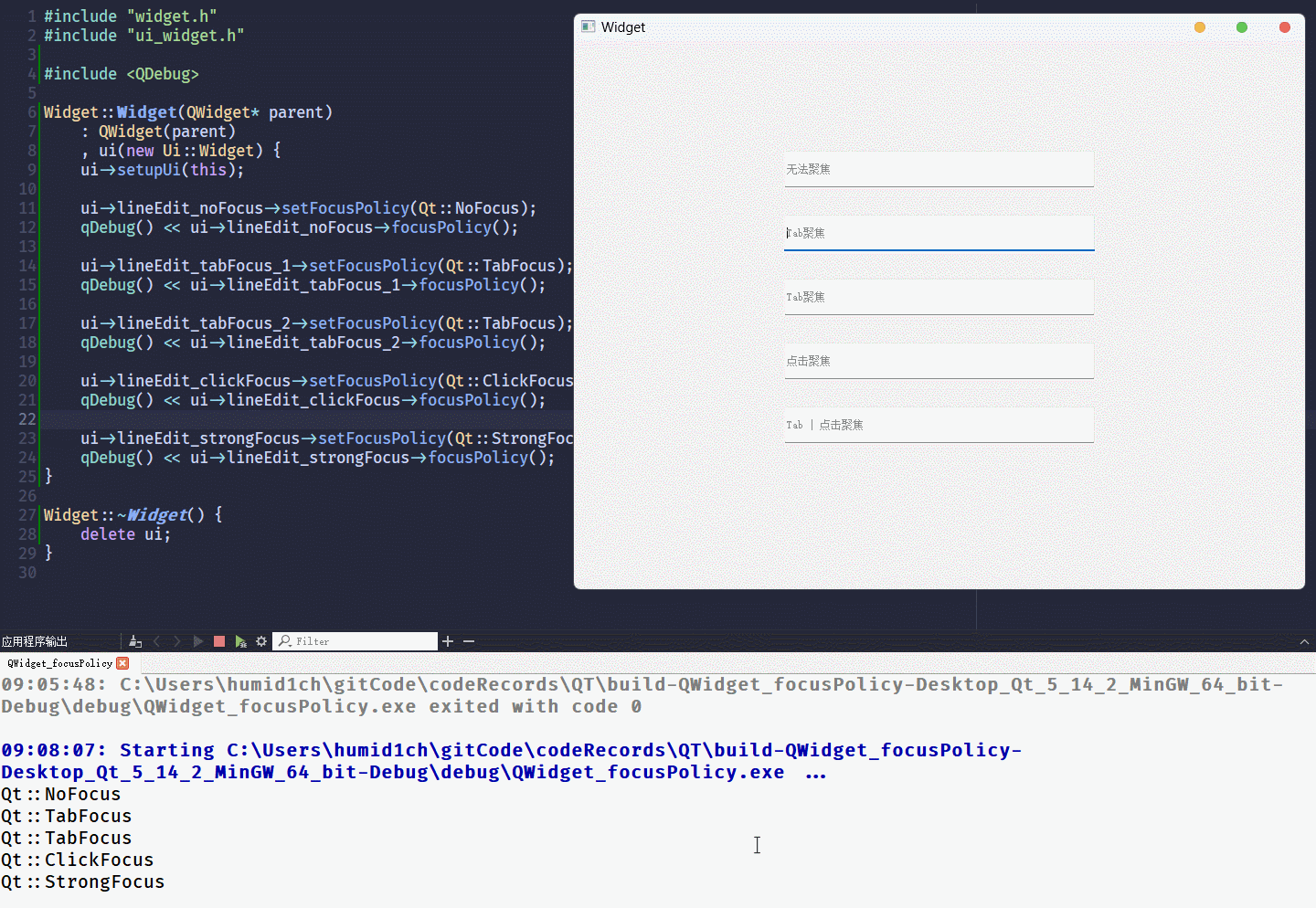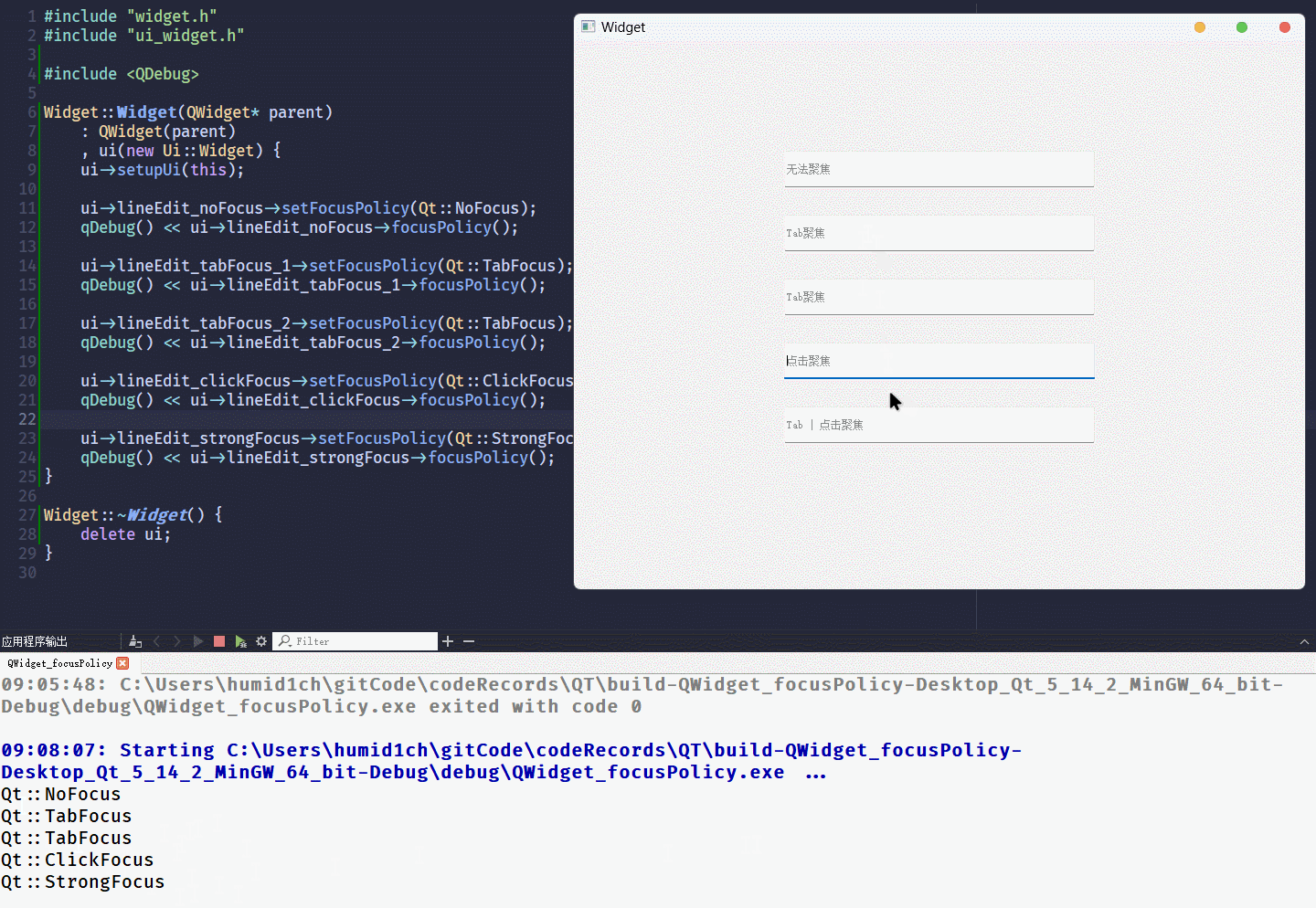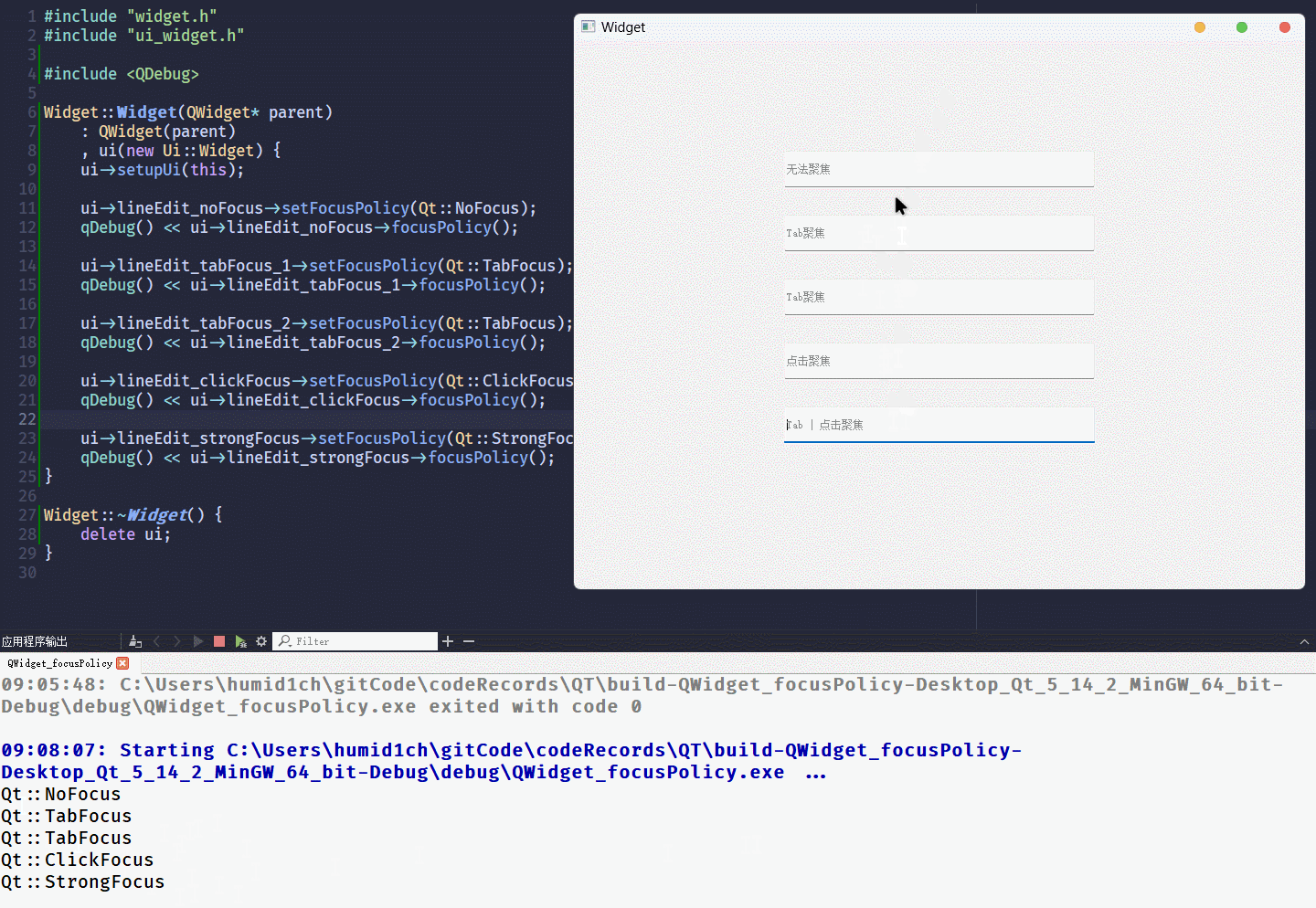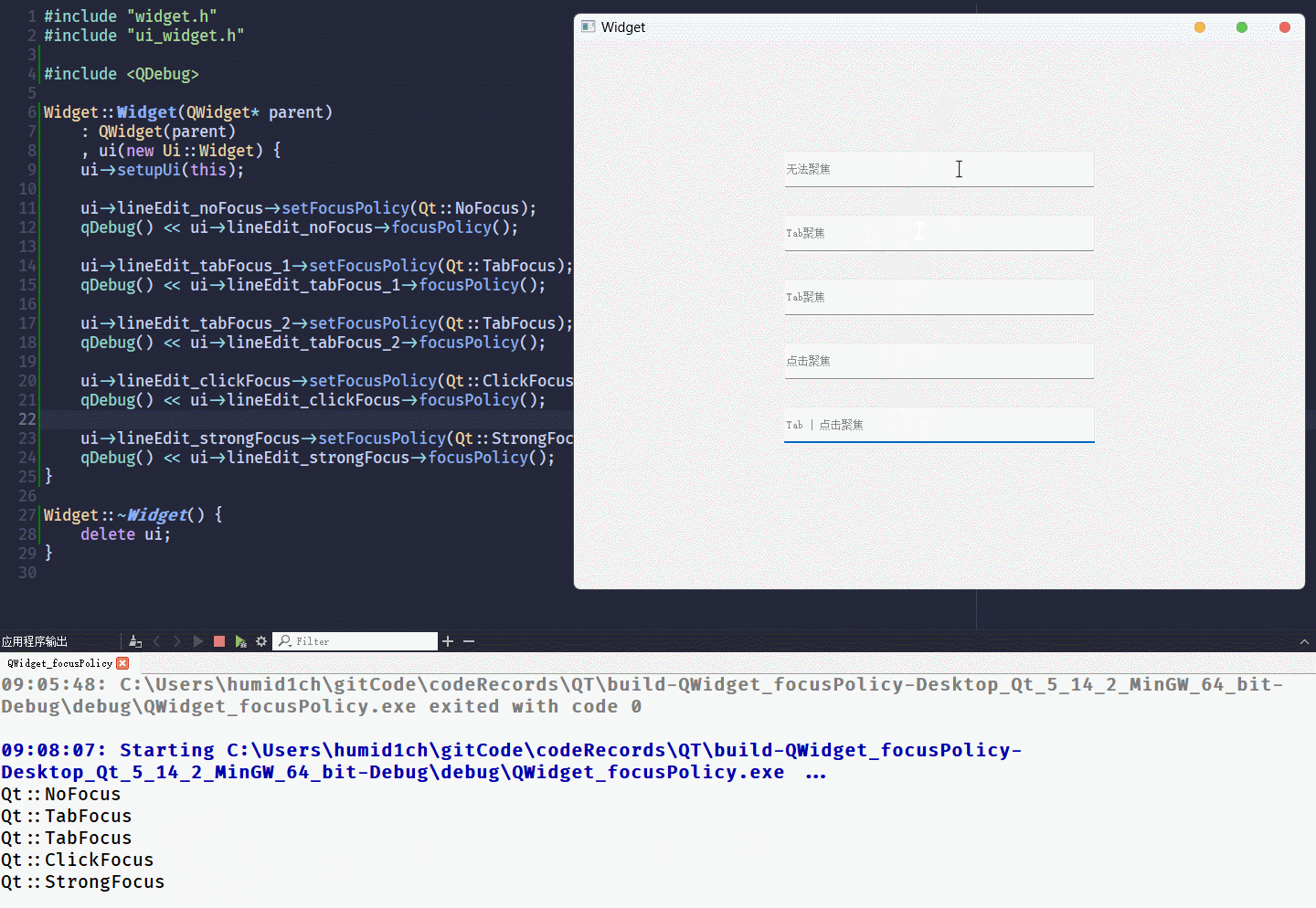
QT Designer创建5个单行文本编辑框, 并分别设置为:NoFocus TabFocus TabFocus ClickFocus StrongFocus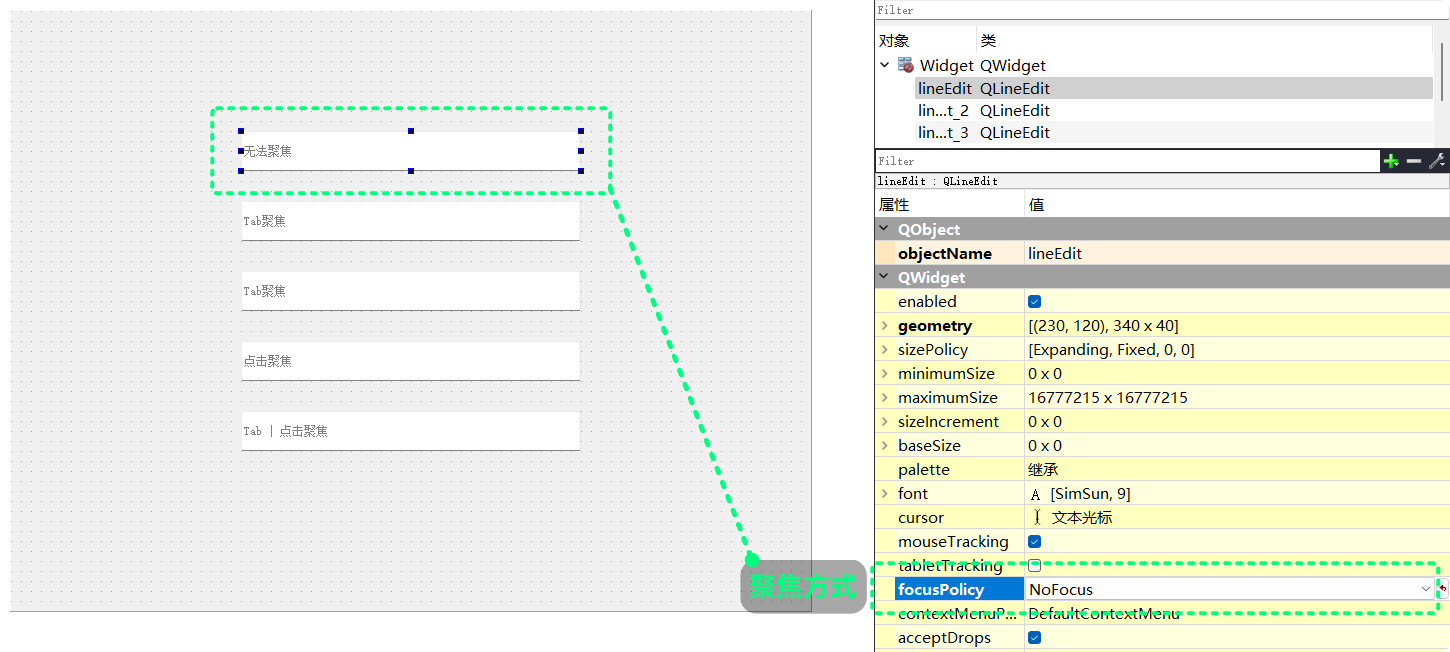
执行结果为:
代码实现
QT相关的接口有:| 接口 | 功能 |
|---|---|
Qt::FocusPolicy focusPolicy() const; | 获取控件当前聚焦方式 |
void setFocusPolicy(Qt::FocusPolicy policy); | 设置控件的聚焦方式 |
用代码的方式, 实现与上面相同的效果:
可以在
QT Designer修改各lineEidt的objectName为:
lineEdit_noFocuslineEdit_tabFocus_1lineEdit_tabFocus_2lineEdit_clickFocuslineEdit_strongFocus
#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QDebug>
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
ui->lineEdit_noFocus->setFocusPolicy(Qt::NoFocus);
qDebug() << ui->lineEdit_noFocus->focusPolicy();
ui->lineEdit_tabFocus_1->setFocusPolicy(Qt::TabFocus);
qDebug() << ui->lineEdit_tabFocus_1->focusPolicy();
ui->lineEdit_tabFocus_2->setFocusPolicy(Qt::TabFocus);
qDebug() << ui->lineEdit_tabFocus_2->focusPolicy();
ui->lineEdit_clickFocus->setFocusPolicy(Qt::ClickFocus);
qDebug() << ui->lineEdit_clickFocus->focusPolicy();
ui->lineEdit_strongFocus->setFocusPolicy(Qt::StrongFocus);
qDebug() << ui->lineEdit_strongFocus->focusPolicy();
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
}运行结果为:
styleSheet
此属性, 用于设置控件的
QSS样式QSS样式是QT中一种类似CSS的东西CSS在网页前端的开发中是必备的, 它一般长这样:
由标签和其所拥有的若干的键值对组成, 设置网页元素的风格, 用于网页元素的渲染
QSS的语法与CSS高度相似, 不过在更复杂场景又存在不同QSS也可以通过标签+键值对的方式, 设置控件的风格, 具体语法不多介绍只需要知道
QT可以通过类似CSS的QSS设置控件的风格了在
QT Designer中, 可以直接对控件进行QSS风格设置: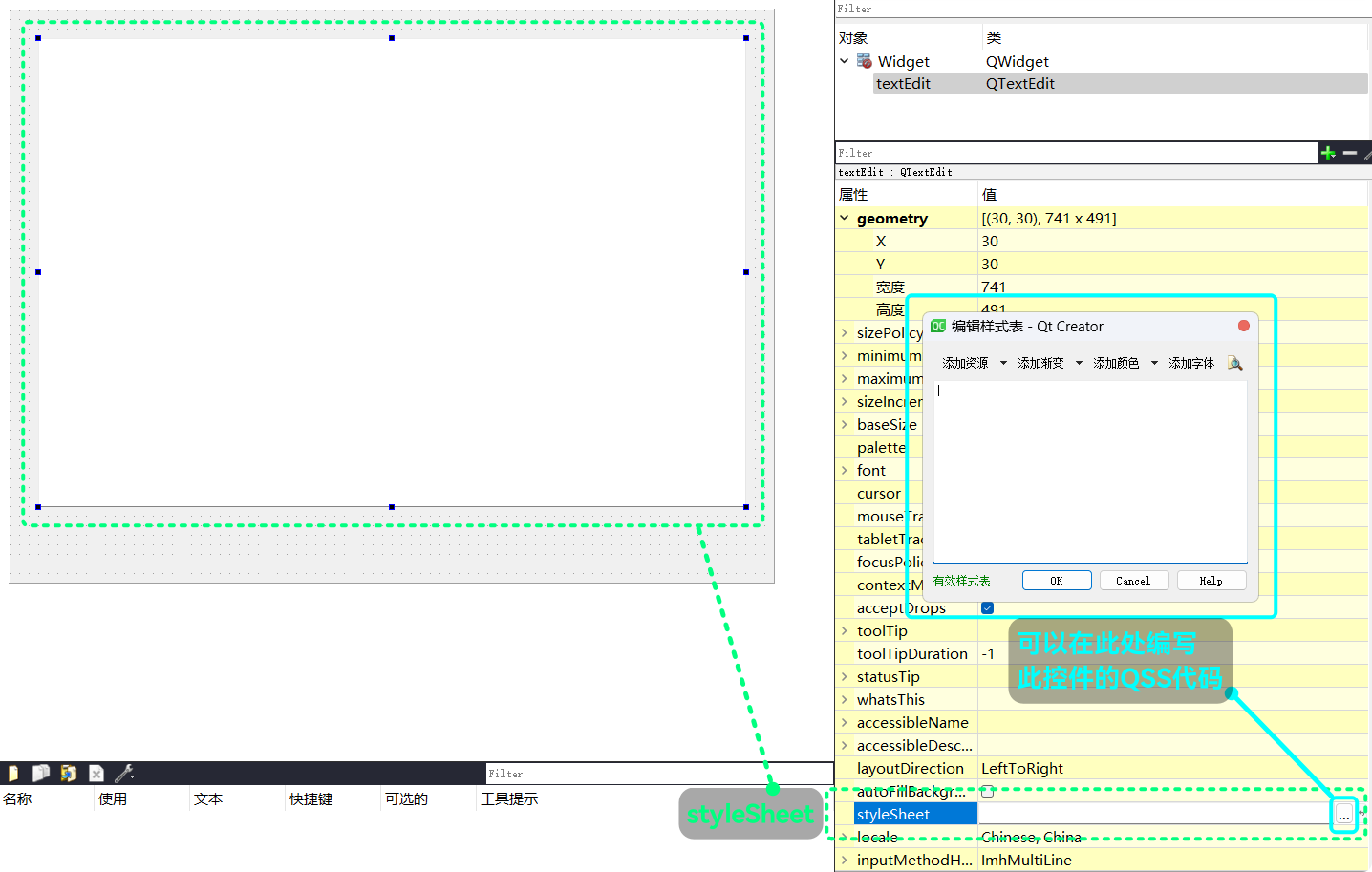
比如:
background-color: rgb(255, 255, 127);
color: rgb(255, 0, 0);
font-family: "FiraCode Nerd Font";
font-weight: 800;
font-size: 16pt;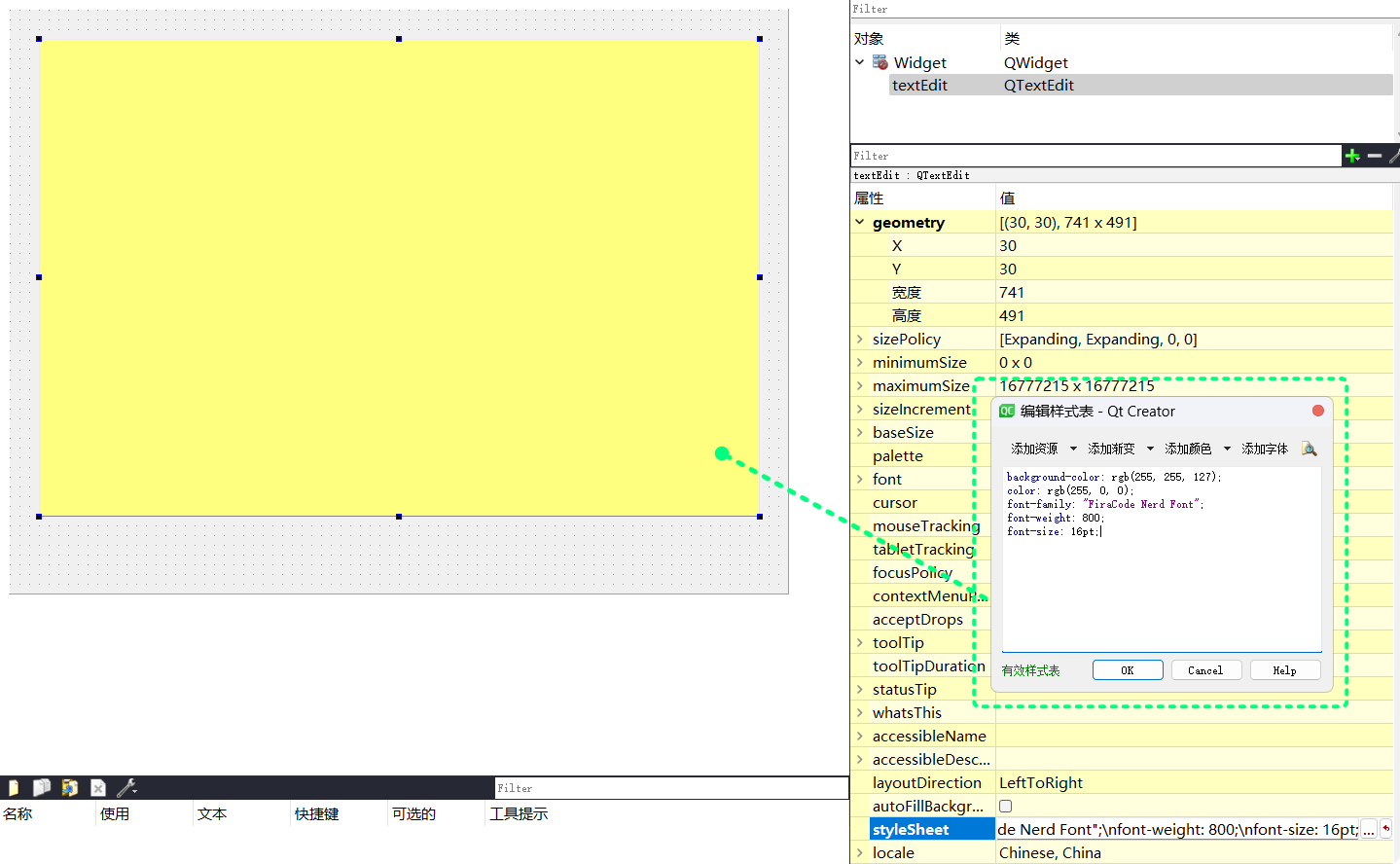
运行, 并输入文本:
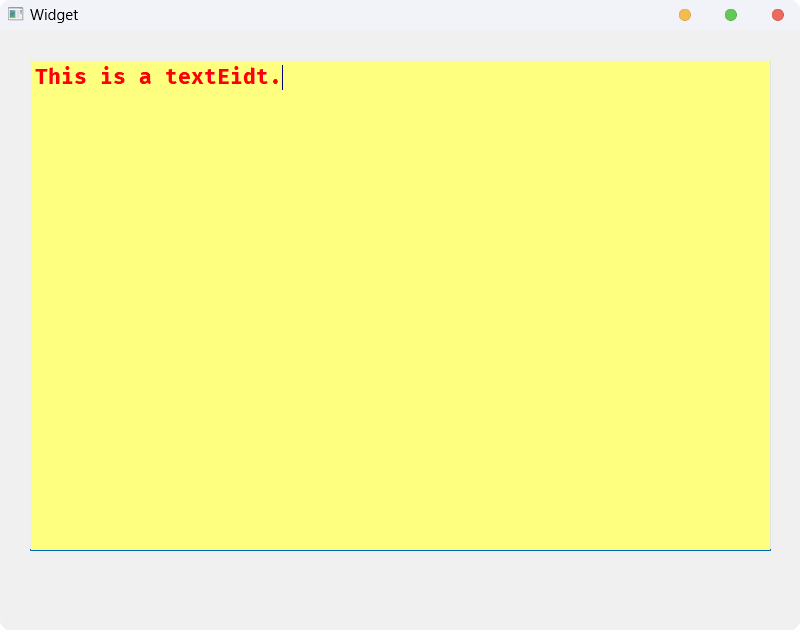
如果要通过代码实现,
QT相关的接口有:| 接口 | 功能 |
|---|---|
QString styleSheet() const | 获取控件当前的styleSheet |
void setStyleSheet(const QString& styleSheet); | 设置控件的styleSheet |
获取和设置都以
QString作为对象用代码的方式实现上面的效果:
widget.cc:#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QDebug>
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget) {
ui->setupUi(this);
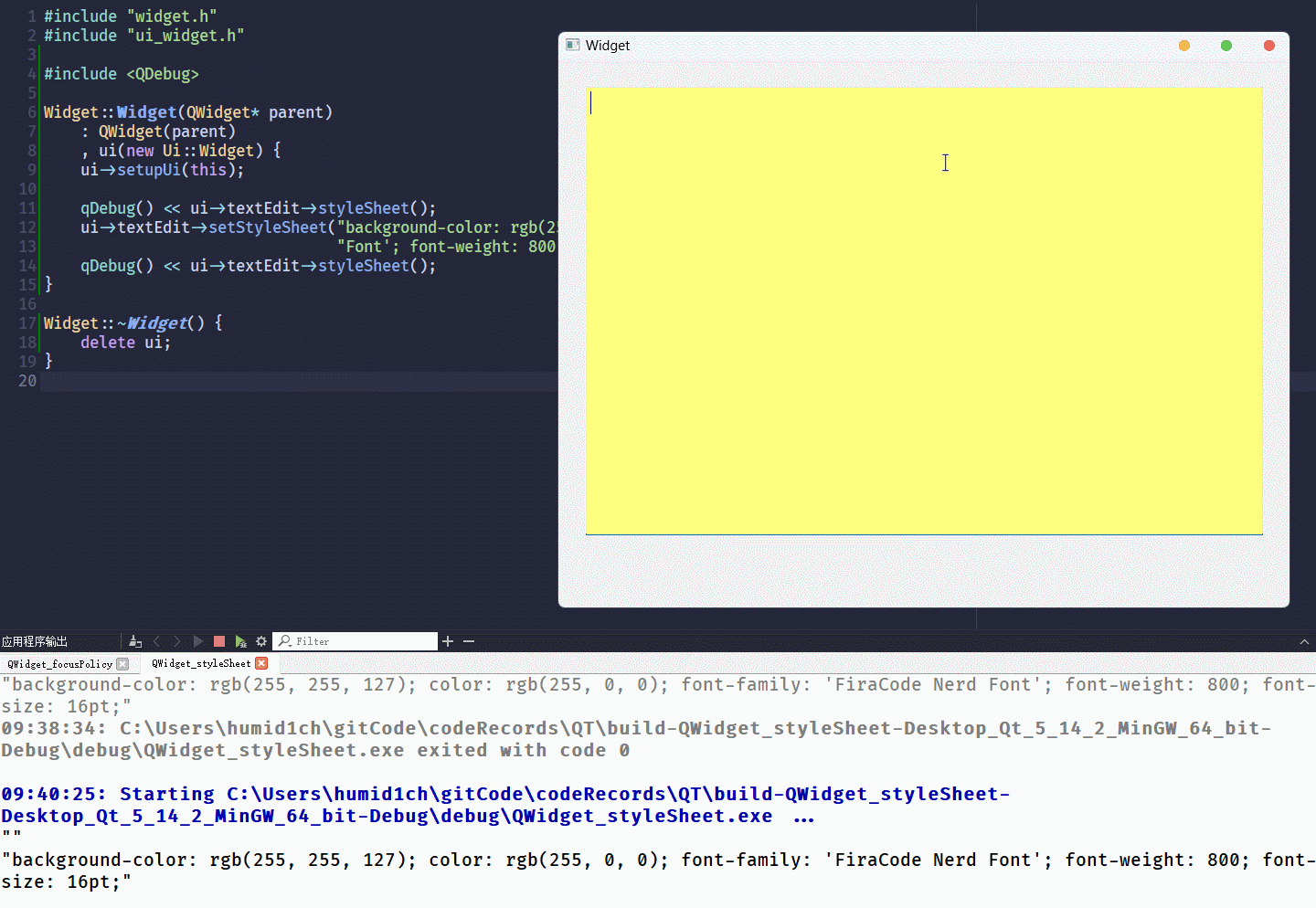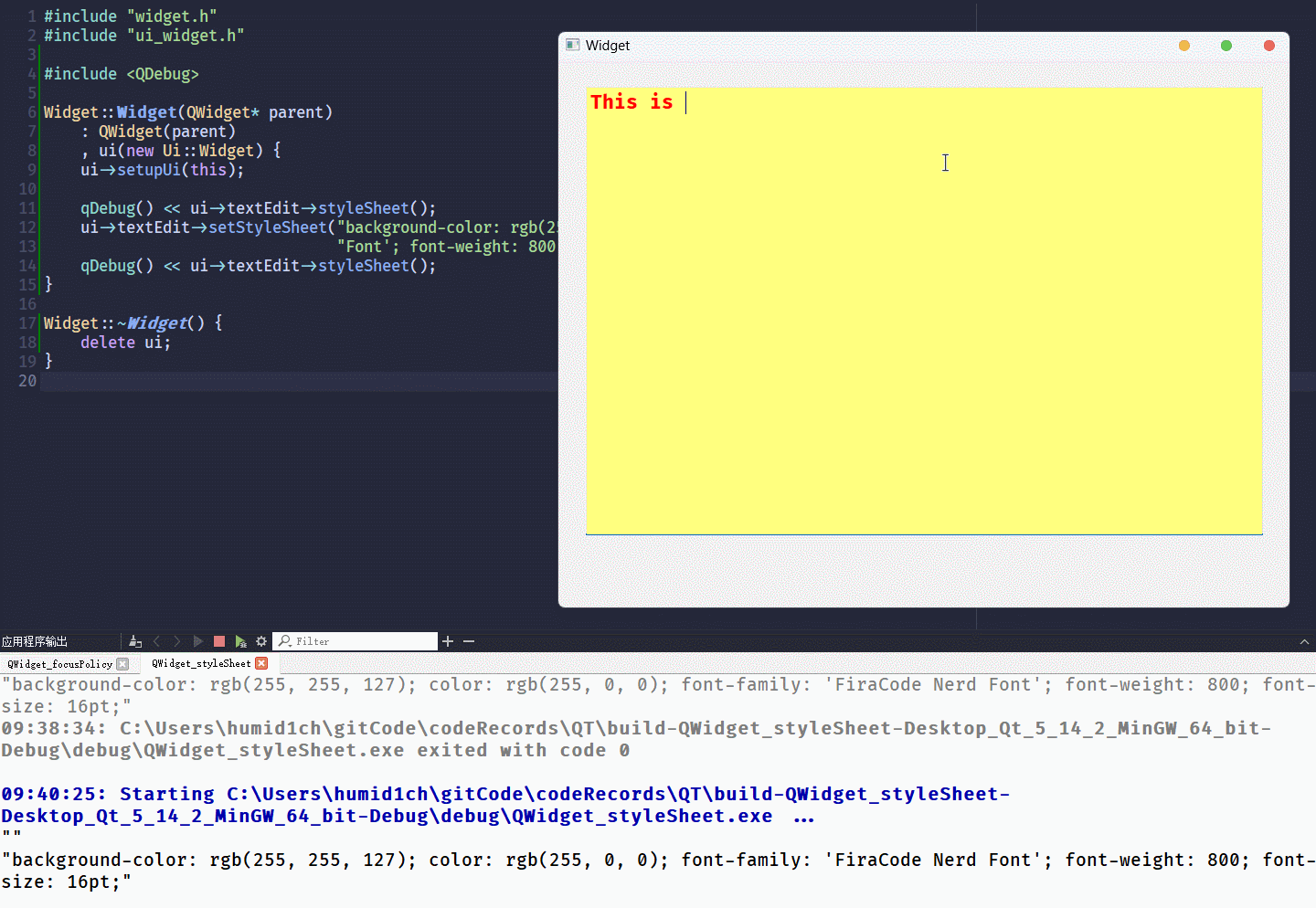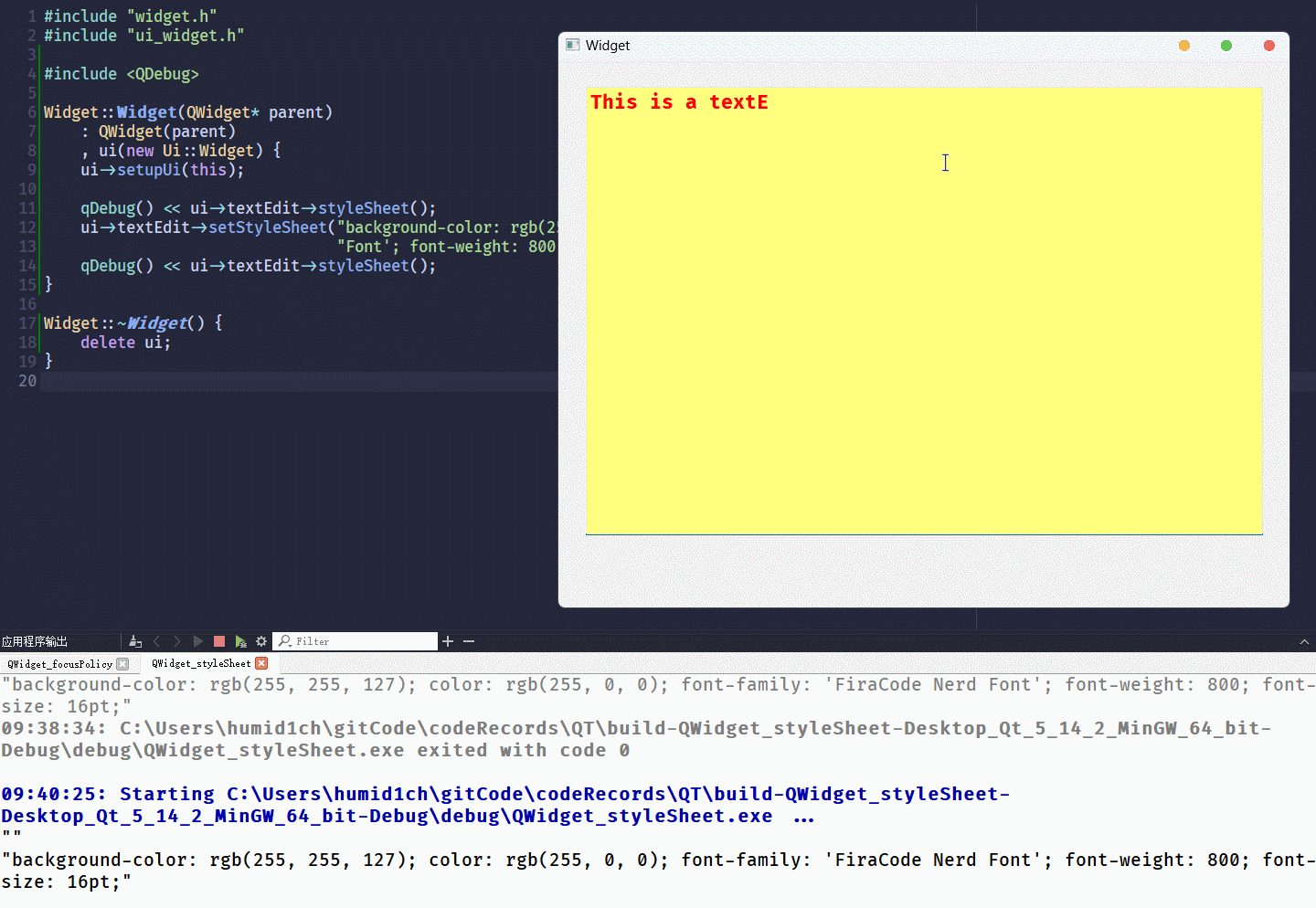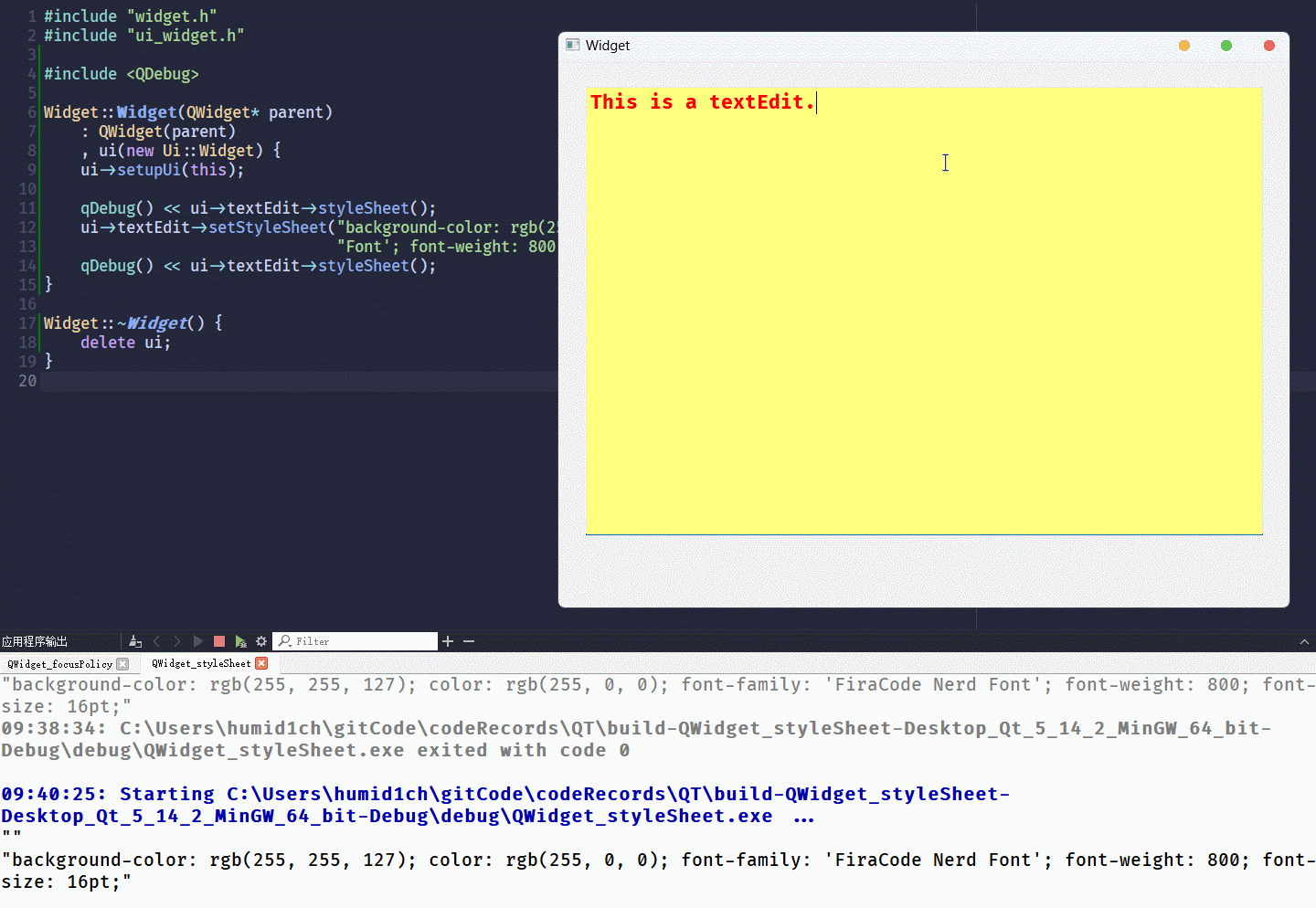
qDebug() << ui->textEdit->styleSheet();
ui->textEdit->setStyleSheet("background-color: rgb(255, 255, 127); color: rgb(255, 0, 0); font-family: 'FiraCode Nerd Font'; font-weight: 800; font-size: 16pt;");
qDebug() << ui->textEdit->styleSheet();
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
}通过
setStyleSheet()设置控件的QSS格式, 只需要以QString的形式将键值对传入其中就可以了运行结果为:
日间与夜间模式(小玩具程序)
QT Designer: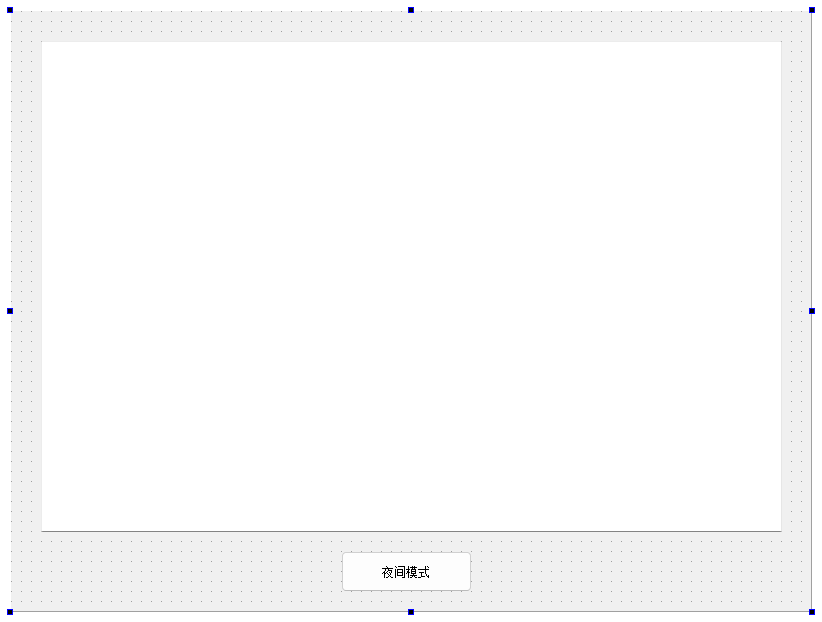
widget.h:#ifndef WIDGET_H
#define WIDGET_H
#include <QWidget>
QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
namespace Ui {
class Widget;
}
QT_END_NAMESPACE
class Widget : public QWidget {
Q_OBJECT
public:
Widget(QWidget* parent = nullptr);
~Widget();
private slots:
void on_pushButton_clicked();
private:
Ui::Widget* ui;
bool isNight;
};
#endif // WIDGET_Hwidget.cc:#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QDebug>
Widget::Widget(QWidget* parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget)
, isNight(false) {
ui->setupUi(this);
ui->textEdit->setStyleSheet("font-family: 'FiraCode Nerd Font'; font-size: 16pt;");
}
Widget::~Widget() {
delete ui;
}
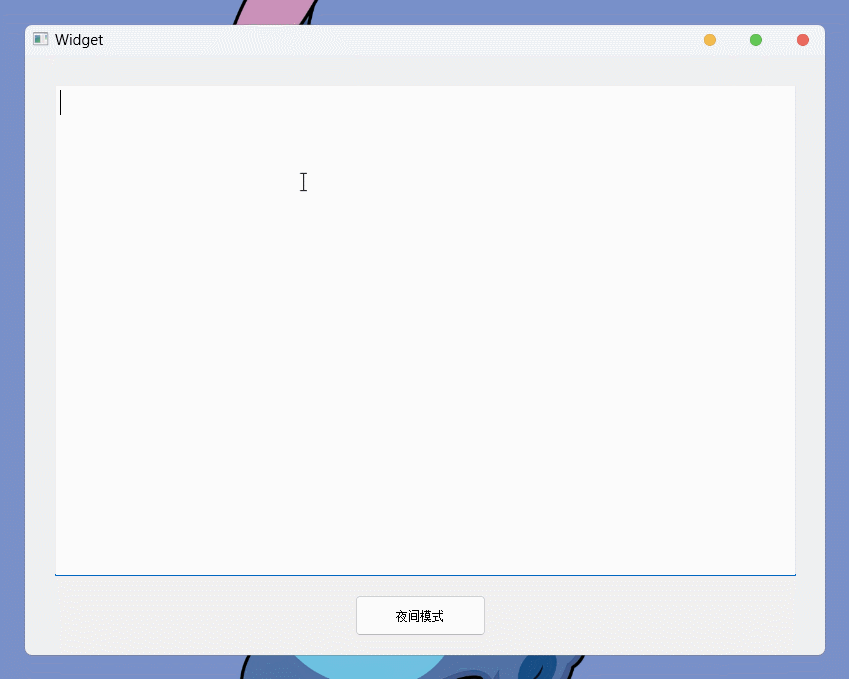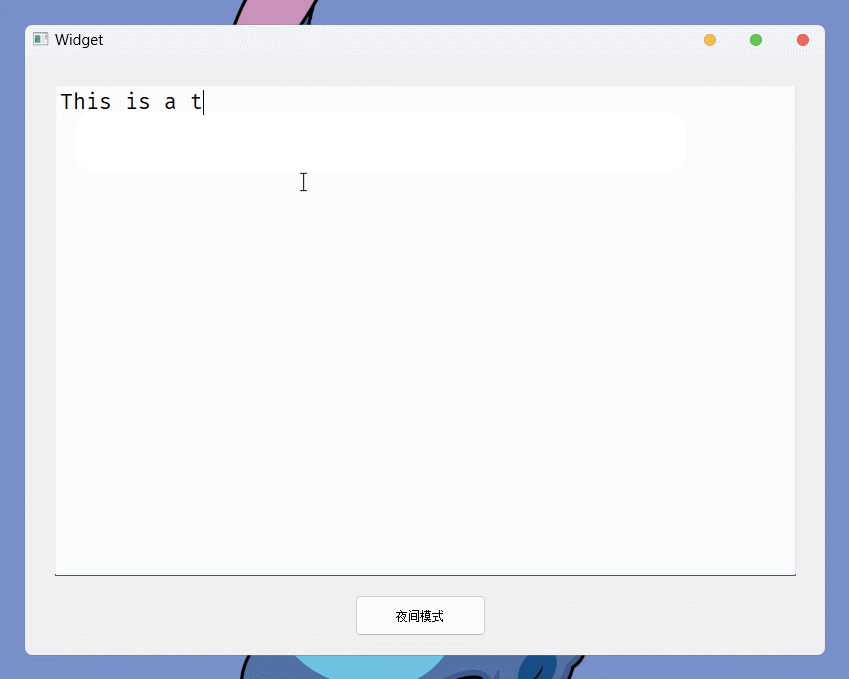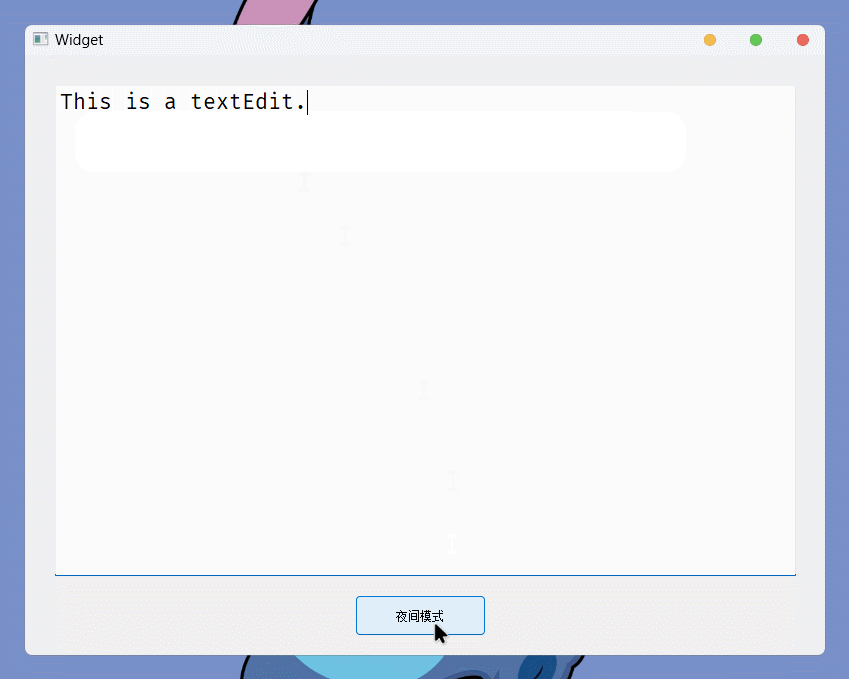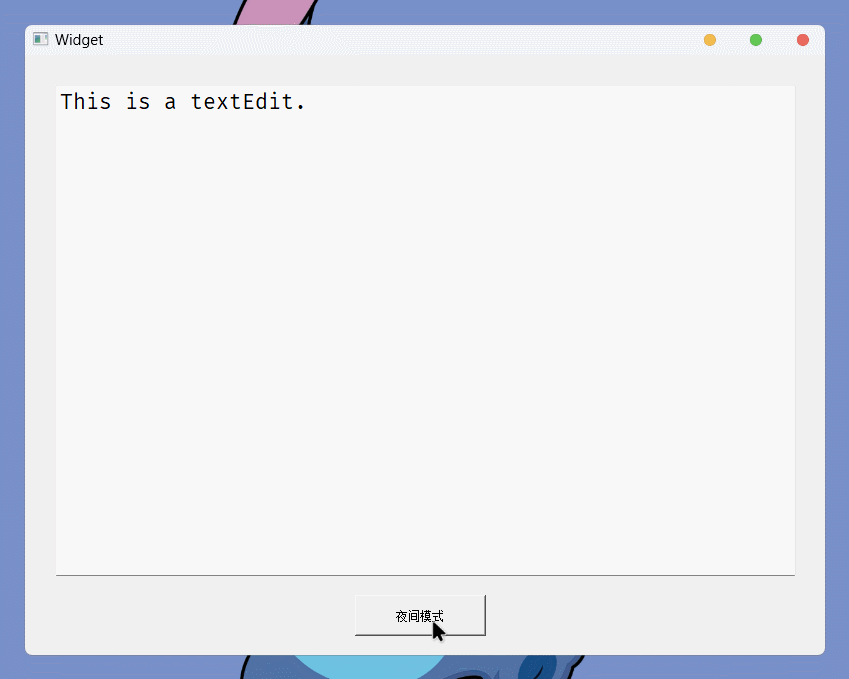
void Widget::on_pushButton_clicked() {
if (isNight) {
// 当前为夜间模式, 需要设置为日间模式
this->setStyleSheet("background-color: rgb(240, 240, 240); color: black;");
ui->textEdit->setStyleSheet("background-color: white; color: black; font-family: 'FiraCode Nerd "
"Font'; font-size: 16pt;");
ui->pushButton->setText("夜间模式");
isNight = false;
}
else {
// 当前为日间模式, 需要设置为夜间模式
this->setStyleSheet("background-color: rgb(36, 39, 58); color: rgb(202, 211, 245);");
ui->textEdit->setStyleSheet("background-color: rgb(36, 39, 58); color: rgb(202, 211, 245); font-family: 'FiraCode Nerd "
"Font'; font-size: 16pt;");
ui->pushButton->setText("日间模式");
isNight = true;
}
}运行结果:
上面就是
QWidget最常用的一些属性, QT中所有的控件基本都是从QWidget继承出来的所以, 相关控件都拥有
QWidget的一些属性, 在后续其他控件的介绍中, 就可以直接使用要了解更多, 可以查看
QT文档感谢阅读~
版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)
作者: 哈米d1ch 发表日期:2024 年 12 月 16 日